2. Label the following parts of an atom: ... 3. Match the subatomic part to its charge:
advertisement
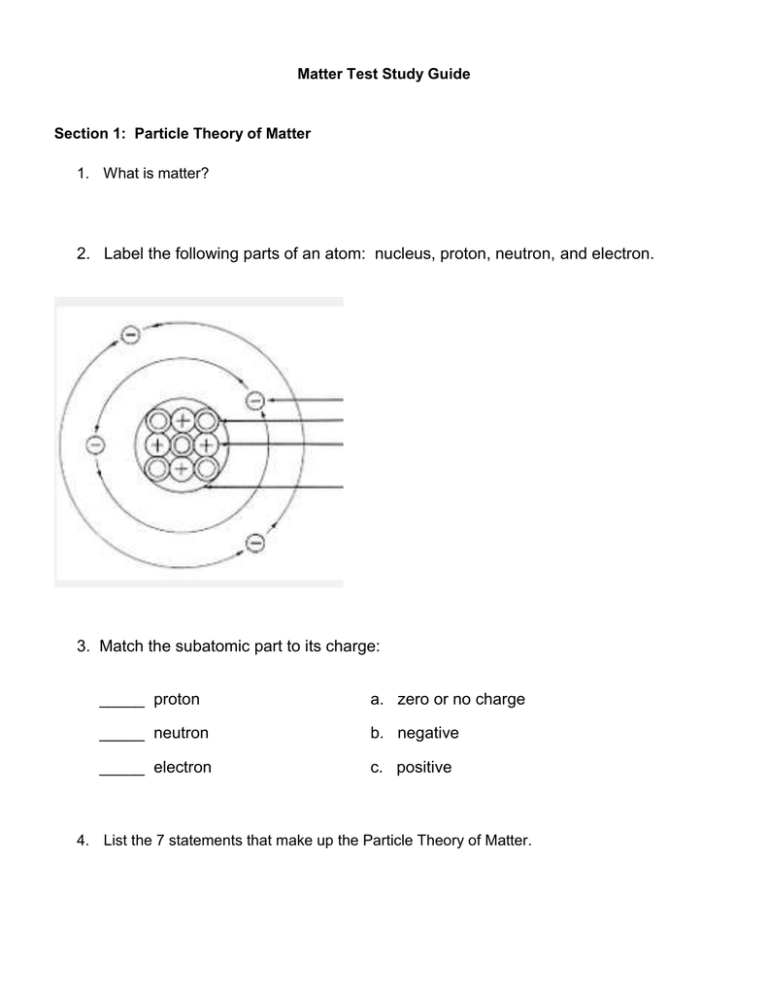
Matter Test Study Guide Section 1: Particle Theory of Matter 1. What is matter? 2. Label the following parts of an atom: nucleus, proton, neutron, and electron. 3. Match the subatomic part to its charge: _____ proton a. zero or no charge _____ neutron b. negative _____ electron c. positive 4. List the 7 statements that make up the Particle Theory of Matter. Section 2: States of Matter 5. What are the four states of matter we learned about this year? 6. What determines what state of matter we say a substance is in? 7. State of Matter Volume (definite or Shape (definite or indefinite) indefinite) How do the particles move? Solid Liquid Gas Plasma 8. How are the particles in plasma different than the particles in a gas? How are they the same? 9. List 3 examples of plasma. 10. What is the most common state of matter in the universe? 11. Place the four states of matter (liquids, solids, gases & plasmas) in the diagram below, according to their level of energy. high ______________ ______________ ENERGY ______________ ______________ low Section 2: Change of state – endothermic and exothermic changes 12. What does the term “change of state” mean? 13. What causes a change in state? 14. List the 5 changes of state we learned about. 15. When energy is taken in by a substance and changes state, it is called a ______________________________________ change. 16. Vaporization is the change of state from a liquid to a gas. This can occur in two ways. What are the two ways? 17. Describe two ways that evaporation is different than boiling. 18. Why is sublimation unusual? 19. Explain how solid air fresheners are examples of sublimation. 20. When energy is lost by a substance and it changes state, it is called a ______________________________________ change 21. Fill in the table below. Name the Change of State Endothermic or Exothermic? Solid to liquid Liquid to solid Liquid to gas Gas to liquid Solid to gas 22. Match the following circumstances with the change of state they describe: a. Melting d. sublimation b. vaporization - boiling c. condensation e. freezing f. vaporization - evaporation _____ Dry ice makes “smoke” for your Halloween party. _____ You put water on the stove to cook pasta and it bubbles, turning to vapor. _____ You leave a Hershey’s bar in the car during the summer, and when you come back it is all gooey. _____ A factory pours molten steel into a mold, and it hardens into a faucet, to be installed in our classroom. _____ It is warm in the evening, but gets very cold overnight. In the morning, the grass is wet, even though it hasn’t rained. _____ You leave 4 ml of tea in a mug on your nightstand, and when you go to put the mug in the dishwasher, you only see a brown ring at the bottom of the mug. 23. What is a physical property? 24. What is a chemical property? 25. What does combustion mean? 25. What does flammable mean? 26. What does reactivity mean? 27. State whether the examples below are physical or chemical properties. ___________ reacts with water ___________ color ___________ odor ___________ state of matter ___________ flammability ___________ combustibility ___________ texture ___________ luster ___________ mass ___________ volume






![Sublimation 101 [2011 Edition]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018443885_1-e8fb12f350b7edc7ca6c78d85f76b875-300x300.png)