Some Genetic Disorders
advertisement

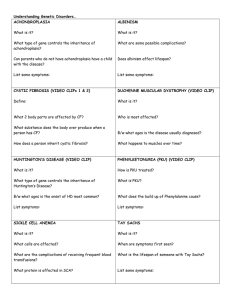
Some Genetic Disorders Genetic Disorders • All of the disorders in this presentation are autosomal. This means they NOT located on the sex chromosomes, but on the other chromosomes. • Dominant (big letters) disorders show up with just one allele present from one parent. • Recessive (little letters) disorders only show up when two alleles are present. Parents don’t have to have it for a child to have it. Huntington’s Disease • Dominant disorder • Symptoms: – – – – – Breakdown of brain and nerve tissue Irritability Loss of coordination and balance Trouble speaking and swallowing Death Huntington’s Disease Other Important Info.: • Rare, but lethal • Symptoms show up between ages 30 – 50 • Affected individuals may have already had children and passed it on to them before they knew they had HD. • Very similar to Parkinson’s Disease. Huntington’s Disease Answer: ______ % chance Practice Problem: A man who is homozygous for HD and a woman that does not have HD have a child. What is the chance that the child will have HD? Achondroplasia (Dwarfism) • Dominant disorder • Symptoms: – Short arms, short legs, but normal sized skull and torso (Disproportionate dwarfism) • Other Important Info.: – Inhibits bone growth- cartilage is slow to turn to bone – Have normal intellectual capacity Achondroplasia (Dwarfism) “Big World Little People” Family Achondroplasia (Dwarfism) Practice Problem: What is the chance of 2 dwards that are heterozygous for the disease to have a normal-sized child? Answer: _____% chance Cystic Fibrosis • Recessive disorder • Symptoms: – Overproduction of/and buildup of mucus in lungs and digestive tract – Salty skin (very salty sweat) – Difficulty breathing – Chronic coughing and wheezing – Inflammation of lungs Cystic Fibrosis • Other Important Info.: – Life expectancy: 30 yrs – Most common genetic disease in Caucasians – Treatments: physical therapy and gene therapy Cystic Fibrosis Answer: _____% chance • Practice Problem: A child’s mom is completely normal. His dad is a carrier for CF. What is the chance that the child will also be a carrier? Tay-Sachs Disease • Recessive disorder • Symptoms: – – – – – Lipids buildup in central nervous system Loss of motor skills Blindness Paralysis Death Tay-Sachs Disease Other Important Info: • Life expectancy 5 yrs • Most common in Jewish and Amish people Tay-Sachs Disease Practice Problem: Two carriers for TaySachs have a child. What is the chance that the child will have Tay-Sachs? Answer: _____% chance Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Recessive disorder • Symptoms: – Phenlyalanine (an amino acid) builds up in body – Damages central nervous system • Causes mental retardation, seizures, tremors, social/behavior problems – Stunted growth – Hyperactivity – Vomiting and bad breath Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Other Important Info.: • Treatment: – Babies receive a special non-milk formula – Affected individuals should eat a special diet, limited in proteinrich foods and avoid artificial sweetners. Phenylketonuria (PKU) Practice Problem: A woman has PKU. A man is completely normal. What is the chance of their child having PKU? Answer: _____% chance Albinism • Recessive disorder • Symptoms: – Causes no or little pigment (melanin) in eyes, skin, and hair • Blue eyes • Pale skin • Light hair Albinism • Other Important Info.: – Sensitive to sun exposure – Vision is impaired Albinism Practice Problem: Is it possible for 2 albino people to have a child with normal pigment? Answer: ______% chance