Big Business and Industrialization A. Life in Industrialized America
advertisement

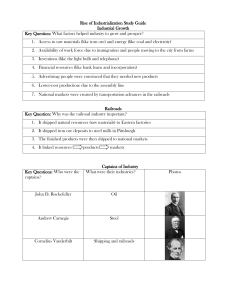
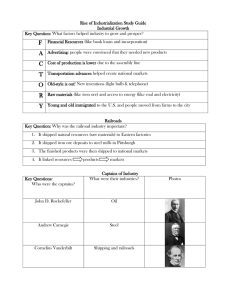
Big Business and Industrialization (use of machines to do work) A. Life in Industrialized America a large variety of products available to buy (because of national markets) more people leaving farms, moving to city to work in factories machines doing more of the work on farms and in the city, improving efficiency more job opportunities for unskilled labor in factories B. Growth and Prosperity Factors (concentrated in cities) Businesses started with raw materials (natural resources) such as coal, iron, wood, or cattle. Natural resources were shipped to factories on the railroad. In factories raw materials became finished products to be sold. More labor was available, so businesses could pay workers less. Assembly lines and cheap labor helped to lower production costs. Lots of capital was needed to start or expand a business. Railroads allowed products to be shipped out to national markets. Advertising tried to get consumers’ interest and expand the business’s market. C. Inventions Bessemer process – make stronger steel more cheaply then before Thomas Edison – improved light bulb, figured out how to use electricity in factories Henry Ford – used assembly line to lower production costs for automobiles D. Major Industrial Centers Many people bought shares (parts of the ownership) of big businesses called corporations. finished products: meatpacking in Chicago, steel in Pittsburgh, automobiles in Detroit, textiles in New England raw materials: cotton from Southeast, beef cattle from Texas E. “Captains of Industry” Rockefeller = Standard Oil, Carnegie = steel, Vanderbilt = railroads, J. P. Morgan = banking, Henry Ford = automobiles used vertical integration – bought other companies so that they would control all the steps in making their products (including natural resources, transportation, factories, and markets) created monopolies (companies that controlled most or all of a certain kind of business) by driving competitors out of business and buying other companies Rise of Big Business: Essential-Facts Check (USII.4b & d) Part One – Growth Factors (Use the answer bank to fill in each blank.) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Businesses started with ____________________ such as coal, iron, wood, or cattle. Natural resources were shipped to factories on the ____________________. In ____________________ raw materials became finished products to be sold. More ____________________ was available, so businesses could pay workers less. Assembly lines and cheap labor helped to _________________________. Lots of ____________________ was needed to start or expand a business. Railroads allowed products to be shipped out to ____________________. _________________ tried to get consumers’ interest and expand the business’s market. Answer Bank: labor capital lower production costs railroads advertising national markets natural resources factories Part Two – Captains of Industry (Match each “captain of industry” with his industry.) ____ 1. Andrew Carnegie A. banking or finance ____ 2. Henry Ford B. oil ____ 3. J.P. Morgan C. steel ____ 4. John D. Rockefeller D. automobiles (cars) ____ 5. Cornelius Vanderbilt E. railroads Part Three – Industrial Centers (Match each city or region with the associated industry.) ____ 1. Chicago F. automobiles (cars) ____ 2. Detroit G. steel ____ 3. New England H. textiles (cloth) ____ 4. Pittsburgh I. meat-packing