Pass-By-Value Services in Object Component Software Group 1
advertisement

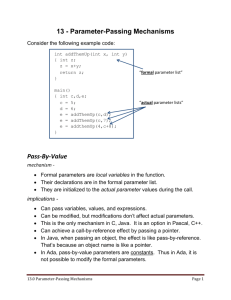
Pass-By-Value Services in Object Component Software Group 1 Yannick Loitiere Andrea Rowan Michele Co Jinze Liu 1 Object Component Software • Middleware with abstraction – Implementation separated from interface • “Client” and “server” share objects – Across a network – Between different programming languages • Popular software – OMG CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) – Microsoft COM (Component Object Model) – Java 2 Object Passing • Pass-By-Reference – Server returns reference to the object – Client calls the server with the reference – Server executes methods and returns the value • Pass-By-Value – Server returns copy, reference to local copy – Client calls the local copy with the reference – Client executes method and returns the value 3 Bank Example • Account – Name Object (immutable) – Balance Object (mutable) • Pass-By-Reference – Consistency for Balance Object – Performance hurt for Name Object • Pass-By-Value – Inconsistency for Balance Object – Performance gains for Name Object 4 Related Work • Ennio Grasso’s Model – Consistency maintained – All objects CORBA objects • CORBA 2.3 OBV Model – No consistency – Separate ValueBase objects 5 Our Project • Analyze CORBA's Object By Value (OBV) service using TAO • Identify problems with the current implementation of pass-by-value • Measure performance differences for different pass-by-value models • Propose a better model of pass-by-value – Identify limitations of our pass-by-value service 6 Evaluation of Models • • • • • • Consistency Orthogonality / Semantics Client Control Language Transparency Location Transparency Performance 7 Consistency Time to Retrieve and Modify One Long (s) Performance for Pass-By-Value Models With and Without Client/Server Consistency 0.005 0.004 Inconsistent Pass-ByValue 0.003 Consistent Pass-ByValue 0.002 0.001 0 1 21 51 201 501 Number of Longs Stored in Object 8 Orthogonality/Semantics • TAO separates ValueBase objects from CORBA objects • Amount of pass-by-value specific code in our simple client/server program: – – – – 2/6 lines of the interface 11/88 lines from the server-side code 1/59 lines from the client-side code Represents 9.15% of all code 9 Client Control • TAO allows client to pass large objects by value • Pass-By-Reference – Performance not affected by object size • Pass-by-value – Performance decreases as size of object increases 10 Client Control Time to Retrieve and Modify One Long (s) Performance for Calling Objects of Different Sizes 0.003 0.0025 0.002 Pass-By-Value 0.0015 Pass-By-Reference 0.001 0.0005 0 1 21 51 201 501 Number of Longs Stored in Object 11 Language Transparency • TAO does not allow for language transparency for pass-by-value • Client must have implementation at compile time • Only C++ mapping currently exists 12 Location Transparency • Because of separation of ValueBase objects from CORBA objects, client can tell if object is passed by value • Interface is written differently for the two types • TAO does not define abstract interfaces • Lack of location transparency breaks CORBA’s Object Model 13 Performance • Pass-by-value improves performance most when – Object is small – Object is referenced multiple times by client – Consistency is not maintained 14 Performance Performance Time (s) Performance For Multiple Accesses of Small Object 0.012 0.01 Inconsistent Pass-ByValue 0.008 0.006 Consistent Pass-ByValue 0.004 Pass-By-Reference 0.002 0 1 10 Number of Accesses 15 Our Model • Consistency – Use classical pass-by-value model (no shared state between client and server) – Only allow pass-by-value for immutable objects • Orthogonality – All objects should be CORBA objects – Add byvalue boolean to CORBA objects – Default value of byvalue is false 16 Our Model • Client Control – Server decides whether object can be passed by value • restricted according to size, immutability, etc. – Client may block pass-by-value • send_object() - lets server choose how object is sent • send_by_reference() - blocks pass-by-value – Give server more control than client 17 Our Model • Language Transparency – No easy solution b/c of range of operating systems, language capabilities – If object’s implementation language is not available on client, default to pass-by-reference – If object’s implementation is not on client, download during first call • Assume performance gain makes up for download time 18 Our Model • Location Transparency – All objects are CORBA objects • assures location transparency for client • Performance – Performance gains for small, remote, immutable objects – Performance is one of the key reasons for passby-value, and was an important factor in our model design. 19 Conclusion • • • • Pass-by-value can improve performance Restricted objects (immutable, small) Good for systems with low bandwidth Simple to allow pass-by-value in older CORBA programs because our model maintains object abstraction • Improvement in many ways over CORBA’s OBV and TAO’s pass-by-value service 20