Solutions Student will learn: solution terminology 3 ways to increase solubility
advertisement

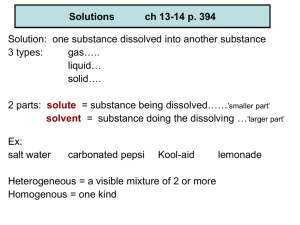
Solutions Student will learn: solution terminology 3 ways to increase solubility Solutions Solution: one substance dissolved into another substance 3 types: gas….. liquid… solid…. 2 parts: solute = substance being dissolved……’smaller part’ solvent = substance doing the dissolving …’larger part’ Ex: salt water carbonated pepsi Kool-aid Heterogeneous = a visible mixture of 2 or more Homogenous = one kind lemonade How to speed up dissolving? l. Stir 2. Increase surface area…. grind large chunks into small grains 3. change temperature of solvent a. increase temp…..solid in a liquid b. Decrease temp…..gas in pepsi Why are GASES ARE MORE SOLUBLE IN COOLER SOLVENTS ?????? A solid dissolves faster in a liquid if the temperature of the liquid is.. 1. Increased 2. decreased A gas dissolves faster in a liquid if the temperature of the liquid is 1. Decreased 2. Increased At which temperature will water in an open vessel dissolve the greatest quantity of oxygen? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 32OC 4OC 100OC 1OC 0OC When a gas is being dissolved in a liquid stirring _______ the dissolving process. 1. Speeds up 2. Slows down The student will : if given a list of chemicals be able to determine which chemicals will dissolve in which chemicals. have conceptual understanding of electrolytes identify electrolytes from a list of chemicals Determining what will dissolve? How do things dissolve? Water is considered the universal solvent… water is a polar molecule with + and – ends. The positive end of a polar molecule will attract the negative end of another polar molecular. Hence…. This is a review of dissolving in Chemical Bonding unit. ” like dissolves like”. “polar dissolves polar” “Nonpolar dissolves nonpolar” How does one figure out if polar or non-polar ? ( all this is reviewed in chemical bonding unit) 1. 2. 3. all Ionics are polar …. Metal + nonmetal Draw Lewis structures calculate electronegativity 1.7chart Solubility ( polar vs non-polar) “like dissolves like” Polar molecules will dissolve polar molecules Non-Polar molecules will dissolve Non-Polar molecules Alcohols will normally dissolve both, both not ionic solids. Solutes 1. NaCl 2. I2 3. Ca(OH)2 4. KCl 5. Br2 6. KNO3 7. CuSO4 8. CO2 9. FeO Water Carbon tetrachloride Alcohol The student will : if given a list of chemicals be able to determine which chemicals will dissolve in which chemicals. have conceptual understanding of electrolytes identify electrolytes from a list of chemicals Electrolyte: a solution that can conduct electricity ex: ionic solutions, ionic compounds … ionize into their separate ions when dissolved in water “They separate into their + and - parts” Non-electrolyte: a solution that cannot conduct electricity ex: nonpolar solutions non-metals and non-metals do not have + or - ends Demo: salt in water Electrolytes Electrolytes dissociate or ionize in water to produce ions. Electrolytes are capable of conducting electrical current. Electrolytes consist of ACIDS, BASES, IONIC COMPOUNDS Chemical 1. NaCl 2. CCl4 3. C8H14 4. HCl 5. CuSO4 6. AgOH 7. KCl 8. H2O 9. H2SO4 10. FeO Electrolyte Non-Electrolyte Which chemical would be a good prospect as an electrolyte to add to an energy drink? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. C2H5OH N 2O 2 HCl H2SO4 MgCl2 AuCl3 Student will be able to: Read, interpret, analyze data from a solubility chart Solubility how much will dissolve at a given temperature. Unsaturated: can dissolve more solute Saturated: dissolved all it can Supersaturated: contains more solute than a saturated . ”unstable” The student will be able to : calculate the concentration of solutions using the Molarity formula. calculate the needed grams for creating specific solutions. [concentration] of Solutions Expressed as …..Molarity [M] = #moles of solute liters of solution 1. What is the molarity of a solution consisting of 45 grams of Sodium Chloride in 500mL of water? 2. A chemist needs half a liter of a 2M solution of ammonia. How do you prepare this solution? 3. Calculate the concentration of a sodium hydroxide solution containing 10.0 grams in 500mL. 4. What is the molarity of a sulfuric acid solution containing 196 grams per liter? 5. What mass in grams of solid calcium chloride is dissolved in 2 liters of water to prepare a 1.2M solution? 6. How many grams of Copper II Sulfate does a chemistr need if he wants 2L of a 3M solution? 7. Calculate the molarity of a hydrochloric acid solution that has a volume of 16o00mL and contains 382g of HCl. 8. You added 2 tablespoons of sugar (C6H12O6) to your morning hot milk. Each tablespoon of sugar is approximately 13 g. What is the sugar molarity of your drink? 9. How many liters are required to make a 6M solution of 3moles of potassium hydroxide? Student will be able to: calculate the needed quantity of concentrate to dilute to the desired solution Molarity by Dilution M1V1 = M2V2 You use this when you already have a solution made and you just want to dilute it to the concentration you want. 1. How much concentrated 12M Hydrochloric acid is needed to prepare 300 mL of a 3.0 M solution? 2. How much water should be added to 200mL of 18M Sulfuric acid to have a l.5M solution? 3. How much of concentrated 15M Nitric acid should be added to make a 1 liter solution of 2M. 4. How many milliliters of 12M HCl needs to be diluted to 200mL to make a 3M solution? 5. What is the molarity of a solution made by diluting 30mL of 8.0M KBr to 500mL? 6. 100mL of commercially available 18M sulfuric acid is diluted to 500mL. What is the new molarity or concentration? 7. A chemist wants to concentrate a diulted solution of sodium chloride. The chemist has one liter of 2M of the salt solution. Ho much water does he need toevaporate to achieve a 5.5M concentration? 8. How do you prepare 250-mL of .5M silver nitrate from a concentrated solution of 3M silver nitrate. 9. How much concentrated 8M Chlorine Bleach(NaOCl) needs to be diluted to make 500mL of 1M Bleach? Student will be able to: calculate the needed quantity of concentrate to dilute to the desired solution