1930’s Note packet Name:_____________
advertisement

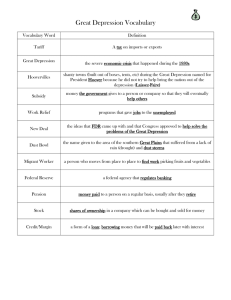
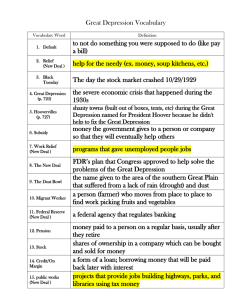
USII.6d 1930’s Note packet Name:_____________ 1 USII.6d Name ____________________________ Great Depression and New Deal notes packet Brother, Can You Spare A Dime? 1 2 3 4 They used to tell me I was building a dream And so I followed the mob When there was earth to plow or guns to bear I was always there, right on the job 5 6 7 8 They used to tell me I was building a dream With peace and glory ahead Why should I be standing in line Just waiting for bread? 9 10 11 12 Once I built a railroad, made it run Made it race against time Once I built a railroad, now it's done Brother can you spare a dime? 13 14 15 16 Once I built a tower to the sun Brick and rivet and lime Once I built a tower, now it's done Brother can you spare a dime? 17 18 19 20 Once in khaki suits, gee we looked swell Full of that yankee doodle dum Half a million boots went sloggin' through hell And I was the kid with a drum 21 22 23 24 Say, Don't you remember they called me Al? It was Al all the time Say, don't you remember, I'm your pal Buddy can you spare a dime? 2 USII.6d “Brother, Can You Spare a Dime?” Questions Question Evidence (lines in song to back up your answer) Answer 1) What is the mood of the song? (Does the song sound mostly happy, sad, angry, frustrated, or some other emotion?) 2) What did the singer do before the depression? 3) How does the singer feel now? 4) How did he survive during the depression? Depression Images –What do the photos tell you about life during the Depression? what you see what it says about the Depression Scene 1 Scene 2 Scene 3 3 Student’s Copy SOL USII.6d USII.6d Changes of the Early Twentieth Century Previous Unit Society Next Unit Great Depression and the New Deal World War II Changes of the Early Twentieth Century 1930s is about the causes and effects of the Great Depression and the major features of Roosevelt’s New Deal sparked by resulting in I. Leading Causes II. Impact on Americans Use of credit Stock speculation Federal banking system collapsed High tariffs slows trade Farmers and manufacturers overproduced Dust Bowl on Southern Plains Banks and businesses failed. One-fourth of the workers - unemployed Record numbers of people - hungry and homeless Farmers’ incomes fell to low levels. SELF-TEST QUESTIONS: 1. What were the causes of the Great Depression? 2. How did the Great Depression affect the lives of Americans? 3. What were the major features of the New Deal? 4. What is the lasting effect of the New Deal programs? Adapted from The Unit Organizer Routine.. www.contentenhancement.org leading to III. Major Features of the New Deal Social Security Federal work programs Environmental programs Farm assistance programs Increased labor rights exemplified by IV. New Deal Programs Relief CCC, WPA, FERA Reform TVA, Wagner Act, Social Security, Fair Labor Standards Act Recovery NIRA, NRA, PWA, AAA, REA TERMS, PEOPLE AND PLACES banking system Black Tuesday collective bargaining credit Dust 4 Bowl economy FDR Federal Reserve Great Depression migration New Deal overproduction recovery Reform Relief Social Security speculation stocks surplus tariffs NOTABLE QUOTE “…the only thing we have to fear is fear itself...” FDR March 4, 1933 USII.6d Impact on Americans (USII.6d) is about … how the Great Depression affected the lives of Americans. Effect on Employment Effect on Production One-fourth of the workers were unemployed. hoovervilles – makeshift towns outside cities for people seeking jobs; named after President Herbert Hoover as an insult Factories produced fewer goods Many banks and businesses failed. Dust Bowl– large area of Great Plains where drought and over-farming ruined farmland and created huge dust storms depression – Effect on Income Effect on Consumption People had less money. Large numbers of people were hungry and homeless. relief – help to ease suffering (for example, bread lines) People bought less. Farmers made less money. 5 USII.6d Depression Effects Diagrams Chart #1 Write each word or phrase from the answer bank into a blank space on the flow chart. Each completed phrase in the chart should lead (point) to something that it directly helped to cause. People became unemployed. Goods were not produced. Businesses failed. Goods were not bought. Businesses could not make profits. Answer Bank #1 failed produced bought unemployed could not make profits 6 USII.6d Chart #2 Write each word or term from the answer bank into a blank line in the diagram so that it accurately shows cause-effect relationships. overfarming black blizzards Dust Bowl drought Answer Bank #2 Dust Bowl Over farming black blizzards drought 7 Full Name: Social Security Administration The New Deal USII.6d Full Name: Civilian Conservation Corps What was the New Deal? Initials: What it does: How did it affect the lives of Americans? Full Name: Works Progress Administration Initials: What it does: Initials: What it does: Full Name: Public Works Administration Roosevelt’s Alphabet Initials: What it does: Soup Full Name: Agricultural Adjustment Act Initials: What it does: Full Name: Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Initials: What it does: 8 Full Name: Tennessee Valley Authority Initials: What it does: USII.6d USII.6d Alphabet Soup Vocabulary Activities 1. What were the 3 R’s of the New Deal? Relief, Recovery, and Reform 2. With 2-3 other people, design a commercial or advertisement to inform Americans about one of the New Deal alphabet-soup agencies from your notes. Be sure to include: a. agency’s full name and acronym (abbreviation) b. purpose of the agency c. whether the purpose can be categorized as relief, recovery, or reform 3. Alphabet Soup Charades: With 2-3 other people, try to silently “act out” the agency that your teacher assigns you secretly. a. Everyone else in the class silently writes down the agency that they think you are representing. b. Everyone who guesses correctly gets a point for his or her group…and a point for yours! 9 USII.6d From March 12, 1933 – FDR Fireside Chat on Bank Crisis http://www.fdrlibrary.marist.edu/031233.html “I hope you can see from this elemental recital of what your government is doing that there is nothing complex, or radical in the process. “We had a bad banking situation. Some of our bankers had shown themselves either incompetent or dishonest in their handling of the people's funds. They had used the money entrusted to them in speculations and unwise loans. This was of course not true in the vast majority of our banks but it was true in enough of them to shock the people for a time into a sense of insecurity and to put them into a frame of mind where they did not differentiate, but seemed to assume that the acts of a comparative few had tainted them all. It was the Government's job to straighten out this situation and do it as quickly as possible -- and the job is being performed. “I do not promise you that every bank will be reopened or that individual losses will not be suffered, but there will be no losses that possibly could be avoided; and there would have been more and greater losses had we continued to drift. I can even promise you salvation for some at least of the sorely pressed banks. We shall be engaged not merely in reopening sound banks but in the creation of sound banks through reorganization. It has been wonderful to me to catch the note of confidence from all over the country… “After all there is an element in the readjustment of our financial system more important than currency, more important than gold, and that is the confidence of the people. Confidence and courage are the essentials of success in carrying out our plan. You people must have faith; you must not be stampeded by rumors or guesses. Let us unite in banishing fear. We have provided the machinery to restore our financial system; it is up to you to support and make it work. “It is your problem no less than it is mine. Together we cannot fail.” Critical Thinking 1) Whom or what does FDR blame for the bank crisis? incompetent and dishonest bankers, bad loans 2) What does FDR say to try to reassure Americans? The federal government is working “to straighten out this situation” as quickly as possible. 3) Give an example of how FDR comes across as honest or straightforward. “I do not promise you that every bank will be reopened or that individual losses will not be suffered.” 4) What does FDR say are the essential elements (parts) of his plan to fix the economy? confidence and courage 10 USII.6d Great Depression Sketch Notes 1. During the 1920s people were wild and crazy. They sat on flag poles, danced the Charleston, and spent money they didn’t have (credit). People bought new things for their homes on credit and they invested in the stock market using credit (margin buying). 2. In October of 1929 the stock market crashed! Banks began to close, and many people lost everything. 3. President Hoover thought the economy would fix itself as it had in the past. Hoover felt that “prosperity was just around the corner.” However, as the economy worsened, many Americans named shanty towns (shack towns) after him: ”hoovervilles.” 4. Franklin D. Roosevelt took office in 1933, and immediately began working on a plan he called his “New Deal,” which was designed to give people jobs and to help those in need. 5. During this time an awful drought affected the Great Plains, which were called the “Dust Bowl” because of the huge dust storms. Because of the Dust Bowl, farmers had to migrate to other places to find jobs, and homes and belongings were covered by the dust. 6. In 1941, after the bombing of Pearl Harbor, the United States entered WWII. The increased need for production of wartime goods, as well as for soldiers, nurses, and other wartime workers, helped to relieve the Depression’s effects and set the stage for a postwar recovery. 1 2 3 4 5 6 11