1 Please list the 4 Vital Signs:
advertisement

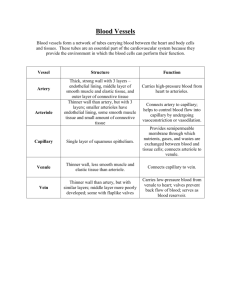
1 Chapter 19 B BSC 2086 Class Notes Summer 2010 Please list the 4 Vital Signs: A ________________ pulse taken at the wrist is routinely counted. Please list the other 8 pulse points: Systemic arterial BP is measured indirectly by the ______________________ (listening) method using a ____________________________. Pressure is increased in the cuff until it exceeds ______________ pressure in the brachial artery: you hear _____________________at this point. Pressure is released slowly and the examiner listens for sounds of ____________________ (tapping) with a stethoscope. Sounds first occur as blood starts to spurt through the artery at _______________ pressure, normally _________________ mm Hg). Sounds _________________ when the artery is no longer constricted and blood is flowing freely at ___________________ pressure, normally __________________ mm Hg. BP ______________ in the morning due to levels of hormones. Please describe Hypotension: Please describe the 3 Types of Hypotension: Please describe Hypertension: Prolonged Hypertension is a major cause of ______________________, ___________________, _________________________, and ___________________. Primary or essential hypertension accounts for 90% of hypertensive conditions. Hypertension if due to several risk factors including (please name 7 risk factors): Secondary hypertension is less common, and is due to identifiable disorders, including __________________, _____________________, and endocrine disorders such as ______________________ and ____________________________ that may be caused glucocorticoid drugs. Please name 4 things in which Blood Flow or Tissue Perfusion is involved: Rate of flow is precisely the ________________ amount to provide for _______________________. Velocity ______________________ related to the total cross-sectional area of the blood vessel. Blood Flow Velocity is fastest in the ______________ slowest in the ______________, increases again in _________________. ________________________ is the automatic adjustment of blood flow to each tissue in proportion to its requirements at any given point in time. It is controlled ________________________ (locally) by modifying 2 the diameter of local arterioles feeding the capillaries, and is independent of ________________________________ which is controlled as needed to maintain constant pressure. What are two types of Autoregulation? Vasodilation of Arterioles and relaxation of precapillary sphincters occur in response to (name 3 things): Relaxation of vascular smooth muscles is mainly caused by the release of _______________________ from vascular endothelial cells. Vasoconstriction is due to ____________________________ stimulation and release of potent ________________________ by the endothelium. ________________________ responses of vascular smooth muscle keep tissue perfusion constant despite most fluctuations in systemic pressure. Passive stretch caused by increased intravascular pressure promotes _______________________ and ____________________. Reduced stretch promotes _____________________ and ___________________ blood flow to the tissue. _____________________ occurs when short-term autoregulation cannot meet tissue nutrient requirements. The number of vessels to a region _________________ and existing vessels __________________. Angiogenesis is common in the heart when a ____________________________, or throughout the body in people in ________________________ areas. Muscle blood flow can increase ______________ or more during physical activity. Blood flow to the brain is ___________________, as neurons are intolerant of ___________________. As skin or body temperature rises, ________________________signals reduce vasomotor stimulation to reduce __________________________ of the skin vessels. Arterioles in skin ________________ and heat from capillary beds ____________________ from the skin’s surface. Sweat also causes vasodilation via ______________________ in perspiration, which stimulates the release of ________________________ that dilates blood vessels to radiate excess heat. Direction and amount of fluid flow depends on which two opposing forces? Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure (HPc) tends to _______________ fluids through the capillary walls. Capillary Colloid Osmotic Pressure (OPc ) is created by ____________________ plasma _______________, which ____________________________. At the Arterial end of a bed, __________________________ forces (fluid outward) dominate diffusion in the capillary. At the Venous end, _________________ forces (fluid inward) dominate diffusion in the capillary. Excess fluid is returned to the blood via the _______________ system. Please briefly describe Circulatory Shock: Please describe the 3 types of Shock: 3