World War II, Part 1: The Rise of Dictators the War
advertisement

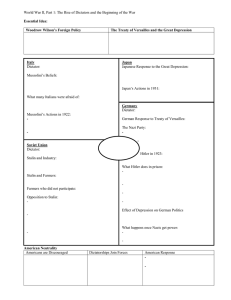
World War II, Part 1: The Rise of Dictators and the Beginning of the War Goal 10 Essential Idea The rise of Hitler and his ignoring of the Treaty of Versailles led to World War II. World Safe for Democracy? Woodrow Wilson’s Foreign Policy: Moral Diplomacy – spread democracy to other governments The Treaty of Versailles The Treaty of Versailles and the Great Depression: Due to the Treaty of Versailles and the Great Depression, many governments fell to dictatorships Italy Dictator: Benito Mussolini Mussolini’s Beliefs: Fascism – aggressive nationalistic movement that considered the state to be more important than individuals What Italians were afraid of: Italians and other Europeans feared the spread of communism Mussolini’s Blackshirts Mussolini’s Actions in 1922: Marched on Rome with a Fascist militia called the Blackshirts Mussolini Takes Power Mussolini’s Actions: Claiming to protect Italy against communism, Mussolini became dictator Japan vs. China (again) Japanese Response to the Great Depression: Military leaders thought the cure for the depression was to expand territory and get more resources Japan’s Actions in 1931: Invaded Manchuria, which was a region in China Soviet Union Dictator: Josef Stalin Stalin and Industry: He industrialized the Soviet Union, raising steel production from 4 to 18 million tons The Abuses of Stalin Stalin and Farmers: Stalin combined private farms into government-run collectives Famers who did not particpate: Died of starvation The Abuses of Stalin Opposition to Stalin: Stalin did not tolerate opposition Stalin used concentration camps in the Arctic to force dissenters into slave labor Stalin killed between 8 and 10 million people (more than Hitler) Germany Dictator: Adolf Hitler German Response to the Treaty of Versailles: Many Germans hated the Allies The Nazi Party The Nazi Party: Political party that was nationalistic and anti-communist Nazis were anti-Semitic, meaning they hated Jews Hitler Arrested Hitler in 1923: Hitler tried to overthrow the local government in Munich (Germany) and was arrested Mein Kampf What Hitler did in prison: Wrote the book “Mein Kampf” (My Struggle) He called for the reunification of Germany He described a “master race” of blue-eyed, blond-haired Aryans He blamed Jews for losing World War I German Desperation Effect of Depression on German politics: People got desperate and voted the Nazis into power Hitler Becomes Leader What happned once Nazis got power: They named Hitler dictator (Der Fuhrer) Hitler began rebuilding the German military The Axis Powers Americans are Discouraged: The rise of dictators and militarism made many Americans feel that World War I was fought in vain Dictatorships Join Forces: Italy, Japan, and Germany joined to form the Axis Powers Americans Support Isolationism American Response: Americans favored Isolationism Neutrality Act of 1935 – made it illegal to sell arms to countries at war What does the bed on the left represent? The bed on the right? What is wrong in Europe? What is the message of the cartoonist? Can you recognize this cartoonist? America Sides with China FDR’s Response to China vs. Japan: FDR authroized the sale of arms to China Getting around the Neutrality Act: The Neutrality Act was not violated because neither side had declared war Consequences of FDR’s Actions: Tension rose between Japan and the United States What does the man represent? Where is the boat likely headed? What is Dr. Seuss saying? Hitler Gets Bolder Hitler’s Action #1: Hitler began rebuilding the Germany military (violating the Treaty of Versailles) What is the difference between Germany prior to WWI and after the Treaty of Versailles? Were the new borders drawn according to ethnicities or national identities? What countries might Hitler want to invade in order to get “old Germany” back? Breaking the Treaty of Versailles Hitler’s Action #2: Hitler moved troops into the Rhineland, which was an area between France and Germany (a demilitarized zone) German-Austrian Unification Hitler’s Action #3: Anschluss – Hitler sent troops into Austria, which had many German speaking citizens Hitler declared the unification of Germany and Austria Hitler Wants More Hitler’s Action #4: Hitler announced that he wanted the Sudetenland, which was a German-speaking area of Czechoslovakia Munich Conference Munich Conference: Leaders of Britain, France, and Italy met with Hitler to discuss Czechoslovakia’s fate and try to avoid war Appeasement Appeasement: To keep peace, Britain and France gave in to Hitler’s demands Britain’s Prime Minister, Neville Chamberlain, famously declared peace had been maintained The Non-Aggression Pact Hitler’s Action #5: Non-Aggression Pact – Hitler and Stalin agreed not to fight, which made Hitler bold enough to claim Poland Who is the groom? Who is the bride? What does the cartoonist wonder? Hitler Demands Danzig Hitler’s Action #6: Hitler demanded Danzig, a German city in Poland September 1, 1939 – Hitler Invaded Poland Hitler Invades Poland Would Hitler have been as likely to invade countries if the Treaty of Versailles had redrawn borders according to nationalism? War! Result: Britain and France declared war and World War II began How has Chamberlain’s tone changed? What would happen if Germany did not agree to leave Poland? Did Germany leave Poland? What is the consequence? Blitzkrieg Blitzkrieg: A German strategy, meaning “lightening war” Large numbers of tanks would quickly break enemy lines Tanks were supported by airplanes dropping bombs and paratroopers Blitzkrieg Poland fell in a month France made the mistake of waiting for Germany to come to them (“Sitzkrieg”) Miracle at Dunkirk Miracle at Dunkirk: Germany overwhelmed French and British troops in France French and British troops were forced back to the port city of Dunkirk The new British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, asked all ships (commercial and military) to help evacuate the troops •850 ships of all sizes evacuated 338,000 troops before Germans arrived •France fell to Germany France Falls France Falls (Full screen video) Battle of Britain Battle of Britian: Fought in the air between Britain’s Royal Air Force and Germany’s Luftwaffe Hitler bombed London’s civilians instead of military targets Excerpt from Churchill’s Speech, summing up the endurance of the British "We shall go on to the end, we shall fight in France, we shall fight on the seas and oceans, we shall fight with growing confidence and growing strength in the air, we shall defend our Island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender, and even if, which I do not for a moment believe, this Island or a large part of it were subjugated and starving, then our Empire beyond the seas, armed and guarded by the British Fleet, would carry on the struggle, until, in God's good time, the New World, with all its power and might, steps forth to the rescue and the liberation of the old. " Hitler Backs Off Britain used a new technology, radar, to fight back despite being outnumbered Hitler was forced to cancel his invasion of Britain