Report of the World Commission on Dams www.dams.org
advertisement

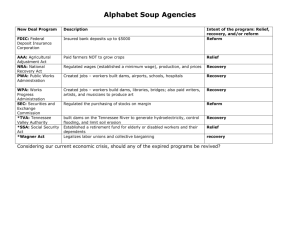
Report of the World Commission on Dams www.dams.org Why a World Commission on Dams ? In response to escalating conflicts over the role of dams in development, all constituents came together to establish the Commission Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Dam projects increasingly questioned … • affected populations strongly oppose dams • proponents point to urgent development demands • opponents point to adverse impacts • uprisings against globalization • little space for constructive dialogue Purposes of large dams • Hydropower • Irrigation • Water supply • Flood control • Multipurpose Types of large dams • Reservoir-type storage – impound water behind the dam for seasonal,annual and, in some cases, multiannual storage and regulation of the river. • Run-of-river dams – weirs and barrages, and diversion dams create a hydraulic head in the river to divert some portion of the river flows to a canal or power station. Hydropower By 1925, falling water generated 40% of electric power. Today, large dams (15 m +) generate 19% of electricity. Hydro production capacity has grown 15 x. Fossil fuel use has risen so rapidly that currently, hydroelectric only supplies one-quarter of electrical generation. One-third of world’s countries rely on hydropower for more than half their electricity supply. Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Irrigation: The Aral Sea • Once the 4th largest inland body of water in the world A series of dams was built to irrigate cotton. • Aral Sea reduced to about 25% of its 1960 volume, quadrupled the salinity of the lake and wiped out the fishery. Pollutants became airborne as dust, causing significant local health problems. • The environmental damage caused has been estimated at $1.25 -$2.5 billion a year. Water supplies • freshwater withdrawals doubled in 50 years • 1 billion lack freshwater & 2 billion lack electricity • competition for water increasing • aquatic ecosystems are declining & wetlands have been lost Major investments … Number Of Dams 6 000 • 45,000 large dams worldwide 4 000 • 2 dams commissioned per day in1970s • total investment exceeds $2 trillion • $40 billion expenditure per year at peak 2 000 0 1900 • estimated 40 – 80 million people displaced • flow in 60% of world’s rivers affected 1990s Dam Drawbacks to Human Communities Human Displacement Flooding of Cultural Sites (Archeological and Modern) Social disruption Cost overruns Socio-economic centralization Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Dam Drawbacks to the Environment Ecosystem Destruction Fish Blockage and Wildlife Losses Large-Scale Flooding Due to Dam Failures Sedimentation and Salinity Herbicide and Other Toxic Contamination Evaporative Losses Nutrient Flow Retardation Release of greenhouse gasses Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Dam Alternatives Low-Head Hydropower - Extract energy from small headwater dams. Run-of-River Flow - Submerged directly in stream and usually do not require dam or diversion structure. Micro-Hydro Generators - Small versions designed to supply power to single homes. Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams WCD Findings • Dams have made a significant contribution • A considerable number have fallen below targets • Economic and financial under-performance • Significant impacts on riverine & downstream ecosystems • Heavy toll on affected communities • Alternatives often exist • Lack of compliance Significant contribution… • 19 percent of electricity from hydropower – more than 50% in 63 countries • dams support 30-40% of irrigated area & 12-16% of global food production • 12% of all dams have a water supply function • 75 countries have dams for flood control Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Considerable number have fallen below targets… • irrigation – almost half have under-performed …opportunities for efficiency gains • hydropower – on average met expectations but considerable variability • flood control – dams have attenuated floods, but some increased vulnerability Kariba • physical sustainability – safety improving, but dams are TWh Predicted vs actual generation 10 Predicted aging and costs rising …loss of storage, 0.5 to 1.0% per year 6 Actual 0 1960 2000 Economic & financial under-performance… • average cost overruns of over 50% • 50% in survey with one year or more delay • cost recovery in hydropower but not irrigation • poor economic and financial results from irrigation • mixed results for hydropower Significant impacts on riverine & downstream ecosystems… • loss of riverine & terrestrial biodiversity • adverse impacts on livelihoods in floodplains • 67% of ecosystem changes in survey are negative • poor record of ecosystem mitigation • some reservoirs have created habitats for biodiversity • reservoirs emit green-house gases Heavy toll on affected communities… • estimated 40-80 million physically displaced • significant number of others affected • failure to adequately recognise & respond to those affected • negative impacts fall disproportionately on disadvantaged • inequity is not addressed in ‘balance sheet’ approach Alternatives often exist… • reduce demand by increasing end-use efficiency • defer new supply by enhancing supply & conveyance efficiency • extend life and performance through improved land & water management • promote alternative supply options, including small-scale & locally appropriate approaches Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Lack of compliance… • weak regulatory frameworks & lack of enforcement • little public participation & scrutiny • top down decision-making, often politically motivated • past conflicts remain unresolved with no legal recourse • vested interests in favour of large infrastructure • no incentives or sanctions What did the Commission find from the knowledge base ? Dams have delivered considerable benefits In too many cases the price paid to secure those benefits has been unacceptable and often unnecessary Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Unprecedented response to the controversy … • WCD created through unanimous agreement • broad based mandate to review development effectiveness & assess alternatives… … and develop internationally acceptable criteria and guidelines • address global problems through local understanding • WCD’s authority and credibility rests on the diversity of the Commissioners which was a guiding theme throughout its inclusive, transparent and participatory work program. Who was the Commission ? Kader Asmal Lakshmi Chand Jain Donald Blackmore Joji Cariño Jan Veltrop Thayer Scudder Deborah Moore José Goldemberg Judy Henderson Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Medha Patkar Göran Lindahl Achim Steiner Inclusive, Participatory & Transparent … • full range of perspectives – civil society to governments, private sector to NGOs, financiers to foundations • outreach through work program and networks • extensive review process • WCD Forum as a reference point • draft studies on website www.dams.org The Way Forward • Move beyond the simple “balance –sheet approach”… …to shared values, objectives and goals • Internationally accepted norms are basis for WCD recommendations • Adopt a rights and risks approach • Define whose rights and what risks Move beyond the simple “balance-sheet” approach that… • trades off losses and gains between groups • impoverishes some people • excludes people and limits awareness • overlooks sustainability aspects • induces conflict and higher costs Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Towards shared values, objectives & goals… • equity • efficiency • participatory decision-making • sustainability • Accountability Define whose rights & what risks… Rights • No party’s rights should extinguish another’s • Where rights compete – negotiated agreements are needed Risks • Move beyond considering voluntary risk takers to include involuntary risk bearers Turning Conflict Into Consensus Seven Strategic priorities • • • • • • • Gain public acceptance Assess options Address existing dams Sustain rivers and livelihoods Recognize entitlements and share benefits Ensure compliance Share rivers across boundaries Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Gaining public acceptance… • dams affect existing rights & create wide range of risks • opportunities exist for achieving a higher level equity of • recognise rights of indigenous & tribal peoples • achieve outcomes through binding formal agreements Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Comprehensive options assessment… • failure to adequately define needs & assess options led to dispute • an early and open examination of options can avoid poor projects • raise the significance of social & environmental aspects • increase the effectiveness of existing systems as a priority Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Address existing dams… • most dams that will operate in the 21st century already exist • considerable scope exists for improving benefits • remedy outstanding social issues …enhance mitigation, restoration & enhancement of ecosystems • use licenses to formalize operating agreements Sustain rivers and livelihoods… • rivers support millions of livelihoods • dams cause significant and often irreversible effects on ecosystems • value rivers, ecosystems & endangered species • emphasise avoidance of impacts • maintain ecosystem integrity through environmental flows Recognize entitlements & share benefits … • many people displaced - many more unrecognised • including those who depend on a river’s resources • recognise rights and assess risks as a basis for negotiations • agree legally enforceable entitlements • adversely affected people become first among beneficiaries Ensure compliance … • many policies and guidelines exist.. • but often a failure to fulfill obligations • need a compliance plan covering all commitments to people and the environment • introduce initiatives to reduce corruption • develop incentive framework for compliance Share rivers across boundaries… • conflicts over transboundary rivers due to power imbalance • experience suggests disputes can be resolved • endorse the UN Convention principles • go beyond sharing water - to sharing the benefits • encourage consistent policies for financing agencies Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Dams in the pipeline - it’s not too late Feasibility - assess all options - gain public acceptance Design - prepare Compliance Plan - contractualize benefit sharing - determine environmental flow Construction - formalize commitments Dams and Development - Report of the World Commission on Dams Improved outcomes for nation, affected people & the environment… Development opportunities for all by.. • respecting human rights • meeting development needs for water, food & energy • sustainable resource use The WCD has … • conducted first comprehensive review of performance • focused on options and compliance • shown that conflict is not inevitable • promoted a rights, risks approach to negotiate outcomes • shown that common ground can be reached Don’t plan, build, protest, operate, decommission, propose, oppose or discuss a dam without it Readings for discussion (pro and con): INDIA (Narmada Valley) CHINA (Three Gorges) SLOVAKIA (Gabcikovo)