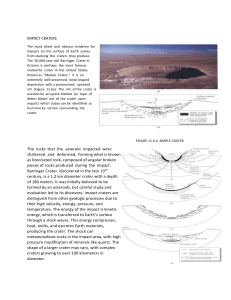
The Three Principles of Geology Lecture Notes – Key Impact Craters Ejecta Material

Name ______________________________________________________________
The Three Principles of Geology Lecture Notes – Key
Impact Craters
1. Ejecta – Material from the crater that was thrown high into the air and landed outside the crater in a blanket.
4.
5.
2.
3.
Rim
Peak
– The
Walls
Floor
– An raised impact
– The
– The crater
area round the
violent enough to melt the
slope down to the floor. bottom
Identify the parts of the crater. edge of the crater.
of the crater; it is usually rock flat.
which formed a central uplift.
Floor
Ejecta
Central Peak
Volcanoes
1. Lava – Hot, molten rock.
1
2.
3.
4.
Vent – Cracks in the planet’s crust.
Caldera – A roughly circular depression found at the top of the volcano.
Shield Volcano – Domes much wider than they are high (shaped like a
Shield ) and have very low slopes.
Stratification – Layers of rock that are laid on top of the previous layer.
River Beds – Long, snake-like formations that resemble dry river beds similar to those found on Earth.
The Three Principles
The Principle of Superposition
Strata located at the bottom of an undisturbed stack of rocks are older than the layers at the top of the stack.
2
The Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
Rocks or geological features such as canyons, river, or cracks in rocks may be cut by other rocks or by other geological features.
The Principles of Horizontal Bedding
If the
Been layers are no longer horizontal they must have bent or folded after they were originally laid down.
3