Critical Thinking Exercise- Spurious Results
advertisement

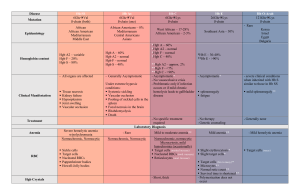
Critical Thinking Exercise- Spurious Results Erroneous hemoglobin values are detected by checking Hemoglobin (Hgb) and Hematocrit (HCT) agreement (rule of three) and the MCHC value. The following are conditions that cause turbidity or cloudiness that may falsely elevate the hemoglobin measurement performed utilizing photometric devices: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperlipemia WBC over linearity Unlysed RBCs Hyperproteinemia Cold Agglutinin INITIAL RESULTS-36- year old male Analyte WBC RBC HGB HCT MCV MCH MCHC RDW PLT Bilirubin, total Total Protein Triglyceride Result 8.4 x 10 / uL 2.45 x106/ uL 9.2 g/dL 21.4 % 87.0 fL 37.5 pg 43.1 % 13.0 % 200 x 103/ uL 0.8 mg/dL 6.7 g/dL 126 mg/dL 3 Reference Range 4.5-11.0 x 103/ uL 4.5-5.5 x106/ uL 14.0-17.4 g/dL 42-52 % 80-100 fL 28-34 pg 32-36 % 12.0-14.6 % 150-450 x 103/ uL 0.2-1.0 mg/dL 6.4-8.3 g/dL <150 mg/dL Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. Do the Hgb and HCT correlate? Are the MCH and MCHC correct? If the MCH and MCHC are inaccurate, why? What can we do to identify the reason for the spurious results? After the specimen was found to have a cold agglutinin, the sample was warmed and the following results were obtained. CORRECTED RESULTS Analyte WBC RBC HGB HCT MCV MCH MCHC RDW PLT Result 8.4 x 103/ uL 2.45 x106/ uL 7.4 g/dL 21.1 % 87.0 fL 30.1 pg 35.1 % 13.0 % 210 x 103/ uL Questions 1. Does the rule of three now correlate? 2. What causes cold agglutinins?