Using online collaborative learning (OCL) for sport and exercise science students
advertisement

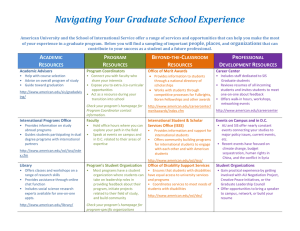
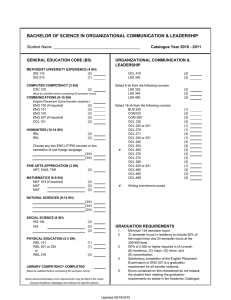
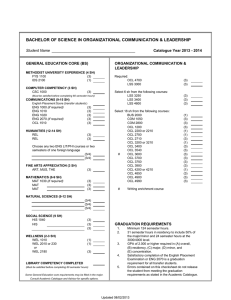
Using online collaborative learning (OCL) for sport and exercise science students »Geoff Walton, Subject and Learning Support Librarian, Staffordshire University »Jamie Barker, Senior Lecturer, Staffordshire University Plan for our talk • • • • • • • • The problem! Context Assessment task Methodology Structure of IL programme Student comments Evaluation: emerging themes Conclusions The problem! • ELICS: Level 1 Core Study skills based module. • Typically, students have had a negative perception of the module. • They over estimate their level of competence on study skills. • Need to make the module more appealing. • Attendance for seminar sessions has been poor. • Use OCL to allow students to take ownership of seminar based content. Context • Our working definition of IL – The ability to find, evaluate and use information appropriately • Embedded: – Effective Learning, Information & Communication Skills in Sport & Exercise Level 1 core – IL one of 5 skills addressed with, statistics, note-taking, essay/ report writing, time management • Blended learning: – Face-to-face (F2F) workshop - find information – Online: collaborative learning via VLE) – evaluate information – Written assessment – use information • Why online collaborative learning (OCL)? – Scaffolded, contributions made by all, available to all, highly interactive, discursive, iterative, reflective, high learning payoff rather than mechanical and/or passive (Walton et al, 2007 a and b) Assessment task • Portfolio exercise (written) – Find 2 books, 2 journal articles & 2 web sites – Write short evaluation of each using criteria which emerged form OCL activities – Reflective statement of 150 words – Reflective essay Methodology • • Experimental group of 15 students, control group and an intermediate group Range of methods used in this study – Post delivery Questionnaire – Content analysis of Focus Group interviews • • Whole group One-to-one – Pre and post delivery tests Overview of IL programme F2F IRPA 1 OCL Activity 1 IRPA 2 F2F - One hour hands-on workshop (One hour, one workshop) OCL 1 & 2 - Online Collaborative Learning Activity (20-30mins, two workshops for each) 1. Creating evaluation criteria 2. Using criteria to evaluate web based information OCL Activity 2 IRPA3 OCL 3 – (20-30mins, one workshop) 3. Using APA referencing style OCL Activity 3 IRPA 4 IRPA - Instant Reflective Practice Activity (5-10mins after each activity) OCL Process for Activities in Blackboard Iteration of initial Thread in greater detail Extracts from student postings Forum Thread IRPA Tutor summary Seed Student postings Web resource(s) You have identified some ‘For when looking at personal 1. Which ONE of this activity excellent evaluation criteria. pagesthese look at their THREE Jamie Geoff lastand year ahave reputation and5what summarised under headings. statements best Creating student Authority -your Kenand argued that ‘it they study For describes what you evaluation is important to check the Jamie Kevin and mentioned Geoff commented thatthe research’ portfolio learned from author or who it was created criteria agree that you with can Kevin get she, Berkeley by’. Tracy pointed outtime that ‘look at‘always the last activity on assignment youthe author could be ‘a a major regarding clues from URLs URL to ensures that a BUT the web page was University evaluating web need to provide company like Microsoft’.when updated especially stress see whether that it need is a web page iswe sites? web page on Jamie & Geoff would argue web pages or stats involved’’ that theare standing of a company to ‘personal be more website reliable before how to 2. Which ONE of sites and give or organisation does not ‘valid links are a good systematic and (therefore) in theyou the way using any evaluate necessarily guarantee these THREE reasons why indicationfree of reliability’ information from bias ask we information analyse their may not information on it’. statements best internet think they are yourself –why the ‘look at theis URL structure be a reliable source’ reflects So, how would you resources information there?what URLs -you Roy good. address and see will that do your mentioned awith good way of decide what makes whether it page is for judging a web can be done new knowledge in a reliable, good example a government by ‘looking at the URL the future? address’. source’ quality web page? Seed instructions using Plain English • 1. Have a look at this example: (BBC website • • • • • on football hooliganism) 2. Go to this webpage for help: (Berkeley University’s guide to evaluating web pages) 3. Read it carefully and make some notes [...] 5. Select the reply button […] 7. Write down how you would evaluate this web page 8. Write a brief statement about the website under each question as suggested by the Berkeley help site Student themes: OCL • • Demonstrating that learning had taken place by realising the value of evaluating web sites Indicating how learning is enhanced and knowledge is extended through: discourse, seeing others views, making comments, receiving feedback from peers and promoting reflection Student themes: Tutor Summary • • • • Recognition of students’ work Opportunity to see everyone’s opinions not just those of lecturer Helped in the learning of new knowledge, making sense of what had been learnt Helped motivate students Evaluation: emerging themes • Students liked being able to contribute in a concrete fashion: – ‘You feel that you’ve done something productive afterwards when you post your reply, something useful like you’ve learnt stuff and soaked it up and that and then managed to extract it in the reply for other people to see ’ • They liked being able to see what fellow students had said: – ‘you got to see what other people thought of the web site’ • students genuinely realised the importance of evaluating web information: – ‘you didn’t realise how many web sites could be frauds because it gave you the links and the ideas to know that web sites you are […] referencing in essays are […] worth looking at […].’ • Students obtained significantly higher scores in the postdelivery knowledge test than in the pre-delivery test OCL Process for Activities in Blackboard Iteration of initial Thread in greater detail Extracts from student postings Forum Thread IRPA Tutor summary Seed Student postings Web resource(s) Revised Process Final summary handout Forum Final summary online Iteration of initial Thread in greater detail with new Seed Thread Web resource(s) Extracts from student postings Seed Tutor summary Student postings • Conclusions Placing Summary, Thread and New Seed on one page enables students to engage in active reflection by: – – • recalling and making sense of previous learning seeing how this learning occurred and fits with the ‘wider perspective’ Whole OCL process promotes: – – – – – – – Sense of enjoyment - hands-on nature of activity Motivation A sense of value by using student output in tutor summaries Ownership of knowledge produced Transferability of skills recognised Critical thinking Adopting vocabulary of IL Using online collaborative learning (OCL) for sport and exercise science students »Geoff Walton, Subject and Learning Support Librarian, Staffordshire University »Jamie Barker, Senior Lecturer, Staffordshire University