Ancient Greek Society Sparta v. Athens
advertisement

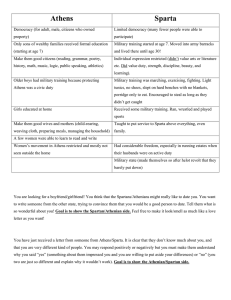
Ancient Greek Society Sparta v. Athens Ancient Greek Society • Early Greek society was broken into two groups – Free people • Adult males; usually wealthy and landowners • Considered to be citizens w/ rights and responsibility for civic participation in the city-state – Slaves • Not based on race/color • Had no political rights and were the property of the wealthy • Women and foreigners have no political rights • Women rarely seen in Greek public life Daily Life in Greece • Daily life very different for men, women & slaves • For Men – life based around the agora – Expected to participate in conversation of the city – Expected to serve in military and be educated • For women – life based in the home – Not expected to be educated – Expected to stay in the home and tend to children • For Slaves – life based on doing daily chores – Expected to run the errands of the home – Expected to protect the family while men are away Forms of Government • Many different ways to govern a city-state – Monarchy – ruling by a king or queen (usually king) • 1st way most Greek city states were ruled – Aristocracy – rule by small group of wealthy land owners • Usually gained power and land from a former king – Oligarchy – rule by a few powerful people • Usually military leaders or a person with a strong army – Tyranny – rule by one very powerful person • Usually came to power by appealing to the poor and starting a revolution against the rich The Emergence of Sparta • Spartan society was far different from Athens – Was located on the Peloponnesus peninsula • Spartans took over lands near them to expand their empire for food – People conquered forced to work their own land- called helots – Helots revolted and almost defeated Spartans – Due to revolt the Spartans build a strong military state Spartan Government • Spartan government was an oligarchy – Rule by a few strong military leaders • Two powerful kings ruled Sparta at all times • Under the kings were two other groups – The assembly – free adult males & elected officials • Voted on the major issues of Sparta – Council of Elders – those who were elder statesmen • Proposed and carried out the approved laws of Sparta • Also in charge of education and the court system Spartan Society Upper Class – those who were family of the original people of Sparta (original land owners) – Citizens usually had to pass a physical test to become a citizen • If a person failed they became a Middle Class citizen • Middle Class – non-citizens but were free people – People worked industrial or commerce jobs (building/selling) • Lower Class – Helots – those forced to work their own land, but conquered by Spartans – Were seen as just slightly better than slaves (farmers mainly) • Slaves – those who were owned by wealthy land owners of the Upper Class – Did the chores of the home, etc. Spartan Society (cont’d) • Women held a higher status in Sparta v. Athens – If they passed a physical test they were citizens too – Able to be seen in society if a citizen – Other Greek city-states questioned this role • Spartan Babies – Babies that were thought to be unfit would be left on mountaintops or tossed away by the father – Unfit babies includes: • Deformed, undersized, or anything not considered strong Spartan Education • Education differed for males and females – Women were given some education in Sparta • For the boys – life centered on military training – Around age 7 boys would be taken to a barracks – Training would last for next 12-15 years • Heads were shaved and their clothes and food was sparse • Trained to fight, kill and always put Sparta before self • For the girls – education involved many things – Girls taught to run, wrestle and play sports – Also focused on placing Sparta before themselves • Neither boys or girls focused on the arts, or other skills such as orating (speaking) The Emergence of Athens • Located on the Balkan peninsula – Was controlled by the Mycenaeans until they were weakened by the Trojan War • Was first ruled by a monarchy • Later switched to aristocracy – Rule by a few rich landowners • For a short period of time they were under tyranny • Eventually they created a limited democracy The Athenian Democracy • Athenians created a democracy to avoid a war – Problems b/w rich and poor were growing – Same problems were similar all through Greece • Solon and Cleisthenes both help reform Athens • Only free adult males were part of democracy – Makes it a limited democracy- limited people – Also a direct democracy- people vote, majority rules • Women, foreigners, slaves not allowed to vote – Not given citizenship or rights either Athenian Society • Athenian society was based on education, arts and knowledge • Society had 2 classes based on wealth/land – Citizen Class- those who owned land and were able to vote and participate in the government – Non-citizen Class- all non-land owners, slaves and foreign people in the city-state of Greece – Women had no rights to vote and mainly stayed in the home to deal with cooking, cleaning, children • Could be a citizen if her husband was, but could not vote Athenian Education • Education in Athens was the most important – Focused on reading, writing, math, and speaking – Also focused on philosophy and music • For the boys– Boys were taught from age 6-7 in the arts at schools – Went to 4 additional years of school around age 18 – Were expected to serve 2 years in the military • For the girls– Girls were taught to read and write at home – Also taught how to weave, cook , etc. Sparta v. Athens • Neither area like the other – Both thought they were better than the other • Sparta had the stronger Army – Athens had the stronger Navy • Athens had the smarter, more rounded people – Sparta had the better fighters • Women had a larger role in Sparta and could be citizens- if they passed the physical test – Women of Athens were only citizens if husband was