Digestive systems Life Process? Nutrition
advertisement

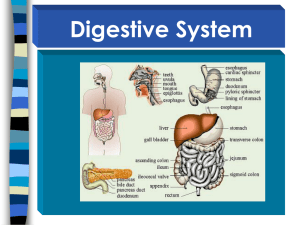
Digestive systems Life Process? Nutrition Transport Autotrophic vs. heterotrophic Eat other things for fuel When is food “in you”? Raw materials for synthesis and assimilation Human Digestive System Bringing food close and broken down enough to be absorbed. Two categories of organs • Alimentary canal AKA digestive tract AKA GI tract – “Food tube”; food passes through these organs • Accessory organs – Add digestive juices to food. Alimentary Mouth: Put food in here Pharynx: Throat Esophagus (5): Peristalsis (squeezing food through the tube) begins. Brings food to stomach. Accessory Teeth (1) : Chew food -> increases surface area of food for enzyme action Tongue (2) : Tastes. Is this food? Salivary glands (3) : Produce saliva: enzymes and lube Epiglottis (4) : Closes trachea (windpipe) during swallowing Alimentary Stomach (7/14): Food is ground into a paste. Protein digestion begins Accessory Liver (6/17) : Produces bile: breaks fat into smaller blobs (emulsifies) Gall bladder (16) : Stores up bile for fatty meals Pancreas (8/15) : Produces other digestive enzymes Alimentary Small intestine (10): Digestion completes and most absorption of nutrients. Has adaptation for increased surface area (more absorption) Large intestine (9):Water absorption Rectum (12): Storage of feces Anus (13): Muscle that holds it in/lets it out Accessory Appendix (11) : Helps control gut bacteria populations?