Document 17613652
advertisement

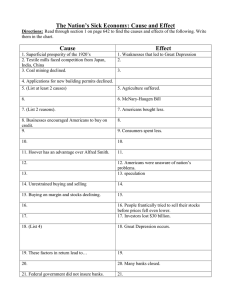
1. Great Depression The time period following the “Roaring 20’s” in which 25% of the United States’ workers were unemployed. 2. Herbert Hoover He was president of the U.S. when the stock market crashed. Ex: His refusal to provide funds for the unemployed during the Depression was based on the belief that it was not the role of the government to control the economy. 3. Franklin D. Roosevelt He served as president of the U. S. during the Great Depression and served as Commander in Chief during World War II. -He introduced many social welfare programs that are still in use today. 4. Speculation Making an investment that is risky but might bring you big earnings based on a feeling of optimism. – Ex: During the 20’s many Americans bought stocks on credit (or margin) and when the stocks fell, they could not pay back their loans; this caused many banks to close. 5. Stock • A single share of a company or corporation a person has invested in. • ex: The more stocks a person owns, the more they can profit if that business does well, however; if the business does poorly or fails, an individual can lose some or all of the money he or she has invested. 6. Stock Market • This is a place where anyone who wishes to may buy “shares” of a business that is traded publicly. – Ex: If a business does well, a “share” goes up in value; if the business does poorly, the “share” goes down in value. Buying stocks can be very profitable, but it is also very risky. 7. Federal Reserve • The “banker’s bank;” where private banks are required to keep a portion of their money, can get loans, & where the federal government keeps its money. • – The job of the FED is to keep private banks from closing & keep the economy healthy. But in 1929, it underestimated how bad the problem was and refused help small banks- many went bankrupt. 8. New Deal A series of new laws and social welfare programs introduced by President Roosevelt as a way to help pull America out of the Great Depression and put citizens back to work. 9. Social Security This program was established to help provide monetary aid for Americans starting at age 65. U.S. citizens make a small payment from every paycheck to avoid, as Roosevelt put it, “a povertyridden old age.” • Ex: The current generation pays for the retirement of those currently over 65 and then when they reach retirement, their children will help pay for their retirement. 10. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) This federal organization was formed to address banking safety and restore confidence in private banks. 11. Works Progress Admiration (WPA) This New Deal program built hospitals, schools, parks, airports, and employed artists, writers, musicians. 12. Public works Admiration (PWA) This New Deal program built ports, schools, bridges, dams, and aircraft carriers. 13. Civilian Conservation Corp (CCC) This New Deal Program put three million strong, young men to work on projects related to conservation and the development of natural resources in the U.S. 14. Agricultural Adjustment Act (AAA) This New Deal program actually paid farmers not to grow crops. 14. Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) This New Deal program built dams to provide cheap electric power to southern states.