Phylum Platyhelmenthes Simple acoeleomates Bilaterally Most flattened
advertisement

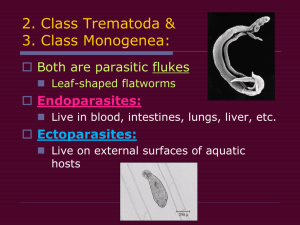
Phylum Platyhelmenthes Planarians, Flukes, & Tapeworms •Simple acoeleomates •Bilaterally symmetrical •Most flattened "Dorsoventrally" •Divided into 4 classes: Class Turbellaria •Most free-living and non parasitic •Include planarians •Lack circulatory and gas-exchange organs. •Simple excretory structures called flame cells that maintain osmotic balance. •Is cephalized and has eye-spots which are sensitive to light •Feeds through ventral feeding tube called a pharanx •Can reproduce sexually, or asexually through regeneration Planarian and assorted marine flatworms… Class Trematoda (Flukes) • Similar in form to turbillarians • Many are parasitic. Example of parasitic fluke is the asian liver fluke • Many have complex life cycles including multiple hosts and alternation of generations. Life Cycle of the Liver Fluke Liver Flukes Cont’d… Liver Fluke Liver Fluke encysted in a liver Class Cestoda (Tapeworms) • Parasitic flatworms • Can grow to enormous lengths (up to 20m) • Parasitize mostly vertebrate hosts • Attach head named scolex to intestinal walls of host, and abosrb host's nutrients • Following scolex is a series of repeating structural units called proglottids • Mature proglottids containing thousands of eggs are released with the host's feces to infect other organisms. Tapeworms cont’d…