1-800-255-4483 Life Alliance Organ Recovery Agency
advertisement

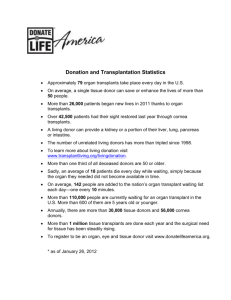
Life Alliance Organ Recovery Agency 1-800-255-4483 Teaching Ethics in a Multicultural Environment: An Organ Donation Perspective Life Alliance Organ Recovery Agency University of Miami Why is Organ Donation important? -There are more than 87,000 patients listed awaiting an organ transplant. -Organ transplants come from Cadaveric donors and by Living donors. However, the issue that exists is a Supply & Demand Problem. Newsroom Facts - UNOS On average, 115 people are added to the nation’s organ transplant waiting list each day – ONE EVERY 13 MINUTES On average, 66 people receive transplants every day from either a living or deceased donor. More than 2,200 children under the age of 18 are on the transplant waiting list. State of Donation/Transplantation 30000 25000 20000 donors organs transplanted 15000 10000 5000 0 1988 1992 1995 1999 2001 2002 2003 New Federal Requirements Hospitals must have working relationships with their area’s OPO, Tissue and Eye Bank. Hospitals must report ALL deaths and imminent deaths to the OPO. Reporting is required for hospital accreditation and Medicare reimbursement. All OPO’s must audit all deaths in their catchment area. Morality The “rightness” or “wrongness” of an act or thought Widely shared beliefs in a particular culture or subculture Ethics The “why” or the actual underpinning for the act or thought. Perspectives that allows one to examine or understand something Major Legislation 1968 Uniform Anatomical Gift Act Revised 1987 Authorizes the gift of all or part of the after death for transplants, research, education, or other therapies. Describes who may donate, how to execute the donation, and who may receive the gift. There is no national registry of organ donors. Even if you have indicated your wishes on your driver’s license or a donor card, be sure you have told your family as they will be consulted before donation takes place. How does one express voluntary donation wishes? Registries: DMV Donor cards Advance directives aka, Living Wills Sharing your thoughts and decisions with your family Major Legislation 1984 National Organ Transplant Act Established a national Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN) Prohibited sale of human organs Established the Scientific Registry of Organ transplantation 1987 Florida Brain Death Law Determination of death must be made by two board eligible or certified physicians Brain death is the irreversible cessation of the entire brain, including brain stem OPO Responsibilities Evaluation of all potential donors Obtaining family consent Maintain the donor after Brain Death has been declared Allocation of the organs Recovery of the organs Aftercare of the donor family Medical Staff Ethical Dilemmas Admitting failure: A patient has died Stepping aside Supporting or Obstructing Patient Management South Florida Communities Haitian African American Hispanic Informed Decision to Informed Consent Does a family need to know what organs and tissues can be donated? Do they need to know the size of the incision? Do they need to know how the body will look after donation? Do they need to know about the various donor suitability tests? Pediatric Ethical Considerations What about children who want to be organ donors? What about adolescents between 16 and almost 18 years old? Can people younger than 18 give consent? Acceptable Donors Severe Head Injuries Cerebral Insults (SAH,SDH,CVA) Primary Brain Tumors Cerebral Anoxia (Near-drowning, Drug ODs,MIs,) Homicides/Suicides Metabolic Disorders (DKA) Brain death vs. Coma? Brain Death Criteria Harvard Medical School Absence of spontaneous movement and response to stimulus Absence of spontaneous respiration Absence of brain stem reflexes Reversible etiology must be considered and excluded prior to the diagnosing of Brain Death Brain Death Patient maintained on ventilator, Heart beating Organs are removed in the operating room while the patient is maintained on a ventilator. Tissue recovery follows organ donation Cardiac Death Patient has no cardiac or respiratory activity Acceptable donations: Tissue & Eyes Body must be kept cool before tissues are removed Removal within12 to 24 hours What’s the difference from a coma? Coma entails some lower level of brain electrical activity, however absence of any cortical activity Coma does NOT equal Brain Death Categories Of Donation Brain Dead Donor Can donate organs, eyes, bone, & tissue Has beating heart, on ventilator Cardiac Arrest Donor Eye, bone, & tissue only: NO organs can be donated Donation After Cardiac Death: Immediate rescue of organs after cardiac death (OPO on Site) Asystole occurs within 30 min of extubation Donation after Cardiac Death Informing ICU and OR staff that after disconnecting the patient from the respirator will result in Cardiac Death. Donation follows pronouncement of patient by the attending physician. How Does It Work? Donors Recipients Organ Procurement Agency Transplant Center UNOS Organ Center Organ Matching Ethical Issues of Transplant Recipients Retransplantation: How many times can a person be transplanted when others are also waiting? Prisoners: Before and now with today’s DNA evidence? Non-resident aliens? Multiple Listing: Being registered at more than one transplant center? Does being a celebrity or being rich influence listing? UNOS allows for multiple listing for certain organs, i.e. Liver, however having available money to travel at a moments notice would help an individual but not change their place on the waiting list. Nurses’ Role in Donation Early identification Referral of potential donors to OPO Support the families’ right to donate Assist in donor management Comfort grieving families Goals of Donor Care Maintain cardiac output Maintain tissue perfusion Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance Ensure adequate ventilation and pulmonary stability Prevent infection Control diabetes Insipidus Regulate body temperature The Medical Examiner The Medical examiner has legal jurisdiction over the body, in the county where the injury occurred. Being a Medical Examiner’s Case does not prevent a patient from being an organ donor. Errors to Avoid With Families Giving false hope Using highly technical medical terms Approaching too early, not allowing the death to be accepted Being stone cold, uncaring, abrupt or pompous Errors to avoid with families Showing an unwillingness to spend time to answer questions Giving the option of organ donation before knowing if the patient is a candidate Jackson Liver Transplant Recipient Liver, stomach, pancreas, small bowel and piece of colon recipient Liver and small bowel recipient heart recipient Trine Liver Recipient Oneisha and Missick Liver Transplant Recipients Erik, heart transplant Life Alliance Organ Recovery Agency 1-800-255-4483