ANXIETY DISORDER GROUP 1 SCL 105
advertisement

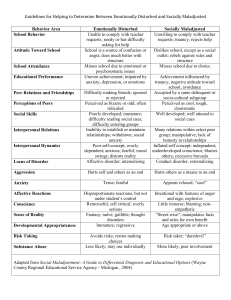
ANXIETY DISORDER GROUP 1 SCL 105 GROUP 1 NA PANG JANELL TROTMAN MARIE JIMENEZ PETRA RAMNARINE MAJORIE JOHNSON STACY MOYSTONDUCKIE ANAISE IKAMA YVONNE PREMPEH EDNENTH FLORES ANXIETY DISORDERS GENERALIZE ANXIETY PANIC DISORDER PHOBIAS POST TRAMATIC STRESS OBSESSIVE COMPLUSIVE DISORDER ANXIETY DISORDER Anxiety disorder is characterized by chronic free-floating anxiety with symptoms such as tension, sweating, trembling, lightheadedness and irritability. These disorders are a serious problem for the entire society because of their interference with patients' work, schooling, and family life. They also contribute to the high rates of alcohol and substance abuse in the United States. Anxiety disorders are an additional problem for health professionals because the physical symptoms of anxiety frequently bring people to primary care doctors or emergency rooms. GENERALIZED ANXIETY DISORDER BY YVONNE PREMPEH NA PANG Generalized Anxiety Disorder Definition Signs & Symptoms Causes By Yvonne Prempeh Definition General anxiety disorder (GAD) is a broad term covering several different forms of abnormal, pathological anxiety, fears, phobias and nervous conditions, which may have sudden onset or may occur gradually over a period of several years Signs & Symptoms of GAD Fatigue Headache Muscle tensions Muscle aches Difficulty swallowing Trembling Twitching Irritability Sweating Nausea Short of breath Hot flashes Difficulty in initiation of maintenance of sleep Causes of GAD Serious or prolonged physical illness Personality type or disorder that is prone Family anxiety disorders Generalized Anxiety Disorder Student Name: Na Pang Generalized Anxiety Disorder Treatment 1.SSRIs 2.Benzodiazepines 3.Cognitive behavioral therapy. 4. Psychotherapy 5. Self-help or support group 6. Stress management techniques 7. The family support Nursing Care Nursing Intervention 1. Allow client to take as much responsibility as possible for self-care practices. 2. Assist client to set realistic goals. 3. Help identify areas of life situation that client can control. 4. Help client identify areas of life situation that are not within his or her ability to control. Encourage verbalization of feelings related to this inability or longer. PANIC DISORDER BY STACY-MOYSTON DUCKIE DEFINITION SIGNS & SYMPTOMS TREATMENT NURSING INTERVENTION PHOBIA BY MARJORIE JOHNSON ANAISE IKAMA POST TRAMATIC STRESS BY MARIE JIMENEZ EDNENTH FLORES Post traumatic stress disorder • • Definition Clinical features Treatment Options for post-traumatic disorder • By Edeneth Flores • Definition Post traumatic stress disorder is a type of anxiety disorder that is triggered by an extremely traumatic event Ex: of traumatic events: childhood abuse, a plane crash, hurricane, terror attack, or war. Post traumatic disorder was first discovered after the Vietnam war. Clinical features Manifestation of post- traumatic disorder typically begins within 3 months of the catastrophic event. Signs/symptoms to watch out for: Recurring thought about the catastrophic event/flashbacks Clinical features Irritability, trouble sleeping, Avoiding talking about the situation, dysphoric feelings and unpleasant thoughts. Outburst of anger SEEK HELP!!!!!!!!!!!! Treatment Options Medications includes: Anti-depressant: - zoloft and paxil commonly prescribed -decrease symptoms of anxiety and depression. Anti-anxiety: -it will improve feelings of anxiety Sleeping pills could also be prescribe due to the patient having hard time sleeping!!! Treatment Options Psychotherapy: Mainly perform by the psychologist A patient is free to just talk about any topic/feels. Other forms of psychotherapy includes: Cognitive therapy: provides psychological treatment Individual therapy All these approaches will help the patient gain control about his/her fear and great distress that happen after a very traumatic event. SEEK HELP AS SOON AS POSSIBLE ESPECIALLY WHEN YOU EXPERIENCE 2 0R MORE OF THE SYMPTOMS!!!!!! Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Nursing care plan Community Outreach Options Test Questions By Marie Jimenez Nursing Diagnosis Problem: Posttrauma syndrome R/T Etiology: distressing event considered to be outside the range of usual human experience AEB Signs & Sx: flashbacks, intrusive recollections, nightmares, psychological numbness related to the event, dissociation, or amnesia Nursing outcome For Posttrauma syndrome: The client will integrate the traumatic experience into his or her persona, renew significant relationships, and establish meaningful goals for the future Nursing Interventions Assign the same staff as often as possible Stay with client during periods of flashbacks and nightmares Encourage the client to talk about the trauma at his or her own pace Discuss coping strategies used in response to the trauma Assist the individual to try to comprehend the trauma if possible Community Outreach Options Project Liberty helps disaster survivors to understand what was happening and how they were reacting, to think about options, and to find people or agencies that could assist with disaster-related problems. http://www.projectliberty.sta te.ny.us The 9/11 Mental Health and Substance Abuse program people to seek professional help for any 9/11-related psychological distress they experienced in the years following the attacks PTSD http://www.redcross.org /911legacy True or False PTSD is an adult psychiatric disorder. Answer: FALSE Although adults may most likely seek treatment for PTSD, this serious anxiety disorder can occur at any age, including childhood and adolescence. Q) Which of the following may be influential in the predisposition to PTSD? a. Unsatisfactory parent/child relationship b. Distorted, negative cognitions c. Severity of the stressor and availability of support systems d. Excess of the neurotransmitter seratonin Answer: c. Severity of the stressor and availability of support systems Several factors contribute to development of PTSD. One of these factors are the nature and intensity of the stressor or event. PTSD is likely to result from trauma or disaster if there are not available resources to assist in debriefing. OBSESSIVE COMPLUSIVE DISORDER BY PETRA RAMNARINE JANELL TROTMAN