1 (Slide 2) The heart is approximately the size of a... Chapter 18 Class Notes Fall 2010
advertisement

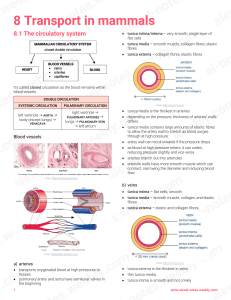
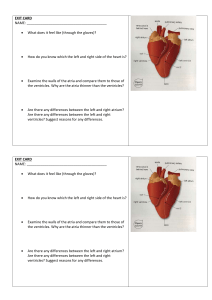
1 Chapter 18 Class Notes Fall 2010 (Slide 2) The heart is approximately the size of a fist, and is located in the _________________________. The heart is enclosed in a ______________________ sac called the ______________________________. (Slide 6) The ________________(outermost) ___________________ Pericardium is made of tough dense connective tissue that ________________, anchors, and prevents ________________of the heart. Concerning the deep two-layered Serous Pericardium, the __________________ layer lines the internal surface of the ________________ Pericardium, and the __________________ layer (Epicardium) is on ___________________ surface of the Heart. These layers are separated by serous fluid-filled pericardial cavity that __________________________ as the heart beats. (Slide 9) The outermost layer of the heart wall is the ______________________________. The _____________________ (middle layer) of the heart wall is the layer that _________________ when the heart beats, and is made of spiral bundles of _________________________________. (Slide 11) The crisscrossing connective tissue fibers of the Myocardium form the ____________________________________________. The _____________________ , or inner layer of the heart wall is continuous with endothelial lining of ____________________________. (Slide 15) Concerning the chambers of the heart, the two Atria are separated internally by the ______________________, the _______________________________ (atrioventricular groove) encircles the junction of the atria and ventricles, and the ___________________ increase Atrial volume. (Slide 16) Two ventricles are separated by the _____________________________________, and the anterior and posterior _____________________________________ mark the position of the septum externally. (Slide 18) The walls of the atria are ridged by ________________________________. Which vessels enter the right atrium? (Slide 18) Which vessels enter the left atrium? (Slide 19) The walls of the ventricles are ridged by _______________________________, and ____________________________ project into ventricular cavities. What vessel leaves the right ventricle? What vessel leaves the left ventricle? (Slide 21) The heart is two side-by-side pumps, the right side is the pump for the ____________________ circuit, the contains vessels that carry blood to and from the __________________. 2 3 (Slide 22) Left side is the pump for the ______________________ circuit, that contains vessels that carry the blood to and from __________________________________. (Slides 24-25) Please write down the path of blood through the pulmonary & systemic circulations: _____________________volumes of blood are pumped to the pulmonary and systemic circuits. The Pulmonary circuit is a ________________, ____________________ circulation. Systemic circuit blood encounters much _________________________ in the long pathways. (Slide 27) How does the anatomy of the ventricles reflects these differences? (Slide 28) The ______________________ is the functional blood supply to the ________________________ itself. 4 (Slide 33) Describe 2 Homeostatic Imbalances of the Heart: Heart valves ensure ____________________________ blood flow through the heart. Name and describe location of the two AV valves, and also describe their function: (Slide 35) __________________________ anchor Atrioventricular (AV) valve cusps to _____________________________________________. Name and describe location of the two Semilunar Valves, and also describe their function: 5 (Slide 43) Cardiac muscle cells are __________________, short, fat, _________________, and _______________________________. ________________________are wide but less numerous; __________________________________ is simpler than in skeletal muscle, and there are numerous large _______________________________ (25–35% of cell volume). (Slide 45) ____________________________________ are junctions between cells that anchor cardiac cells together, which have __________________________ that prevent cells from separating during contraction, and _____________________________ that allow ions to pass to electrically couple adjacent cells. Since cardiac cells are coupled by __________________________, heart muscle behaves as a single coordinated unit, or Functional _______________________________.