MLAB 2401: C C K B
advertisement

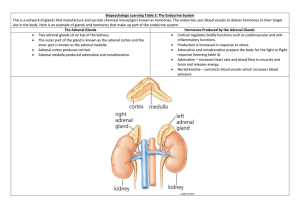
MLAB 2401: CLINICAL CHEMISTRY KERI BROPHY-MARTINEZ The Adrenals: An Overview ADRENALS Pyramid-shaped, located just above & medial to kidneys Glands are about the size of a grape Produces both steroid hormones from cholesterol and other non-steroid hormones Conditions affect blood pressure & electrolyte balance. Hypofunction is treated with exogenous hormone replacement, hyperfunction with pharmacologic suppression or surgery. ADRENAL ANATOMY Three domains Capsule Cortex Consist of Endocrine tissue Medulla Consists of neurosecretory tissue ADRENAL MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY Zona Glomerulosa outer 10% Synthesize mineralocorticoids Zona Fasciculata middle 75% Synthesize glucocorticoids Zona Reticularis inner 10% Secrete gonadocorticoids (androgens) Adrenal Medulla catecholamines Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry. Upper Saddle River: Pearson CLASSES OF ADRENAL CORTEX HORMONES Mineralocorticoids Regulate electrolytes Critical for sodium retention, potassium, & acid–base homeostasis Aldosterone Controlled by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Promotes potassium secretion Increases plasma sodium Increases water retention CLASSES OF ADRENAL CORTEX HORMONES Glucocorticoids Involved with metabolism of protein, and minerals Enhances fat lipolysis Involved with gluconeogenesis and glucose homeostasis Critical to blood pressure Plays a role in suppression of inflammatory and allergic reactions GLUCOCORTICOIDS Cortisol- principle member Functions Acts by penetrating cell nucleus, binding DNA, and altering the transcription of RNA Insulin antagonist Primarily circulates bound to a protein Breaks down muscle proteins with enzymes Mobilizes fat for energy purposes Lessens immune response by inhibiting antibody formation CORTISOL REGULATION Hypothalamus secretes CRH (Corticotropin- releasing hormone) CRH activates adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in the anterior pituitary ACTH controls cortisol production Low levels of cortisol, promote ACTH release Elevated levels of cortisol, inhibit ACTH release Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry. Upper Saddle River: Pearson CORTISOL TESTING Normal plasma concentration follows diurnal variation Fluctuates between 6-25 µg/dL Cortisol is conjugated and excreted in the urine as 17-hydroxycorticosteroids (17-OHCS) CLASSES OF ADRENAL CORTEX HORMONES Gonadocorticoids Androgens Testosterone is the principal androgen DHEA: dehydroepiandrosterone TESTES Function Produce sperm Production of reproductive steroid hormones Testosterone Maintains secondary sex characteristics and sperm production Principle androgen in the blood 95% bound to albumin/sex hormone binding protein HORMONAL CONTROL OF TESTICULAR FUNCTION • • • • • Hypothalamus generates GNRH in a pulse-like fashion GNRH is released into the system GNRH determines the rate of production of LH and FSH FSH and LH activate testosterone production Testosterone converted to dihydrotestosterone to effect protein synthesis and cell growth Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry. Upper Saddle River: Pearson OVARIES Function Ovum production Steroid hormone production Hormone Production Requires cholesterol HORMONAL CONTROL OF OVULATION GNRH controls FSH and LH secretion During reproductive years, FSH increases in follicular phase of menses and LH surges mid-cycle to cause ovulation. Following ovulation, FSH decreases Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry. Upper Saddle River: Pearson FEMALE SEX HORMONES • Estrogens • Includes estradiol, estrone, and estriol – – – • Progesterone – • Promotes breast, uterine and vaginal development Secondary sex characteristics Produced by placenta & ovaries Prepares endometrium for implantation Androgens – – Testosterone & DHEA (dehydroepiandrosterone) Promote development of masculine characteristics PLACENTAL HORMONES hCG= Human Chorionic gonadotropin Composed of two subunits: alpha & beta Classic hormone marker of pregnancy Human placental lactogen Aids hCG in estrogen & progesterone synthesis Promotes mammary gland development Progesterone Promotes growth and thickening of mucosal cells Ensures adequate uterine blood supply ADRENAL MEDULLA HORMONES Produced in small amounts and extremely potent, rapidly inactivated Mobilize energy stores and prepares body for muscular activity Released into the bloodstream during stress Catecholamines Nonsteroid, amine-type hormone CATECHOLAMINE MEMBERS Norepinephrine/ Noradrenaline Synthesized in the CNS Epinephrine/Adrenaline Produced by adrenal gland Increases blood glucose via breakdown of glycogen Increases heart rate and blood pressure Causes sweating and dilation of the eyes Dopamine METABOLISM OF CATECHOLAMINES IMPORTANCE OF VMA & HVA Pheochromocytoma Benign or malignant tumors in the adrenal medulla Causes hypertension Neuroblastoma/Ganlioneuromas Common malignant tumors in pediatric patients Elevations of VMA or HVA REFERENCES Bishop, M., Fody, E., & Schoeff, l. (2010). Clinical Chemistry: Techniques, principles, Correlations. Baltimore: Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Sunheimer, R., & Graves, L. (2010). Clinical Laboratory Chemistry. Upper Saddle River: Pearson . 21