IMPERIALISM IN AFRICA Imperialism is a policy of
advertisement

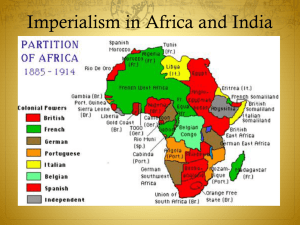
IMPERIALISM IN AFRICA Imperialism is a policy of conquering and ruling other lands A – African takeover - (Slide 1 of 2) • King Leopold II of Belgium signs treaties with local chiefs of the Congo River Valley becomes known as Belgian Congo • Leopold ruled Congo like his own private estate. Natives worked in rubber fields & those that did not supply enough rubber had their hands cut off. 5-8 Million Victims! (50% of Population) It is blood-curdling to see them (the soldiers) returning with the hands of the slain, and to find the hands of young children amongst the bigger ones evidencing their bravery...The rubber from this district has cost hundreds of lives, and the scenes I have witnessed, while unable to help the oppressed, have been almost enough to make me wish I were dead... This rubber traffic is steeped in blood, and if the natives were to rise and sweep every white person on the Upper Congo into eternity, there would still be left a fearful balance to their credit. -- Belgian Official A – African takeover – (Slide 2 of 2) Ethiopia • Ruled by Menelik II • Conflict with Russians, Italians, & French • Led the only successful resistance movement against Europeans F – Fighting for Africa (slide 1 of 2) •Soon after BelgiumEuropean powers engaged in a “Scramble for Africa” starting in the 1870s. •By 1890, most of Africa came under European control. F – Fighting for Africa The major European powers to acquire African territories were Great Britain, France, Germany, Belgium, Portugal, & Italy. By 1914, only Liberia & Ethiopia remained independent R – Riches in Africa (Slide 1 of 2) •The discovery of diamonds and gold in South Africa increased European interest. • This caused European powers to come in conflict with one another. R – Riches in Africa (Slide 2 of 2) South Africa •Dutch settlers (Boers) move to South Africa in 1600s •British attempt to colonize in 1800s conflict with Boers over slavery •Boers make “Great Trek” to move north to get away from British British followed them! •Conflict between British, Boers, & Zulus (1st Boer War) •Discovery of gold in north region led to 2nd Boer War – 1st modern “total war” I – Imperial powers meet at Berlin Conference (1884-1885) (Slide 1 of 2) • Competition was getting hot! 14 countries got together & established territory claims • At the Berlin Conference, rules were laid out as how to divide Africa: 1. Any European country must notify others when land is claimed 2. Demonstrate the area can be controlled • No African natives were invited to the conference. I – Imperial powers meet at Berlin Conference (1884-1885) Outcome: Africa is divided amongst European powers – Arbitrary boundaries are created – Some cultures are divided, while others are forcibly combined – No thought was given to religions or rivalries C– Colonization by European imperialists had both positive and negative effects on Africa Positive Negative Positive Effect: Introduction of modern transportation & communication systems, such as telegraphs, railroads, & telephones. Positive Effect: Introduction of European medicine & improved nutrition; led to population increases. Negative Effect: African peoples were treated as inferior (lesser peoples) to Europeans. Video (a little graphic!) Negative Effect: Europeans divided Africa & ignored tribal, ethnic, & cultural boundaries of African people led to tribal conflicts in many African nations that continue to this day. A – African Imperialism Motives Source for Raw Industrial Materials Revolution European Nationalism Markets for European Motives Finished For Colonization Goods Social Darwinism European Racism Humanitarian “White Reasons Man’s Burden” Missionary Activity Military & Naval Bases Places to Dump Unwanted/ Excess Popul. Soc. & Eco. Opportunities African Trade [15c-17c] Video WHAT IF AFRICA WAS NEVER COLONIZED? GOOD OPTIONAL VIDEO, TIME PERMITTING