Name:__________________________ Date: ____________Period:_____ Unit 1 EXAM 9/16/10
advertisement

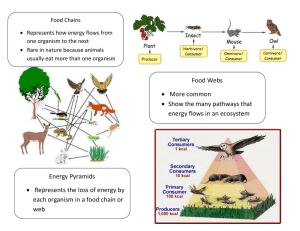
Name:__________________________ Agenda Week of 6 Sep – 10 Sep 2010 Date: ____________Period:_____ Class website: www.marric.us/teaching Unit 1 EXAM 9/16/10 Standards: 6. c. Students know how fluctuations in population size in an ecosystem are determined by the relative rates of birth, immigration, emigration, and death. 6. e. Students know a vital part of an ecosystem is the stability of its producers and decomposers. 6.b. Students know how to analyze changes in an ecosystem resulting from changes in climate, human activity, introduction of nonnative species, or changes in population size. Monday 9/6/10 – Labor Day HW: Ch4/5 Study Guides Tuesday 9/7/10 – No School A few more review questions For Exam on 9/16/10 1. What is the most common explanation for population growth by a non-native (invasive) species? Recall that invasive species are organism not normally found in the area and may have been introduced into an area by humans. 2. When organisms die, what prevents the environment from being overwhelmed by the bodies of these organism? 3. What characteristic determines whether an organism is a producer, a consumer, or a decomposer?. - Professional Development HW: Ch 4/5 Study Guide 4. What is the main element in fertilizers that can pollute waterways? Wednesday 9/8/10 – Late Start 5. What is the main cause of fish kills in rivers polluted by fertilizers? - Quiz #4 Population Dynamics K/r strategies HW: Ch 4/5 Concept Map 6. Diagram eutrophication. Thursday 9/9/10 – - Review Ch 4/5 Study Guide Collect - Review Quiz Results Complete Human Population Analysis HW: Complete Population Project Friday 9/10/10 – Present Country Findings Wolf Population Project HW: Study for EXAM on Th 9/16 Practice Questions and Analysis and organize portfolio. - 7. List three reasons why habitat protection is important. 8.What is the maximum percentage of food energy available to a wolf that consumes a herbivorous mouse? 9.The maintenance of a self-sustaining ecosystem requires a _________________________. 10.The water cycle would not occur if plenty of water were present, but __________________________ was missing? Parents/Guardian – 11. Fungi, such as mushrooms and molds, get their nutrition I have reviewed my child’s activities primarily by______________________________ and homework for the week of 9/6/10 – 9/10/10. I understand that is important for me to make sure that my child is studying to be prepared for the quiz and has completed all assignments this week. There will be a Unit EXAM on 9/16/10 Parent/Guardian Printed Name Signature Date Bell Ringers: Week of 6 Sep – 10 Sep 2010 Monday – Labor Day Tuesday – Professional Development Wednesday - Local and federal legislation have placed limits on the amount of nitrogen-containing fertilizers to be tolerated in field run-offs into a lake. The reason for this legislation is that run-off of the fertilizers would most likely produce _______. A increased algae growth. C evaporation of ground water. B more acidic lake water D fertility of predatory fish. Explain what would happen next to the oxygen levels available for fish. Thursday - While visiting a history museum in Montreal, Danielle observes a graph on display that records the number of lynx (predator) and hare (prey) trapped in the Hudson Bay area between the years 1845 and 1935. The graph has two different lines one each for lynx and hares. She notices that the two lines on the graph follow a pattern. Which pattern does she observe? A. Both hare and lynx populations remain constant. B. Both hare and lynx populations rise and fall together. C. The hare population decreases shortly after the number of lynx decreases. D. The lynx population decreases shortly after the number of hares decreases. Explain. Friday - Which organism/s is affected negatively by increased temperatures? Explain. Identify the areas on this logistic growth curve labeled a, b, and c A FEW MORE REVIEW QUESTIONS FOR EXAM ON 9/16/10 1. What is the most common explanation for population growth by a non-nave (invasive) species? Recall that invasive species are organism not normally found in the area and may have been introduced into an area by humans. The invasive species find unoccupied niches where competition pressures are low. 2. A community of organisms interacting with abiotic environmental factors is called a(an) Ecosystem. 3. A group of similar-looking organisms that breed with each other and produce fertile offspring make up a(an) species and a(an) population if they live in the same area. 4. The ultimate source of energy for life on Earth is the sun. 5. What is the variety of species in a given area called? biodiversity According to the food web: 6.Which organism(s) is a carnivore? Snake, hawk, and lizard 7. Which organism(s) is an omnivore? Mouse and bird 8. Which organism(s) is a herbivore? Ants, chipmunk, and grasshopper 9. Which organism(s) is a producer? Cactus and shrub 10. A top predator may increase the diversity of species lower on the food chain by decreasing competition amoung the survivers. 10. List three reasons why habitat protection is important. Species do not live independently. Protecting habitat protects species Without habitat, the balance of nature could be disrupted. 11.In Sacramento, automobile exhausts cause dirty, brown haze known as smog. 12. Ecosystem connectivity must be considered because human pollution travels by wind, river, and ocean currents. Name:__________________________________ Date:______________ Period:_____ Identify the Producers Herbivores Omnivores Carnivores Explain why removing the snake from this food web might result in a decrease in the grasshopper population