Scientific Method and Experimental Design
advertisement

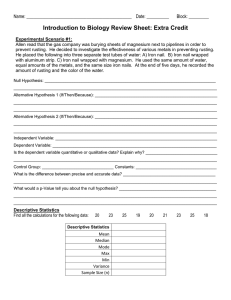
Scientific Method and Experimental Design Name ________________ Date _____2013 1. Watch this video on the Scientific Method and take notes on the experimental design: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GKGtkzgKfkc&list=PL4275A5DE33B0E496 a. Research Questions – b. Hypothesis – c. Independent variable – d. Dependent variable – e. Controlled variables (constants) – f. Control group - 2. Read the following descriptions of experiments. Identify for each experiment: (1) independent variable(s) – underline once (2) dependent variable(s) – underline twice (3) control group – put parentheses around (or write one if not included in experiment) (4) constant(s) - circle (5) Write a hypothesis A. Leah read that bees were attracted to certain colors and wondered if crickets also had a color preference. She divided an aquarium into three sections containing different-colored dishes (red, blue, yellow) and put 2 grams of mustard seeds in each dish. She place 30 crickets into the aquarium. She observed the number of crickets in each section at the end of 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes. She recorded the mass of the mustard seeds consumed at the end of 120 minutes. She was careful to place the aquarium so that the amount of light was equal throughout the aquarium. Hypothesis: _____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ B. Joan read that the gas company was burying sheets of magnesium next to pipelines to prevent rusting. She decided to investigate the effectiveness of various metals in preventing rusting. She placed the following into for separate test tubes of water: 1. iron nail 2. iron nail wrapped with magnesium strip 3. iron nail wrapped with copper strip She used the same amount of water, equal amounts of the metals, and the same size iron nails. At the end of five days, she recorded the amount of rusting and the color of the water. Hypothesis: _____________________________________________________________ Mr. Luis A. Velazquez _______________________________________________________________________ 3. Review the Scientific Method below. Not all science is done in this way, but it is one approach that we will use in class this year. Research Idea Ideas come from observation, reading scientific articles, and many other sources. Research the Literature Researching the topic tells us what is known and what is not known. This can lead to a research question to study. Research Question Experiment Analyze Data Draw Conclusions Publish Next Question After we have a research question, more research can lead to a better, more refined question. Good Experimental Design is important in order to get meaningful answers. (See experimental design below.) What are the data trying to tell you? Are there patterns? Did the independent variable really affect the dependent variable? Why did the independent variable affect the dependent variable (or not)? Knowledge of the subject will help us here. Scientists share their findings. Learning something usually leads to more questions. These can then be used to study the subject further. 4. What is the value of doing research on what is already known? (You will need at least 3-4 sentences to answer this completely.) Mr. Luis A. Velazquez 5. Create an experimental design with ONE independent variable (called a controlled experiment) for the following research question. RESEARCH QUESTION What is the relationship between the amount of homework given and students’ test grades in Honors Biology classes? HYPOTHESIS This is the predicted outcome. Write it in the form of a statement. (Example: Plants exposed to country music will grow taller than plants exposed to classical music or no music.) INDEPENDENT VARIABLE What the scientist changes. What I put IN to the experiment. (Example: type of music) Experimental groups: Different levels or values of the independent variable (Example: country music, classical music, no music) Control group: Which experimental group is the most common? What will the scientist compare the results to? (Example: no music) DEPENDENT VARIABLE What will the scientist measure? How? In what units? (Example: The height of each plant in cm after 20 days) IMPORTANT CONSTANTS Things that will be the same in EVERY trial (be sure not to include the independent variable here). (Example: type of plant, amount of light and water, temperature, humidity, type and amount of soil) Mr. Luis A. Velazquez 6. Calculate the means (averages) in the data table below. Graph the means of the data. Be sure to include a title, labels for the x- and y-axes, and a label for each bar. Average % test grades Trials 1 2 3 4 5 Mean (average) Mr. Luis A. Velazquez Minutes of homework per class 10 88 87 85 82 83 30 94 93 98 92 98 60 99 97 99 92 98