1
advertisement

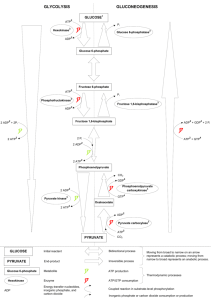
1 outline glycolysis to pyruvate with the yield of ATP and reduced NAD+ 10 steps in Glycolysis ADP phosphorylation ATP hexokinase 1 Glucose receives a phosphate group from ATP to form glucose-6phosphate. Process: phosphorylation Enzyme: hexokinase Next Review 2 isomerization Glucose-6phosphate converted to its isomer, fructose-6phosphate. Process: Isomerization Next Review 3 ADP phosphorylation ATP Phosphofructokinase Another ATP is invested to molecule, forming fructose1,6-bisphosphate. Process: Phosphorylation Enzyme: Phosphofructokinase Next Review 4 GlyceraldehydeDihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP) 3-phosphate (G3P) Fructose-1,6bisphosphate is then split into two 3carbon sugars, glyceraldehyde-3phosphate (G3P) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP). Process: Lysis / Cleavage Next Review 5 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is converted to its isomer, isomerization glyceraldehyde-3phosphate Glyceraldehyde- (G3P) a.k.a Dihydroxyacetone phosphoglycerate Phosphate (DHAP) 3-phosphate (G3P) (PGAL) Process: Isomerization Next Review 6 G3P/ G3P/ 2NADH + 2H+ oxidation 2NAD+ G3P undergoes dehydrogenation with NAD+ as hydrogen acceptor. Product of this very exergonic reaction G3P reacts with inorganic phosphate present in cytosol to yield 1,3bisphosphoglycerate (BPG). Process: Oxidation / Dehydrogenation Next Review 7 BPG/ BPG/ ATP (3PG) Substrate-level phosphorylation ADP (3PG) One of phosphates of BPG reacts with ADP to form ATP resulting in 3phosphoglycerate (3PG). Process: Substratelevel phosphorylation Next Review 8 (3PG) (3PG) isomerization (2PG) 3PG is rearranged to 2phosphoglycerate (2PG) Process: Isomerization. (2PG) Next Review 9 (2PG) (2PG) dehydration H20 ONE molecule of water is removed, which results in formation of double bond. The product, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Process: Dehydration (removal of water) Next Review 10 ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation ADP Phosphate group of PEP molecules is transferred to ADP to yield ATP and pyruvate. Process: Substratelevel phosphorylation. Next Review Answer the following questions 1 2 3 4 • Energy investing phase • Energy yielding phase • Where reduced NAD+ is produced • Name of enzymes at 1 & 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 14 15 THREE BIG IDEAS BIG IDEA #1 BIG IDEA #2 BIG IDEA #3 ENSURING THAT STUDENTS LEARN BUILDING A CULTURE OF COLLABORATION A FOCUS ON STUDENTS” OUTCOME 4 CRITICAL QUESTIONS 1. What do we want our students to learn? (Focus) 2. How will we know they are learning? (Inquiry) 3. How will we respond when they don’t learn? (Innovation) 4. How will we respond when they do learn? (Impact) Source : www.allthingsplc.info Learning Outcomes • By the end of the lesson, study should be able to: • outline glycolysis to pyruvate with the yield of ATP and reduced NAD+ Question 1 What is do you we want our students to learn? (Focus) 18 Learning Objectives At the end of the tutorial lesson, 80% of the students are able to: • state the definition of glycolysis and the location where it occurs in a eukaryotic cell • state the 10 steps of reaction involved glycolyis • identify correctly at least 4 types of chemical reactions during glycolysis • state the reactions where hexokinase and phosphofructokinase are involved in glycolysis • state the steps during glycolysis when energy is invested and steps where energy is yielded 19 Learning Objectives • indicate the free energy level for each intermediate product during glycolysis • show where ATP is invested & yielded and where NAD+ is reduced during glycolysis • indicate the two phases in glycolysis • justify the total ATP produced during glycolysis • able to score 80% of quiz questions the end of the lesson Question 2 How do we know they are learning? (Inquiry) 20 Glucose Glycolysis: The Reactions Glucose 2 Fructose 6-phosphate 3 Phosphofructokinase ADP Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Aldolase 4 5 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) 6 NAD+ Pi NAD+ Pi NADH NADH 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) 7 ADP ADP ATP ATP 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) 3-Phosphoglycerate ATP 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) 9 H2O H2O Phosphoenolpyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) (PEP) ADP ADP 10 ATP ATP Pyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) 2-Phosphoglycerate 8 Pyruvate Pyruvate Review of Glycolysis Glucose 6-phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Hexokinase ADP 1,3-Bisphospho- Dihydroxyacetone Fructose Fructose glycerate Phosphate 1,6-bisphosphate 6-phosphate Glucose 6-phosphate 1 ATP BIG IDEA #1: Ensuring that Students Learn Question 3 What will we respond when they don’t learn? (Innovation) 22 BIG IDEA #2: Building a Culture of Collaboration BIG IDEA #3: A focus on Students’ Outcome Question 3 What will we respond when they don’t learn? (Innovation) 23 Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate & Glucose PhosphoenolGlycolysis: The Pyruvate Reactions pyruvate 10 2 Pyruvate Fructose 6-phosphate 3 ATP Phosphofructokinase ATP ADP H2O ADP Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Aldolase 4 5 Dihydroxyacetone phosphate Glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) 6 ATP NAD+ 2NADH ATP Pi NAD+ Pi NADH NADH 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) 2ATP 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) 7 ADP ADP ATP ATP 2ATP 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) 2ATP Phosphoenolpyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) (PEP) ADP 10 ADP ATP ATP Progress of Reaction Pyruvate Pyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate H2O Pyruvate 9 Substrate-level Phosphorylation Dehydration Isomerization Substrate-level Phosphorylation Isomerization Oxidation & Phosphorylation Cleavage Phosphorylation Isomerization Phosphorylation H2O 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) 2-Phosphoglycerate 8 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate Glucose 6-phosphate Pyruvate Hexokinase ADP 9 Glucose 6-phosphate ATP 1 ATP ADP Phosphoenolpyruvate Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) (PEP) H2O 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) 2-Phosphoglycerate (2PG) 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) 8 3-Phosphoglycerate (3PG) ATP ATP 7 ADP Glucose 1,3-Bisphospho- Dihydroxyacetone Fructose Fructose glycerate Phosphate 1,6-bisphosphate 6-phosphate 2-Phosphoglycerate 3-Phosphoglycerate 3-Phosphoglycerate ADP NADH 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) 6 Pi NAD+ Dihydroxyacetone phosphate 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) NADH NAD+ Pi Glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) 5 4 Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate ADP 3 ATP Fructose 6-phosphate Fructose Fructose Dihydroxyacetone 1,3-Bisphospho6-phosphate 1,6-bisphosphate Phosphate glycerate 2 Hexokinase ADP 1 ATP Glucose Free energy level Glucose 6-phosphate Glucose 6-phosphate Glucose Documentation and sharing When Students’ learn…. Lesson Study Sharing session Question 4 in KMPh (Jun 2016) Convention (6-8 Sep How willPLC we respond when 2016) they do Learn? (Impact) 25