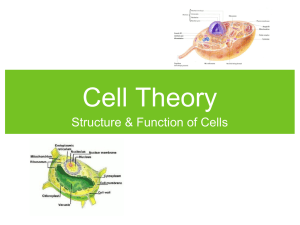
Name:______________________ Date: ___________Period:____
advertisement

Name:______________________ Date: ___________Period:____ Agenda Week of 6 Oct – 10 Oct 2009 Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Exam 10/21/09 1c. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses differ in complexity and general structure. Unit 2 Quiz #2 Oct 13, 2009 1. 2. Which of the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have __________________ and prokaryotes do not. Monday 10/6/09 - Osmosis Experimental Design and Write Up 3. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a HW: Study for Quiz #2 Ch.7 Science Notebook due 10/10/09 Tuesday 10/7/09 Unit 2 Quiz 2 (15 min). Cell City HW: Ch 7 Sci Notebooks Wednesday 10/8/09 –Late Start A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a _______________________ _______________________ 4. The function of a cell membrane is to __________ ______________________________________ 5. Osmosis is defined as the movement of _________ ___________________________________ Cell Basics HW: Ch.7 Science Notebook 6. Thursday 10/9/09 7. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and - Osmosis Lab Setup Ch 7 SciNotebook HW: Ch.7 Science Notebook - Friday 10/10/09 Osmosis Lab Observations and Reporting - Collect Ch 7 SciNotebook HW: Ch.8 Science Notebook - Parents/Guardian – I have reviewed my child’s activities and homework for the week of 10/5/09 – 10/10/09. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the quiz and has completed all assignments this week. Parent/Guardian Printed Name Most cell membranes are mainly composed of ___________________________________ viruses all share? __________________________ 8. Explain the differences between: Active transport Passive transport Facilitated transport 9. The cell structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are _________________ Vocabulary Chlorophyll Eukaryote Osmosis Hypotonic Passive transport Ionic Concentration Active transport Facilitated transport Signature Diffusion Isotonic Hypertonic Denaturation Date Bell Ringers: Week of 5 Oct – 10 Oct 2009 Monday – The structure of the sugar sucrose, C12H22O11, is shown below. It can be broken down to yield simpler sugars and energy for the cell. To which class of organic compounds does sucrose belong? a. Lipids c. Carbohydrates b. Proteins d. Nucleic acids Explain Tuesday - Soto puts a drop of green food dye into a glass of water and observes the dye forming colorful swirls before eventually turning the water green. Explain Soto’s observations. Wednesday - Science students in Alma’s class are observing prepared slides of the cells of maple tree leaves and mammal skin cells. As they study the cells under the microscope’s highest magnification, their teacher records their observations on the board. Which would be included in the teacher’s list? A. Both the animal and plant cells have an oval shape and are about the same size. B. Both types of cells have a membrane that is also surrounded by a cell wall. C. The leaf cells have green organelles called chloroplasts; the animal cells do not. D. The skin cells have a nucleus, but the cells of the leaves have no nucleus. Explain. Thursday - Identify a structure other than a cell wall or a vacuole that might be found in a plant cell but not in an animal cell. Explain why an animal cell would not have the structure you identify. Friday - Which is a structure common to all cells? A. mitochondria B. nucleus C. endoplasmic reticulum D. plasma membrane Explain Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz 2 1. An example of an organism that is a prokaryotes is a _______________________ 2. Which of the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that eukaryotes have __________________ and prokaryotes do not. 3. Most cell membranes are mainly composed of ________________________________________ 4. The function of a cell membrane is to __________ ______________________________________ 5. Which parts do prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, and viruses all share? __________________________ 6. A student could tell the difference between onion skin cells and cheek cells because the onion skin cells have a _______________________ 7. Osmosis is defined as the movement of _________ ___________________________________ 8. Which of the following functions does active transport perform in a cell? a. packaging proteins for export within c. distributing enzymes throughout the and out of the cell cytoplasm b. equalizing the concentration of water d. moving substances against a inside and outside a cell concentration gradient 8. The cell structures that make proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus are _________________ 10. Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? a. diffusion c. facilitated diffusion b. osmosis d. active transport Chlorophyll Osmosis DNA Passive transport Denaturation Ionic Concentration Active transport Facilitated transport Diffusion Hypertonic Eukaryote Hypotonic Isotonic Prokaryote _______________________ A. a nucleic acid which is the hereditary material of most organisms _______________________ B. simple cell without specialized membrane-bound structures _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ C. net movement of particles from an area where there are many particles of the substance to an area where there are fewer D. destruction of a proteins structure that inactivates the protein’s function E. same concentration of a solute inside as outside of a cell membrane _______________________ F. the movement of a particle from low concentration to high concentration. _______________________ G. A type of transport that does not require energy but does require a transport protein. _______________________ H. the concentration of salts that affect cell shape and protein structure and function. _______________________ I. Molecule that absorbs solar energy which is the first step of photosynthesis _______________________ _______________________ J. a higher concentration of a solute outside of a cell membrane than inside K. cell with specialized structures, which include the nucleus and other organelles _______________________ L. diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane _______________________ M. a higher concentration of a solute inside of a cell membrane than outside. _______________________ N. the movement of particles across a selective membrane that does not require energy and may or may not require a protein. Extra Credit Lipids and carbohydrates are important in animal cells because both — a. store energy _ b. contain nitrogen c. form cell walls d. provide insulation Cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate. Which of the following compounds is the basic unit of the cell wall? a. amino acids c. nucleotides b. sugars d. lipds Because the cell membrane is highly selective with respect to the materials that can cross its boundary, it is described as being selectively… a. permeable c. mosaic b. porous d. fluid Name:________________________________ Date:________________ Period:_______ Unit 2 Quiz #3 Oct 14, 2009 1. Name two structures are found in every living cell? 2. A cellular process in which one molecule of glucose is broken down via a number of steps to produce a total of 38 ATPs is called ______________________________. 3. The structure and function of membrane proteins are described as ___________________________________________________________________. 4. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is observed using high power (400x) of a compound light microscope. Which structures would most likely be observed? 5. _________________ is an anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates to produce a small amount of ATP. 6. Factors that increase the rate of diffusion of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane are: - _________________________ - __________________________ - __________________________ - _____________________________________________________. 7. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is __________________________________ _______________________________________ 8. Diffusion occurs because _______________________________________________ 9. The type of particle transport that requires input of energy from the cell is ______________________. 10. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are _________________________________________________________________ _____ Ribosomes A. a colored molecule like chlorophyll. _____ Vacuoles B. site of aerobic cellular respiration (krebs cycle and electron transport chain) _____ Virus C. small structural units that perform specific functions in cells. _____ Enzyme D. first step in the breakdown of glucose occurs in the cytoplasm. _____ Nucleolus E. membrane-bound organelle where DNA is stored in eukaryotic organisms. _____ Peptide F. organelles involved in protein synthesis using coded information from the nucleus. _____ Phospholipids G. membrane-bound storage organelle _____ Mitochondria H. dense area within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA is produced. _____ Glycolysis I. a non-living biological active structure make of a protein coat and nucleic acid core. _____ Nucleus J. bond between amino acids _____ Organelles K. molecules that make of cell membranes composed of a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails. _____ Pigment L. biological catalyst usually made of protein and sensitive to pH, temperature and ionic conditions. 1. The structure and function of membrane proteins are described as globular proteins that create narrow passageways or channels _. 2. A cellular process in which one molecule of glucose is broken down via a number of steps to produce a total of 38 ATPs is called aerobic respiration . 3. fermentation is an anaerobic breakdown of carbohydrates to produce a small amount of ATP. 4. Which structures are found in every living cell? a cell membrane and ribosomes 5. Factors that increase the rate of diffusion of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane are 1)distance involved, 2)concentration of the substances, and 3) weight of the molecules. 6. The series of diagrams represents a process carried out by a cell. This process is known as phagocytosis. 7. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is usually made of cellulose that are tough fibers. 8. Diffusion occurs because molecules constantly move and collide with each other. 9. The type of particle transport that requires input of energy from the cell is known as active transport. 10. Two organelles that are common to plant cells but not to animal cells are 1) cell wall and 2) chloroplasts. 11. A wet mount of unstained elodea (a green aquatic plant) is observed using high power (400x) of a compound light microscope. Which structures would most likely be observed? Nucleus, chloroplast, and cell wall.