Circulatory System Topic: 3202H Melinda Klockziem
advertisement

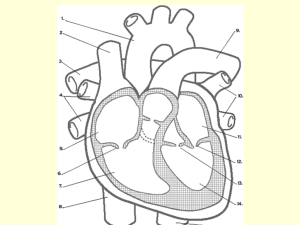
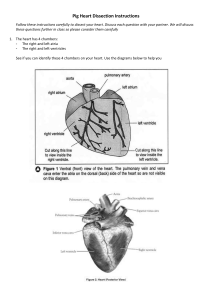
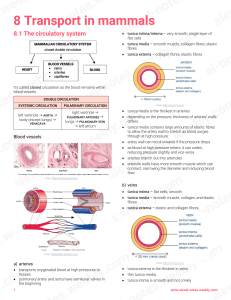
Circulatory System Topic: 3202H Melinda Klockziem Circulatory System Functions • Respiratory – O2 and CO2 exchange • Excretory – removes waste from body cells • Protection – clotting, transports white blood cells to infections • Nutrition – carries energy and food throughout the body • Regulatory – helps to maintain pH and temperature • Hormonal – transfers hormones to organs Body Circulation Vena Cava Right Atrium Right Ventricle Pulmonary arteries Lungs Pulmonary veins Left atrium Left Ventricle Aorta Body Circulation Heart Sounds • Heart sounds are created by closure of the valves • First heart sound – Lubb – Closure of atrioventricular valves • Second heart sound – Dubb – Closure of aortic and pulmonary valves Electrocardiography • Evaluate the rhythm of the heart is with an electrocardiogram, known as an ECG or EKG Electrocardiography • ‘P’ wave – Reflects the flow of electricity through the atria, and tells us that the atria have received a normal impulse, and have contracted. • The 'q, r, s' waves – tell us that the electrical circuit has traveled through the atrioventricular node, and through the ventricles, and has resulted in the ventricles contracting. Electrocardiography • The 't' wave – is the most important one, in a way - it tells us that the electrical impulse has traveled all through the heart, and that the heart is now 'repolarizing', or getting ready for the next impulse to start Hill’s Science Diet