Great Britain By: Adam Gates, Allison Pentony, Angie Broglio, Dylan Seavey,
advertisement

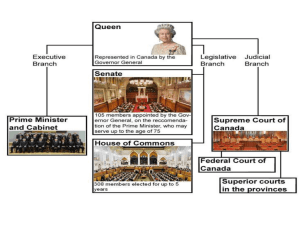
Great Britain By: Adam Gates, Allison Pentony, Angie Broglio, Dylan Seavey, David Garvis History • The Romans invaded Britain in 55 B.C. • As Rome’s was declining the country was again invaded by Angles, Saxons, and Jutes in the 5th and 6th century; up to the Norman conquest of 1066. • Under Norman rule, Britain was safe from any other invasions. And during this time Britain developed a political, administrative, cultural and economic center in London; a separate but established church; a system of common law; distinctive and distinguished university education; and representative government Geography • Area: 243,610 sq. km. (94,058 sq. mi.); slightly smaller than Oregon. • Cities: Capital--London (metropolitan pop. about 8.615 million). Other cities-Birmingham, Glasgow, West Yorkshire, Leeds, Sheffield, Liverpool, Bradford, Manchester, Edinburgh, Bristol, Belfast. • Terrain: 30% arable, 50% meadow and pasture, 12% waste or urban, 7% forested, 1% inland water. • Land use: 25% arable, 46% meadows and pastures, 10% forests and woodland, 19% other. • Climate: Generally mild and temperate; weather is subject to frequent changes but not often to temperature extremes. Economic Conditions • The United Kingdom has the sixth-largest economy in the world, has the second-largest economy in the European Union, and is a major international trading power. • GDP (2010): $2.247 trillion. • Annual growth rate (IMF, 2010): +1.25%. • • Natural resources: Coal, oil, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica. Agriculture (0.8% of GDP; 2009): Products--cereals, oilseed, potatoes, vegetables, cattle, sheep, poultry, fish. • Industry (15.9% of GDP; 2009): Types--steel, heavy engineering and metal manufacturing, textiles, motor vehicles and aircraft, construction (23.8% of GDP), electronics, chemicals. • Services (83.3% of GDP; 2009): Types--financial, business, distribution, transport, communication, hospitality. • Trade (2010): Exports of goods and services--$664.3 billion. Major goods exports--manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals, food, beverages, tobacco. Major export markets--U.S., European Union. Imports of goods and services--$740.8 billion. Major goods imports--manufactured goods, machinery, fuels, foodstuffs. Major import suppliers--U.S., European Union, and China. Social Conditions • Underclass: Long-term unemployed, elderly pensioners, economic immigrants and those dependent on state benefits. • Working Class: These people would work in blue collar jobs, traditionally in the construction and manufacturing industry. They would typically have left school as soon as legally permissible and not have been able to take part in higher education. • Middle Class: The majority of the population of Britain. They include industrialists, professionals, business people and shop owners. Mostly white collar workers. • Upper Class: Statistically very small and consists of the peerage, gentry, and hereditary landowners. These people were traditionally the wealthiest in the land having inherited money and position. Ethnic, Caste, Religious Groups • • • • • • • • • Population (July 2011 est.): 62,698,362. Annual population growth rate (2011 est.): 0.557%. Major ethnic groups (2001 census): White 92.1% (of which English 83.6%, Scottish 8.6%, Welsh 4.9%, Northern Irish 2.9%), black 2%, Indian 1.8%, Pakistani 1.3%, mixed 1.2%, other 1.6%. Major religions (2001 census): Christian (Anglican, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian, Methodist) 71.6%, Muslim 2.7%, Hindu 1%, other 1.6%, unspecified or none 23.1%. Major languages: English, Welsh, Irish Gaelic, Scottish Gaelic. Education: Years compulsory--12. Attendance--nearly 100%. Literacy--99%. Health: Infant mortality rate--4.62 deaths/1,000 live births. Life expectancy (2011 est.)--males 77.95 years; females 82.25 years; total 80.05 years. Work force (2009, 31.25 million): Services 80.4%; industry 18.2%; agriculture 1.4%. No official caste Ideologies • Systematic Ideology – developed by Walford – Study of Great Britain’s ideologies • Neoliberalism is Great Britain's dominant philosophy and Tony Blair’s main ideology appoints members of the Cabinet is also, by tradition, the First Lord of the Treasury- and draws his or her salary in that role, rather than as Prime Minister • • • • • presides over the Cabinet, is responsible for allocating functions among ministers and, at regular meetings with the Queen, informs her of the general business of the government. These include high-ranking members of the Church of England, senior judges and certain civil appointments. Englands electoral system is first-past-the-post system. The winning party needs a simple majority vote in the House of Commons The Prime Minister can call an election any time within a five year period he was voted into the government. This can work to his advantage because he can call an election when his population is up. The Prime Minister can serve for as long as he wants. The prime minister has a ‘Prime Minister’s Question Time’ once a week to answer to the House of Commons. With a recent change he is allowed to know the questions before the session. The Cabinet • The Cabinet is the committee at the centre of the British political system and the supreme decisionmaking body in government. • The Prime Minister is first among equals simply in recognition of the responsibility held for appointing and dismissing all the other Cabinet members. • Every Tuesday while Parliament is in session, the cabinet room at 10 Downing Street to discuss the issues of the day. • Fun fact: Government Cabinets have met in the same room since 1856, when it was called the Council Chamber. Political Parties • The Labour Party- The centre- Left party currently led by Ed Miliband • The Conservative Party- the centre- Right Party currently led by David Cameron • The Liberal Democrat Party- the centrist, libertarian part currently led by Nick Clegg Civil Society • A Free Media- Basically As long as they are not being libelous, newspapers, radio and television can say what they want about the Parliament, the government and politicians How political institutions exercise power • Government and State Officials exercise all powers of the Crown • It has a parliamentary democracy, so the parliament can pass, repeal, or alter laws which has to go through the House of Commons and House of Lords Inter-relationships between political institutions • There are two levels: County council and District Council – County council: provide public services, such as social services, public transportation, school. Rule over large areas – District council: provide local services, such as council housing, gyms, leisure facilities, recycling, trash collection, and local planning. Cover smaller areas Restraints on Political Institutions • The Parliament System of Government was started to be made through restraints on the monarchy in the fifteenth century • There are no legal restraints written in the constitution, it can change or make laws, overturn established conventions or turn them into laws as long as parliament meets their responsibility as a member of the European Union. Functions performed by Political Institutions • British Monarchy- The sovereign, Queen Elizabeth II, asks the leader of the majority party in the House of Commons to form a government and become Prime Minister. The monarch gives a speech and as Head of State, represents the sovereignty of the State. They also grant military and civil honors and is Commander in Chief of the Armed Forces. Functions performed by Political Institutions The Cabinet- The Cabinet relies on special committees to handle political issues. They have responsibility to Parliament. Parliament- Public bills, Private bills, and Hybrid bills are introduced in Parliament. The bills go through several stages through the 2 houses. The first stage is formality or “first reading.” Bills are debated and voted on in the second stage. Parliament restricts the power of the House of Lords to reject bills passed by the House of Commons. The last stage is the granting of the Royal Assent. Establishment of Internal Order • Used to monitor costs and the revenues of organizations or internal jobs • Ex. Collecting business transactions • Allows management to review Internal Order activity for better decision making External security • M15- Great Britain's security service that includes the protection of the British parliamentary democracy, economic interests, and counter-terrorism • Secret Intelligence Service- focused on foreign threats (SIS or M16) Resolving conflict between different groups • United Nations- peacemaking resolutions and strengthens state institutions • The Security Council and the General Assembly work together to prevent and manage conflict National Service in Great Britain • Great Britain is one such country in the world that has a centralized, single payer health care system. The spending on health care is quite low (about 7.5% of the GDP) as compared with the United States, who spends 16 percent of their GDP. However, Great Britain has long lists of patients who are waiting for some specialized treatment. Also the patients have little choice of the provider and little access to the specialists. Service in Great Britain • As of now, about 10% of the people of Great Britain have private health insurance. The private health insurance provides the same coverage that is provided by the National Health Service (NHS), but people availing the private health insurance can get better access to higher quality care with reduced waiting times. Education • Education in Great Britain is compulsory and free for all children between the ages of 5 and 16. At the age of 16 about 2/3 of pupils leave school and get jobs. About 1/3 stay at school until the age of 18. There are about 30,000 state schools with 2,000 private fee-paying schools. School System • PRIMARY SCHOOLS Children attend a primary school for 6 years, from 5 to 11. Primary school may be housed in a single building with two departments: Infant and Junior or in separate schools, Infants (5 to 7) and Junior (7 to 11). SECONDARY SCHOOLS A comprehensive school offers 5-year courses to pupils of all levels of ability. Promotion to a higher class every year does not depend upon examination results, it is almost automatic. Pupils never repeat the year. THE NATIONAL CURRICULUM One of the most important changes in education brought the Education Reform Act in 1988. It was the introduction of a National Curriculum for children aged 5 to 16 in all state schools. It consists of 10 subjects which all children must study at school. They are: Foundation subjects: English, Math, Science, a modern foreign language (for 11-16 year olds), Technology and Design, History, Geography, Music, Art and Physical Education. Religion in School • Religious Education is required for pupils as part of the basic curriculum, although parents have a right to withdraw their children from religious classes. Pupils progress in subjects is measured by written and practical tests. Taxation in Great Britain • Taxation in the United Kingdom – involves payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: • The central government Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. • The local government Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England and Wales, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those from on-street parking. • In the fiscal year 2007-08, total government revenue was 39.2 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at 36.9 per cent of GDP. Income tax: taxable bands and rates 2011/2012 Taxable income rate of tax • 0 - £2,560 10 percent • 0 - £35,000 20 percent • £35,001 to £150,000 40 percent • Over £150,000 50 percent Parliament • The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom. It is located in Westminster, London. Parliament alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and its territories. At its head is the Sovereign, Queen Elizabeth II. This Government is Legitimate. • The parliament is bicameral, with an upper house, the House of Lords, and a lower house, the House of Commons. The Queen is the third component of the legislature. The House of Lords includes two different types of members: • Lords Spiritual • Lords Temporal • These members are not elected by the population at large, but are appointed by the Sovereign on advice of the Prime Minister. • The House of Commons is a democratically elected chamber with elections to it held at least every five years. Great Britain's Court System The Constitutional Reform Act 2005 created a new Supreme Court of the United Kingdom to take over the judicial functions of the House of Lords and devolution cases from the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. The Supreme Court began work in 2009, and serves as the highest court of appeal in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, and for civil cases in Scotland. The High Court of Justiciary remains the court of last resort in Scotland for criminal cases. Sources • • • • • • • • • • • • http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/3846.htm http://www.direct.gov.uk/en/Governmentcitizensandrights/UKgovernment/Localgovernment/DG_073310 http://www.direct.gov.uk/en/Governmentcitizensandrights/UKgovernment/Parliament/DG_073604 http://www.zeblog.com/blog/uploads/t/titiflo77/Modern_political_institutions_in_the_United_Kingdom.pdf https://www.mi5.gov.uk/ http://cmbc.ucsd.edu/content/1/docs/mirovitskaya.pdf Government of the United Kingdom - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. (n.d.). Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved March 23, 2012, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Government_of_the_United_Kingdom Government of the United Kingdom - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. (n.d.). Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved March 23, 2012, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Government_of_the_United_Kingdom#Government_Departments Income tax rates. (n.d.). Choose your country. Retrieved March 23, 2012, from http://www.adviceguide.org.uk/england/your_money/tax_index_ew/income_tax_rates.htm custom., agenda, b. c., & forma, a. b. (n.d.). Parliament of the United Kingdom - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Retrieved March 23, 2012, from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parliament_of_the_United_Kingdom post. (n.d.). GREAT BRITAIN - Education System. КрНУ. Retrieved March 23, 2012, from http://www.polytech.poltava.ua/education/europa/gb_