Glossary
advertisement

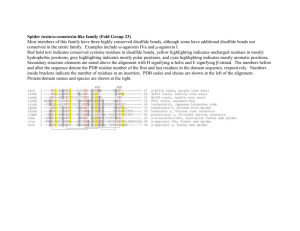
Glossary Covalent Bond - Atoms held together by sharing of electrons. Disulfide - Covalent bond between 2 sulfur molecules. Researchers- Personnel who use or work with disulfide bonds, e.g. scientists, teachers, students. Data Visualizations - 3D models of the bonds with descriptions. Resources - Assets available to a server to process jobs, e.g. processor, memory, storage, network bandwidth. Information System - Components used to capture, store, retrieve, compute, and display facts and statistics. Users - Researchers that utilize the information system. Job - User request for resources to perform a task. Big Data – Information in large amounts and/or variety, accessed at high velocity. Data – Statistics and information taken from a user. Database – Collection of data, organized to be easily accessible. Query – Request for data from a database. Queuing System – Places jobs in line to wait for execution. Cluster – Set of servers performing as a single entity. Title - Name of the sequence. Sequence - String of characters representing a protein strand. Prediction - Context-Based scores to estimate the favorability of a crystalline residue in a disulfide bonding state as well as a crystalline pair in a disulfide pair connectivity. Process – Execution of a computer program. Deadlock – Processes at a standstill, each waiting for the other to finish computing. Race condition – Two or more processes attempt to modify a shared variable. Crash – Server or computer ceases to function. Vulnerability – Weakness in a computer program. Hacker – Exploits a system by finding its vulnerabilities. Script – List of commands to automate the execution of processes. D-RMS – Distributed Resource Management System – Three subsystems used to improve cluster performance, i.e. job management, resource management, and queuing.