IMPROVING PUBLIC EXPENDITURE IN MEXICO ROLF ALTER
advertisement

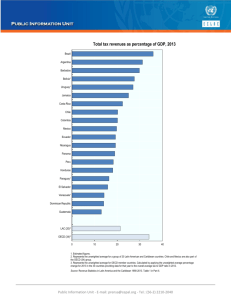
IMPROVING PUBLIC EXPENDITURE IN MEXICO ROLF ALTER DIRECTOR PUBLIC GOVERNANCE AND TERRITORIAL DEVELOPMENT A healthy budget situation, and improved budget practices • Mexico in top category – “close to 3% deficit; low consolidation requirement” • Recent reforms have strengthened budgeting function: for example: – More co-ordinated budget process – Performance budgeting available and used – Enhanced financial management in lie ministries Performance budgeting now harmonised across government Does the Central Budget Authority have in place a standard performance budgeting framework which is applied uniformly across central government organisations? No, line ministries/ agencies have their own: 8 countries Yes, but optional for line ministries and agencies: 1 country Yes, for both line ministries and agencies: 18 countries, incl. Mexico Yes, but only for line ministries: 5 countries OECD Budget Review of Mexico – reforms need to be continued and built upon Mexico has lowest overall public expenditure in OECD % of GDP 100% Public expenditure as a % of GDP (2010) 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% * 2009 Source: OECD National Accounts There is scope to increase investment in key public services, but taking care to strengthen expenditure frameworks… Improving public expenditure in Mexico: more and better… Key issues to address include: 1. Addressing the (dis)incentives in the fiscal transfer system 2. Enhancing value for money in procurement systems 3. Improving accountability and monitoring in public expenditure (budget, spending at sub-national level…) 4. Ensuring high standards of integrity in the public sector 1. States are crucial actors for more effective public spending • Mexico has the lowest sub-national fiscal autonomy among OECD federal countries Taxes User fees Grant Oth 100 90 80 70 • Transparency in public expenditures low, though recent legislation is on the right track 60 50 40 30 • Incentives and scope for regional action are low 20 10 0 DEU CAN CHE USA AUT ESP BEL MEX OECD reviews can help identify measures to improve the fiscal transfer system and its effectiveness in promoting regional growth and quality services 2. Procurement systems can be strengthened to ensure value for money • SLIDE TO ADD 3. Accountability and monitoring in spending helps policy learning • Concern that public expenditures is not accountable enough • And that monitoring and evaluation is not systematic – does not lead to improved policies • In other leading economies, the audit office now plays key role in ensuring accountability, value for money and improved outcomes (e.g. Brazil) 4. Transparency and integrity in the public sector remains a key challenge Across OECD, restoring trust is seen as a key prerequisite for economic growth President Elect announcements show that this is a priority in Mexico – Creation of the National Anti-Corruption Commission – Manifesto for a Democratic presidency – Making public the list of assets owned by senior government officials Integrity needs holistic approach: OECD integrity framework links diverse facets – lobbying, conflict of interest, procurement… even political financing) How can the OECD be useful? • Strengthening comparative data on government performance (data on key indicators for Mexico not always available) • Support anti corruption efforts with an Integrity Review • Follow up on recent reviews of procurement systems with implementation support • Examine fiscal transfer system to identify key reforms; promote competitiveness policies at state and city level