Tides
advertisement

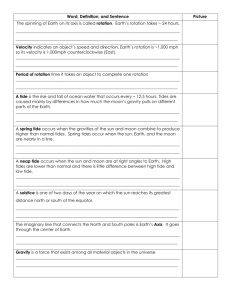
Tides Tides are the daily changes in the elevation of the ocean surface. Tides are the daily rise and fall of the Earth’s waters on its coastlines. Tides are caused by the interaction of the Earth, the moon and the sun. A. Tides form from the gravitational attraction exerted upon the Earth by the moon. B. Tidal Cycle-Is influenced by the sun and moon. When they are aligned together their forces are added. Gravity is the force exerted by an object that pulls another object toward it. As the distance between two objects is greater the force becomes weaker. Daily Tides Tides happen regularly no matter what the wind is doing Tides occur in all bodies of water but are most noticeable in oceans. High Tide- as the tide comes in toward the beach and reaches its highest point Low Tide-as the tide flows back toward the sea and reaches its lowest point Daily Tides The moon gravity pulls on the water on the Earth’s Surface. The moon pulls on the water on the side closest to it more than it pulls on the center of the earth. This pull creates a Tidal bulge, a bulge of water on the side of the earth that is facing the moon . On the other side of the earth is a bulge of water that is pulled less strongly than the center of the earth. Where the tidal bulges are is where high tides occur. As the earth rotates different part of the earth's surface pass by these areas and experience the water level changes. Tide Causing Force The Moon is the primary tide causing force. The gravitational pull of the moon causes bulges of water towards and away from the moon. The Daily Tidal Cycle 1. All areas of the world oceans pass under the 2. 3. moon every 24 hours and 50 minutes. The cycle takes more than one day, each day the tides occur at different times Every coastal area has at least one high tide and one low tide every day Factors which influence the daily Tidal patterns are: 1. The earth’s surface 2. Shape of the ocean floor/coastline 3. Coriolis effect Tidal Patterns determined by how many high and low tides in a 24 hour period. 1. Diurnal Tides-Include a single high tide and a single low tide each day. Example-Southeastern US along Gulf of Mexico 2. Semidiurnal Tides-Include two high tides and two low tides each day. Example-Atlantic Coast of US 3. Mixed Tides-Inequality of tide levels that has multiple high and low tides. Example- Pacific Coast of US Tide patterns around the world Monthly Tide Cycle 1. The sun’s gravity also effects the Earth, even though it is far away it is very large. The sun’s gravity pulls the earth’s water toward it. Sometimes the moon and sun pull the earth’s water in the same direction other times they pull in different directions. Spring tides 1. Twice a month at the new moon and the full moon, the sun and moon are lined up. 2. These combined gravitational pulls cause the greatest tidal ranges. 3. Spring comes from the word to jump and does not refer to the season!!! Neap Tides 1. At the first quarter (waxing) and third quarter (waning) moons, the sun and moon pull at right angles to each other. 2. Least tidal range due to the sun’s gravity pulling some of the water away from the tidal bulge facing the moon thus evening out the difference between low and high tide. Spring and Neap Tide Cycle Tidal Range Tidal Range is the difference in height between high and low tides. 1. Spring Tides-Are the highest tidal range 2. Neap Tides-Lowest tidal range http://home.h iwaay.net/~kr cool/Astro/mo on/moontides / Monthly Tide Tables Scientists can fairly accurately predict tides at various locations. These are published as tide tables. Who is it important to, in order to know the times and heights of the tides?