Weather Climate Forecast
advertisement
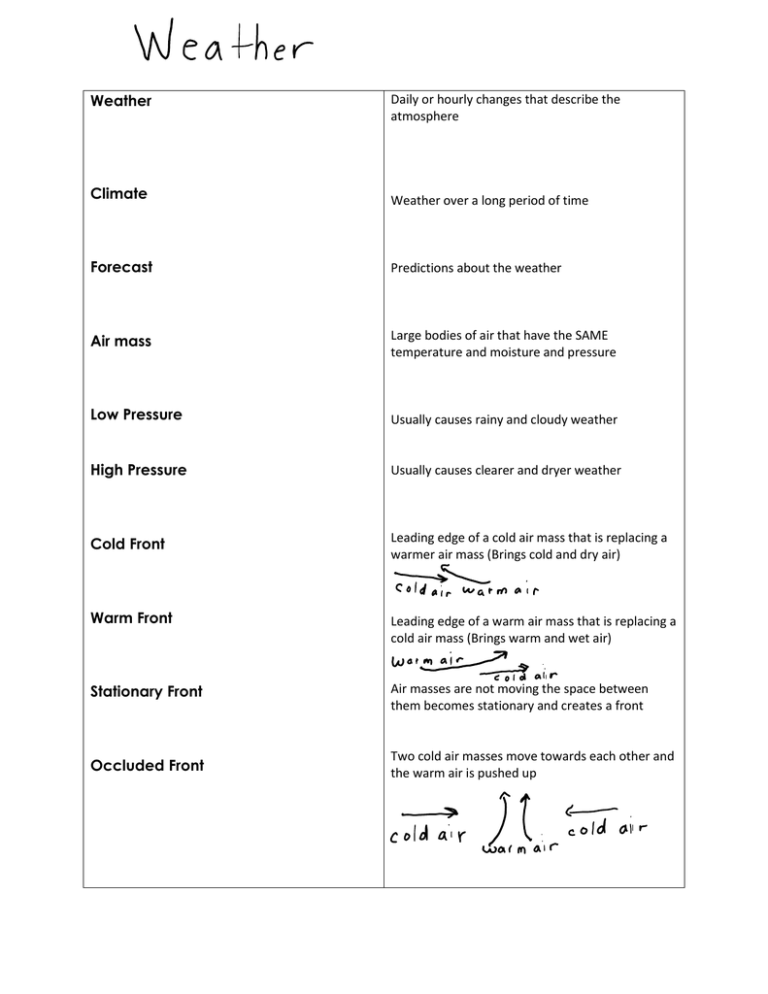
Weather Daily or hourly changes that describe the atmosphere Climate Weather over a long period of time Forecast Predictions about the weather Air mass Large bodies of air that have the SAME temperature and moisture and pressure Low Pressure Usually causes rainy and cloudy weather High Pressure Usually causes clearer and dryer weather Cold Front Leading edge of a cold air mass that is replacing a warmer air mass (Brings cold and dry air) Warm Front Leading edge of a warm air mass that is replacing a cold air mass (Brings warm and wet air) Stationary Front Air masses are not moving the space between them becomes stationary and creates a front Occluded Front Two cold air masses move towards each other and the warm air is pushed up Cumulus Form when moist air collects quickly over a small area (Pile up and are fluffy) Stratus Form as air rises slowly over a large area and cools slowly (spread out) Cirrus -Highest in the atmosphere -Form when water vapor condenses into ice crystals -Wispy Nimbus Thunderstorm Barometer Measures air pressure Greenhouse Effect -Sunlight reaches the earth and most is absorbed -Some is reflected back -Gets trapped by the water and carbon dioxide -Warms the atmosphere Global Warming Increases the temperature Maritime Polar Cold and wet Continental Tropical Warm and dry Maritime Tropical Warm and wet Continental Polar Cold and dry Meteorologists -Use trends to help predict the weather -Climate can help them predict the average temperatures for an area Humidity -Amount of water vapor in the air (increases with rainy and hot weather) Wind -Hot air rises and cool air sinks forming a convection cell -Created because of uneven heating of the Earth -Wind doesn’t always blow in one direction because Earth is spinning -US wind blows from west to east Jet stream Fast moving narrow zones of air in the atmosphere that blow west to east in the US Prevailing Westerlies -Middle latitudes where the US is (wind moves west to east) Trade winds Between the equator and 30 degrees the winds blow east to west Polar Easterlies Between 60 degrees and 90 degrees they blow east to west Sea Breeze Air moves from high to low pressure so air flows from the sea to the land (beaches are windy) Land Breeze Warmer air over the water causes air to rise and forms lower pressure so then wind moves from the land to the sea Coriolis Effect Affects moving objects and the direction of wind; makes objects moving in straight lines appear to turn; caused by the spinning of the Earth Gulf Stream The Atlantic Ocean circulates warm water up the east coast of the US; brings warm moist air to the northern areas; keeps the coast mild Hurricane Begins as a tropical storm and gets powered by warm waters; characterized by the wind speed and rain; loses power when it hits land El Nino and La Nina -Cycle every 3-7 years of cooling and warming water that impacts weather around the world El Nino- extremely warm water because the trade winds are weaker; causes US to be wetter and other places are drier La Nina- Water is cooler than usual; trade winds are stronger




