Module Summary
advertisement
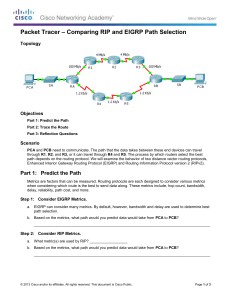
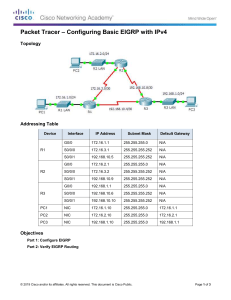
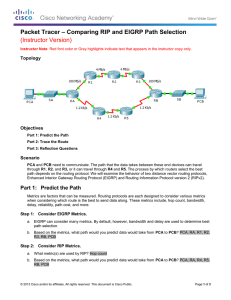
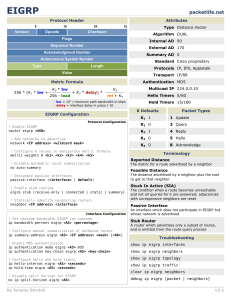
Module Summary EIGRP starts by building a table of adjacent neighbors. Route exchanges with these neighbors result in an EIGRP topology table. The DUAL process calculates the best EIGRP routes, which are moved into the IP routing table. Steps to configure basic EIGRP are: define EIGRP as a routing protocol, define attached networks participating in EIGRP, and, if desired, define interface bandwidth. The configuration of a passive interface, IP default-network, and summarization are all advanced steps to improve network scalability and decrease the number of EIGRP updates exchanged between EIGRP neighbors. © 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ROUTE v1.0—2-1 Module Summary (Cont.) Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) supports EIGRP, allowing service provider PE-routers to be aware of EIGRP and P-routers to be hidden from the customer network. EIGRP supports MD5 authentication, which checks and authenticates the source of each routing update packet received. Features such as stub routing and active process enhancement help improve network stability and performance. © 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ROUTE v1.0—2-2 © 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. ROUTE v1.0—2-3