Brazil, overview of a country
advertisement

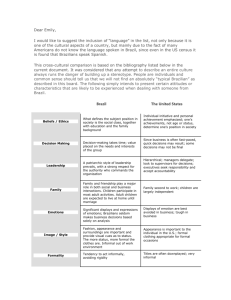
Brazil, overview of a country 1. What do you know about Brazil and Brazilians? The largest and most industrialized country in South America The 6th consumer market in the world and the largest economy in Latin America Capital Brasília Language Portuguese, the 8th language with most speakers in the world, 191 million (Mandarin, English, Hindustani, Spanish, Russian, Arabic, Bengali). Political Regimen Democracy President Luíz Inácio (Lula) da Silva Largest cities São Paulo, Rio, Brasília, Recife, Salvador, Porto Alegre Climate generally tropical with some variation in the South Population 173,790,810 (45% below 20 years of age) Most of the population live in the urban areas Currency Real Money distribution A few rich, some middle-class, lots of poor people 2. A bit of history: Brazil was discovered in 1500 by the Portuguese and was a colony of Portugal till 1822. The name Brazil comes from the dyewood "pau brasil" (brazilwood) Invaded many times by the French, the Dutch and the Spanish armadas. Under dictatorship from 1937 to 1945 and then again from 1964 to 1985. Voting is mandatory for everyone over 18 and under 70 years of age. Main political parties: Brazil Social Democratic Party, Liberal Front Party and the Brazilian Labor Party. 3. A typical city 4. The people in the cities: Ethnic complexion. The races: Whites (from European descent), Blacks (from African descent), Native-Americans and immigrants from many different countries. Relaxed attitude towards interracial relationships. Race and socioeconomic situation are closely related. The social importance of carnival and soccer. Religion: Catholicism, Espiritismo, Macumba, Candomblé Leisure activities: beaches, movies, soccer, bars, music, "o clube", nightclubs, "o shopping". The Brazilian soap operas. Violence in the big cities. 5. Brazilian music: Samba Lambada Rock, Rap Bossa-Nova Main names: Caetano Veloso, Chico Buarque, Daniella Mercury, Gilberto Gil, Gal Costa, Maria Bethania, Lulu Santos. 6. Family structure. How we live, study and work in the urban areas. The family and the extended family Apartments (in urban areas) The phenomenon of the maid Brazilian cuisine: the daily food, special dishes (feijoada, churrasco, vatapá) Public X Private education Commuting to work Salaries The favelas and the "menino de rua" or "trombadinha" 7. Brazilian economy Among the World Bank's Upper-Middle Income countries (others are Mexico, South Africa, Greece and Portugal) High foreign debt Inflation in the 90s and now Main products: minerals, motor companies (one of the world's major steel producers and car manufacturers), telecommunications, food processing, textiles and chemicals. Member of the International Monetary Fund, the Latin American integration Association and the Mercosur (a customs union with Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay) Brazil and US economical relations Americans working and living in Brazil 8. Challenges for the future: Avoiding ecological disasters Cleaning pollution from urban areas Preserving the Amazon and, simultaneously, exploit it's natural resources. Saving endangered species (the Blue Macaw, monkeys, felines) Stabilizing the economy Fighting corruption Solving poverty problems and economical disparities (thus curbing violence) Finding an alternative to petroleum (alcohol)