Chapter 6: Molar Quantities Purpose
advertisement
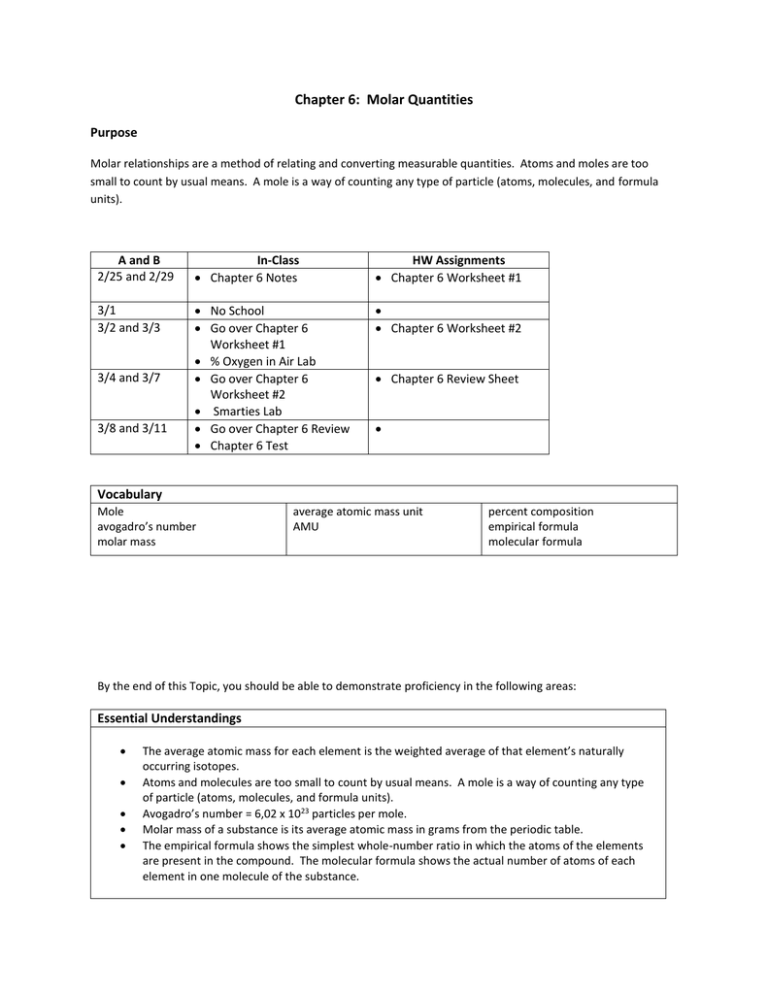
Chapter 6: Molar Quantities Purpose Molar relationships are a method of relating and converting measurable quantities. Atoms and moles are too small to count by usual means. A mole is a way of counting any type of particle (atoms, molecules, and formula units). A and B 2/25 and 2/29 In-Class Chapter 6 Notes HW Assignments Chapter 6 Worksheet #1 3/1 3/2 and 3/3 No School Go over Chapter 6 Worksheet #1 % Oxygen in Air Lab Go over Chapter 6 Worksheet #2 Smarties Lab Go over Chapter 6 Review Chapter 6 Test Chapter 6 Worksheet #2 3/4 and 3/7 3/8 and 3/11 Chapter 6 Review Sheet Vocabulary Mole avogadro’s number molar mass average atomic mass unit AMU percent composition empirical formula molecular formula By the end of this Topic, you should be able to demonstrate proficiency in the following areas: Essential Understandings The average atomic mass for each element is the weighted average of that element’s naturally occurring isotopes. Atoms and molecules are too small to count by usual means. A mole is a way of counting any type of particle (atoms, molecules, and formula units). Avogadro’s number = 6,02 x 1023 particles per mole. Molar mass of a substance is its average atomic mass in grams from the periodic table. The empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio in which the atoms of the elements are present in the compound. The molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the substance. Essential Knowledge, and Skills In order to meet this standard, it is expected that students will perform calculations to determine the “weighted” average atomic mass. perform conversions between mass, volume, particles, and moles of a substance. perform stoichiometric calculations involving the following relationships: - mole-mole - mass-mass - mole-mass SOL Standards CH.2 The student will investigate and understand that the placement of elements on the periodic table is a function of their atomic structure. The periodic table is a tool used for the investigations of a) average atomic mass, mass number, and atomic number CH.4 The student will investigate and understand that chemical quantities are based on molar relationships. Key concepts include a) Avogadro’s principle and molar volume