Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________ Per : _____
advertisement

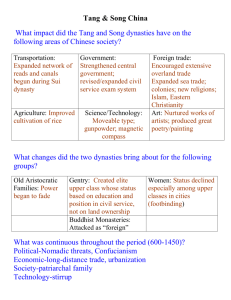
Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________ Per : _____ Chapter 12: Reunification and Renaissance in Chinese Civilization: The Era of the Tang and Song Dynasties AP World History I Overview o With the fall of the ______________ Dynasty in 220 CE, China alternates between periods of political unity and fragmentation o Not as traumatic as the fall of Rome for ______________ Europe o Between 589 and 906 CE, China enjoyed a political ______________ under the Sui and Tang Dynasties. o China will also be rocked by the advances of the ______________ armies in the 1200s. The Sui Dynasty o The first strong ______________ to emerge after the fall of the ______________ was the Sui Dynasty (589-618 CE). o ______________ China o Expanded China’s ______________ as a result of ______________ conquest Tang Dynasty o Under the Tang (618-906 CE), China became ______________ than ever before. o Rulers extend China’s influence to parts of Central Asia, ______________, Manchuria, Tibet, and to the south, the ______________ Coast. o Like the Han Dynasty, the ______________ forced many of its neighbors into a ______________ System, whereas ______________, Vietnam, Japan and others had to make regular payments to avoid ______________. o Tang economy was very strong due to advanced ______________ (roads, waterways, canals) o ______________ Canal: Begun in the Sui Dynasty to link the ______________ and Yangzi Rivers. o Increased trade stimulated the Tang ______________ o Silk industry made China exceptionally ______________ Means of Trade/Exchange o Indian ______________ Trade Network: China’s ______________ of the southern coast allowed participation in the ______________ Ocean Trade Network. o China also traded along the ______________ mile Silk Road with the Middle _________. Culture in Tang China o Tang rulers were ______________ patrons o Emperor ______________ sponsored the creation of the Han Lin Academy of Letters, a key institution of ______________ o The Tang exerted a strong artistic and religious influence over ______________ and Japan. o Tang monarchs expanded and reworked the imperial ______________ o Revived Scholar-gentry elite reworked ______________ ideology Tang Examination System o Tang emperors patronized ______________ to train state officials and educate them in Confucian classics. o Examination system was greatly ______________. o Patterns of advancement were ______________ o While most bureaucrats won their position through success in the ______________ Service Examination system, birth and family connections still played a role in securing office. State and Religion o ______________ thrived in the time before the Sui and Tang dynasties o Many pre-Tang rulers from nomadic origins were devout ______________ o ______________ variant of Buddhism (Zen) stressed meditation and appreciation of natural beauty. Zen had great appeal to Chinese ______________ classes. Tang support of Confucianism threatened to undercut Buddhist success…however, Tang Emperors and Empresses supported the ______________ establishment (Empress Wu r. 690-705 CE). State and Religion o Support of Buddhist aroused the envy of ______________ and ______________ rivals. o Confucian leaders stress the economic impact of not ______________ Buddhist monasteries, and losing out on labor because they couldn’t conscript peasants who worked on monastic estates. o Under Wuzong (r. 841-847) China openly ______________ Buddhists. o Never again would Buddhism gain the strength it had in the early-Tang era…however, it would ______________ in China o Confucianism becomes dominant ______________ of Chinese civilization from the 9th to early 20th century. Tang Decline o During the 800’s, a series of peasant ______________ and military disasters weakened the Tang. o In 906, the Tang Dynasty ______________ and several centuries of disunity will follow. China after the Tang o Following the Tang breakdown, China ______________ into separate states until the late 1200s. o The largest and longest lasting was the ______________ Empire. o Song empire will last until ______________. o Until 1121, the primary threat to the Song was the ______________ empire to the north. o The Song paid tribute to the Liao via silk and cash, but then destroyed them with the help of ______________ tribes from the North (even farther north). o However, the Jurchen then proclaimed their own Empire, the ______________, and turned on the Song. o The Song gave up territory and retreated to the South. The smaller Song state, the Southern Song Dynasty, will survive until the ______________ Conquests of the 1270s. Northern and Southern Song Song Characteristics o Culturally and ______________ impressive o Steady ______________ growth o World’s largest ______________ society o Largest ______________ on earth at the time (population over 1 million) o ______________ contacts lessened, but still active. o More involvement with the ______________ coast and Southeast Asia. o Port of ______________ (______________) became the world’s busiest and most cosmopolitan trading centers. o Large trading vessels, known as junks, cruised the eastern seas and Indian Ocean carrying goods for ______________. Song Culture and Religion o With the exception of the ______________ Caliphate, Song China was of the most scientifically and ______________ advanced societies in the world. o Excellent ______________ and astronomers. o Accurate ______________, compasses (used at sea in 1090). o Su-Song’s ______________ clock was built in 1088 CE ______________ feet tall Time of ______________, day of month, positions of the ______________, moon, planets, and major stars. First device in world history to use a chain-driven mechanism powered by flowing ______________. o Chinese Inventions of the Song Era o ______________ o Paper ______________ (flying money) o Made use of Block ______________ (adopted from the Koreans) Religion o Great revival of ______________ teachings, known as ______________ -Confucianism. o Reinforced Chinese culture’s tendency toward ______________ and obedience. o Put a premium on ______________ and cultured behavior Civil Service ______________ system Women in Chinese Society o Neo-Confucianism was used to justify the greater ______________ of women. o Earlier, a husband’s family had to produce a ______________ for a new bride, but during this time period, it reversed…______________ were arranged for the groom’s benefit. o Chinese subjugation of women was most obvious in ______________ -______________. Kept women’s feet tiny and ______________, but crippled them. Established in the 1200’s, and ______________ to the 1900’s. o Women of lower classes were freer than those in the upper classes, but still occupied a ______________ status to that of men. o Women of all classes had property ______________ rights, and retained control of their dowry after death or ______________ of husband.