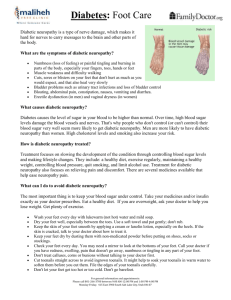
Unit 4 Discussion: Group B (Tammy, Heather and Merissa)

Unit 4 Discussion:
Group B
(Tammy, Heather and Merissa)
What is Radiculopathy and how would it differ from a Neuropathy?
The term Radiculopathy is used to specifically describe pain and other symptoms including:
Numbness
Tingling
Weakness
Radiculopathy usually creates a pattern of pain and numbness that is felt in your arms or your legs in the area of skin supplied by the sensory fibers of the nerve root.
Muscle weakness may also be present in the muscles supplied by the same nerve root. (Back.com, 2009)
Common Example of
Radiculopathy Pain
SCIATICA
This is pain that radiates from the back into the buttocks and down the legs into the feet (Back.com, 2009)
Neuropathy is a disorder of the peripheral nerves which include:
Motor
Sensory
Autonomic
Which connect the spinal cord to muscles, skin and internal organs.
Like radiculopathy, neuropathy causes:
Weakness
Numbness
Tingling
Pain
HOWEVER ;
Radiculopathy usually refers to injury of nerve roots along the spine due to compression, inflammation or trauma (McCance & Huether,
2003; Wikipedia, 2009). Causes may include osteoarthritis, disc herniation and scoliosis
(Answers.com, 2008).
Neuropathy normally occurs in older adults with
30% of cases being idiopathic in origin, 30% related to diabetes and the remaining related to other causes including autoimmune disorders
(The Neuropathy Association, 2008).
Peripheral Neuropathies may:
Come and go
Progress slowly over many years
Become severe and debilitating (The
Neuropathy Association, 2009)
Neuropathy may progress from numbness, tingling, abnormal sensations or pain in the feet .
Some people feel like they have socks on, even though they are barefoot. Over time, this feeling spreads to your legs and hands (The
Neuropathy Association, 2009) It may become harder and harder to walk ; the legs feel heavy . The individual may feel as though they have to drag themselves up the stairs. Next, it may be difficult to maintain balance because the individual is not exactly sure where their feet are, causing stumbling and a risk for falls .
To keep balance, the gait may become widened and walking may become less rhythmic or fluid.
Radiculopathy and Neuropathy present very similarly with tingling, numbness and weakness.
General Differences:
Radiculopathy Radiating
Pain
Neuropathy Debilitating and
Progressive
References
Answers.com (2008). Neurological disorder: Radiculopathy. Retrieved
January 25, 2009 from http://www.answers.com/topic/radiculopathy
Aronowski, J. & Labiche, L. (2003). Perspectives on Reperfusioninduced Damage in Rodent Models of Experimental Focal Ischemia and
Role of γ-Protein Kinase C. ILAR Journal. 44(2).
Back.com. (2009). Radiculopathy. Retrieved January 26, http://www.back.com/symptomsradiculopathy.html
2009 from:
The Neuropathy Association. (2009 ). About peripheral neuropathy: signs and symptoms. Retrieved January 26, 2009 from: http://www.neuropathy.org
McCance, K., & Huether, S. (2006). Pathophysiology: The biologic basis for disease in adults and children. (5 th ed.). St. Louis, MI: Elsevier Mosby.
Wikipedia (2009). Radiculopathy. Retrieved January 25, 2009 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radiculopathy
Wikipedia (2009). Neuropathy. Retrieved January 25, 2009 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuropathy