1
CJE2600 CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION
CHAPTERS 11 – Crimes Against Children
Dr. E. C. Buchholz
CHAPTER 11
Crimes Against Children
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Recognize types and patterns of burn injuries found in child abuse
Define and discuss shaken-baby syndrome
Explain Munchausen syndrome by proxy
Identify types of child molesters, and explain investigative and interview techniques for
cases of child molestation
Define and describe human trafficking, especially as it relates to child sex trafficking
Understand relationship between child pornography and sex tourism
Outline types of child pornography
Discuss the use of the computer and the Internet in child pornography
Discuss additional ways the internet is used to exploit children
Be able to differentiate between sudden death syndrome and physical abuse
LEARNING OBJECTIVES (continued)
Understand what sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is and its misconceptions
Discuss the prevailing theories in SIDS research
Understand criminal homicide as a possibility in SIDS deaths
Describe the profile of infant abductors
Outline the assessments and investigative procedures used to determine whether a child
has run away or has been abducted
Discuss sex-offender registration and community notification laws
Describe the personality traits and behaviors of individuals inclined to commit school crime
Understand the role of law enforcement in school crime
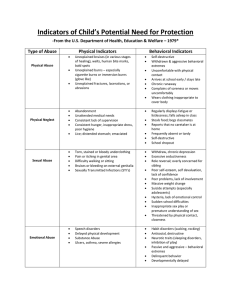
ASSAULTS AGAINST CHILDREN
The most common cause of children's death is physical abuse, often by their own parents
The clinical term commonly used to describe physically abused children is the battered-child
syndrome
Abuse of children takes various
forms, from minor assaults to
flagrant physical torture
Although abusers use a wide variety
of instruments, the two most common
are the belt and electric cord
2
BURN INJURIES AND CHILD ABUSE
Typologies of Burns
– A burn may be classified by how severe or “deep” it is, or by how the injury
occurred.
Medical Classification of Burn Severity
– Physicians primarily categorize burns as having either “partial thickness” or “full
thickness.”
Causes of Burn Injuries
– Scald burns occur when the child comes into contact with hot liquid
– Contact burns occur when the child encounters a hot solid object or fla
CLASSIFICATION OF BURNS
3
CAUSES OF BURN INJURIES
Scald burns
o most common
caused by hot liquids
Spill/Splash injuries
o hot liquid falls from a height onto victim
Immersion burns
o child falls or is placed into tub or other container of hot liquid
Contact burns
o skin comes into contact with a flame or hot solid object
Deliberate immersion burn patterns
• Doughnut pattern in the buttocks
– Child thrust down in hot bath-water
• Sparing the soles of the feet
– Absence of burns on bottom of child’s feet
– Child’s buttocks and feet are burned, but whose soles have been “spared”
• Stocking or glove-pattern burns
– Occur when child’s feet or hands are held in the water
• Waterlines
– Reflects child was held because a child who fell into the water would
show splash and irregular-line patterns.
If an investigator sees burns such as those pictured, they should:
o –become highly suspicious
o –look for other signs of abuse
o –question the parents/guardians
CONTACT BURNS
Occur when a child’s skin comes into contact with a flame or a hot solid object
Cigarette
Lighter
Fireplace
Stovetop burner
Outdoor grill
Steam iron
Leaves a distinct pattern
SUDDEN INFANT DEATH SYNDROME
Simply defined, SIDS (“crib death”) is the sudden and unexpected death of an apparently
healthy infant that remains unexplained after the performance of a complete autopsy.
4
CHARACTERISTICS OF SIDS VICTIMS
Appearance
Usually normal state of nutrition and hydration
Blood-tinged, frothy fluids around mouth and nostrils, indicative of pulmonary edema
Vomitus on the face
Diaper wet and full of stool
Bruise like marks on the head or body limbs (postmortem pooling or settling of blood in
dependent body parts)
MISCONCEPTIONS
Aspiration or choking
Unsuspected illness
Freezing (usually due to postmortem change)
Accidental injury, neglect or abuse
Recent Findings
Dr. Richard Naeye, Penn State University
Chronic lack of oxygen, attributable to repeated and relatively long periods of
apnea
New England Journal of Medicine
Infants who usually slept in the face-down position had a significantly higher
risk of SIDS than those who slept on their back
The air passage of an infant is impaired when the body is placed face down on
any type of mattress or pillow
Children’s Hospital Boston & Harvard Medical School
Infants that die of SIDS often have abnormalities in the brainstem, particularly
those that control breathing, blood pressure, temperature, and heart rate
Police Response
Be sensitive, yet keen to the possibility of criminal homicide
The most commonly missed method of homicide in infants and young children,
after impulse homicides, is smothering
May be petechial hemorrhaging of the eyes and surrounding areas
Traumatic Brain Injuries and Death
Most child deaths are directly related to injuries that are a result of a specific act
of hitting, striking, or physically abusing the victim
Blunt-Force Trauma
Injuries derives from forces transmitted by objects that have relatively broad
surfaces, with thick or round surfaces
Brain Hemorrhage
Significant injury causing extensive bleeding into the surrounding tissue.
5
Coup—Contrecoup Injuries
Coup (French for “head”)
Injury at the direct site of the impact of the head and a moving object
Contrecoup
Injury inside the skull on the opposite side of the area of impact
A moving head is abruptly stopped and inertia keeps the brain moving within
the skull
SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME
Shaken-baby syndrome (SBS) is the severe intentional application of violent force (shaking),
in one or more episodes, that results in intracranial injuries to the child.
The mechanism of injury in SBS is thought to result from a combination of physical factors,
including the proportionately large cranial size of infants, the laxity of their neck muscles,
and the vulnerability of their intracranial bridging veins.
Often a parent or caretaker, usually in anger, shakes a baby so hard that serious head injury
results
Usually show evidence of previous trauma
Child will often show no outward signs of injury
Blunt trauma injuries are often found in conjunction with SBS
Caused from infant’s head being whipped forward and backward from the chest
to the back
Average age of infant victims is 6 months
MUNCHAUSENS SYNDROME BY PROXY
Munchausen syndrome is a psychological disorder in which the patient fabricates the
symptoms of disease or injury in order to undergo medical tests, hospitalization, or even
medical or surgical treatment
o Pseudologia fantastica is present in classic cases (patient makes false claims about
distinguished accomplishments, educational credentials, relations to famous
persons)
In cases of Munchausen syndrome by proxy (MSBP), a parent or caretaker suffering from
Munchausen syndrome attempts to bring medical attention to himself or herself by injuring
or inducing illness in a child
o
o
o
o
Often only one child in a family is chosen as the target
Marital partner tends to be protective of abusive parent
In over half the cases, the abuse results in hospitalization
The child is frequently taken to different hospitals
“doctor shopping”
6
MSBP Maternal Behaviors
medically knowledgeable, educated
may have worked in the health care field
mother prefers to stay in the hospital rather than home
uncharacteristically calm
welcomes medical tests
reluctant to leave hospital
more interested in the medical procedures than in her child’s welfare
spends more time with hospital staff than with her child
excessive praise for medical staff
exaggerates child’s symptoms
intolerant of minor problem and demands work-up
is calm about child’s illness
describes an illness that seems unexplainable
symptoms observed only if mother is present
illness resolves after separation form mother
Jennifer Bush
Jennifer Bush had been in and out of hospitals.
By the time she was 8, she had been hospitalized more than 200 times, and had
undergone more than 40 surgeries.
Doctors had removed her gallbladder, her appendix and part of her intestines.
She was often nourished through feeding tubes.
Once removed from her parents care, she lived a normal life, free of hospitals
and drugs.
In October 1999, Kathy Bush was found guilty of aggravated child abuse and
sentenced to 5 years in prison. She served 3 years, and was released in June
2005.
SITUATIONAL CHILD MOLESTORS
For purposes of discussion Kenneth V. Landing of the FBI divides child molesters into two
categories:
o situational
o preferential
7
SITUATIONAL CHILD MOLESTORS
Have no true sexual preference for children
Numbers of abusers has been increasing faster than preferential
Morally Indiscriminate
Part of a general pattern of abuse in his life
User and abuser of people
Victim criteria is vulnerability and opportunity
Regressed
Low self-esteem and poor coping skills
Uses children as a sexual substitute for the preferred peer sex partner
Sexually Indiscriminate
“Try-Sexual”—Will try anything sexual
Motivation is sexual experimentation
Inadequate
Social misfit
Withdrawn
Unusual
Involved with children out of insecurity or curiosity
Nonthreatening to him
Criteria for victims, new and different
PREFERENTIAL CHILD MOLESTERS
Definite and erotic Imagery focus on children
Seduction
“Seduces” children
Grooming
Courts them with attention, affection, and gifts
Knows how to talk to and listen to children
Targets children who are victims of emotional or physical neglect
8
Introverted
Preference for children but lacks the interpersonal skills necessary to
seduce them
Engages in a minimal amount of verbal communication with his victims
Usually molests strangers or very y7oung children
Hangs around playgrounds and other areas where children
Engages them in brief sexual encounters
Sadistic
Sexual preference for children, but psychological or physical pain or
suffering on the child.
More likely than other preferential child molesters to abduct and even
murder their victims.
PREFERENTIAL CHILD MOLESTERS
INTERVIEWING MOLESTED CHILDREN
Common sense and formal research agree that children are not merely miniature adults
Waterman has identified three types of developmental issues that are important when
allegations of sexual abuse arise
o First, the child's developmental level relative to other children in his or her age
group
o Second is the child's development level with regard to sexuality
o Third is the child's ability to respond adequately to interviews and to testify in court
Children think in concrete terms.
Children do not organize their thought logically.
Children have limited understanding of space, distance, and time
Children have a complex understanding of truth and lying
Children see the world egocentrically.
Children have a limited attention span.
Children may have varying degrees of comfort with strangers.
9
INTERVIEWING MOLESTED CHILDREN
When anatomically detailed dolls were first introduced in the late 1970s they were widely
hailed as an important advance in techniques for communicating with troubled children
One alternative that is being used by some police agencies either in connection with or
instead of an anatomically detailed doll is to have the child draw his or her own picture
o As with the anatomical dolls, leading questions are widely used as a courtroom
technique to assist child witnesses
o They are seriously challenged when used in investigative interviews
ANATOMICALLY DETAILED DOLLS
These dolls are used by some investigators
They show all body parts including genitals
Some experts disagree at to their overall usefulness
Professionals have yet to reach a consensus on “proper” use of anatomically detailed dolls.
Social psychological theory of social influence:
Children’s responses to questioning are heavily influenced by the perceived
authority or power of the adult interviews
When they are praised or otherwise “rewarded” for disclosing elements of
abuse, children learn what the interviewers want to hear; that is, they answer to
please adults
This effect is magnified in child sexual-abuse cases
o Infusing/reinforcing: Children are typically interviewed repeatedly by
different adults who contribute to their expanding story
Sexually Abused Child Syndrome
Child possesses age-inappropriate sexual knowledge
Child Engaged in sexualized play
Child displays precocious behavior
Child engages in excessive masturbation
Child is preoccupies with his or her genitals
There are indicates that pressure or coercion was exerted on the child
Child’s story remains consistent over time
Child’s report indicates an escalating progression of sexual abuse over time
Child describes idiosyncratic details of the abuse
There is physical evidence of abuse
p. 319
PAUSE
 0
0