Energy Study Guide: Potential, Kinetic, Conservation
advertisement

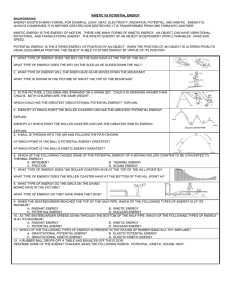
Energy (PS. 6a, 6b, and 5) Test Date: _________________ Essential Concepts and Skills Assignments Starter Quizzes Potential and kinetic energy (PS 6a) Energy is the ability to do work Energy exists in two states: potential (energy of position) and kinetic energy (energy of motion) PE= weight x height KE= mv2 2 Diagrams can be used to compare the relative amounts of potential and kinetic energy Mechanical energy (ME)= PE + KE Forms of energy (PS 6b) Thermal energy: total energy of particles that make up an object Chemical energy: energy of a compound as its atoms are rearranged to form new compounds Electrical: energy of moving electrons Sound: caused by object’s vibrations Light: produced by vibrations of electrically charged particles Nuclear: associated with changes in the nucleus Students will be able to describe the benefits and drawbacks to nuclear energy Law of Conservation of Energy (PS 5) Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; total amount of energy is always the same Energy can be transformed from one type to another. In any energy conversion some of the energy is transferred to the environment as thermal energy (due to friction) Labs (Roller Coaster and Egg Drop) Notes GIZMOs and Jason.org Rollercoaster design Pages: 214-237 STUDY GUIDE: ENERGY & ENERGY RESOURCES Potential & Kinetic Energy 1. Identify the two factors that affect potential energy. 2. Draw a pendulum swinging and label the following: 100% PE, 100% KE, PE KE, KE PE. 3. How could the potential energy of your egg container be increased during the egg drop lab? 4. Compare the height of the first hill in a roller coaster that works off of gravity to the height of the successive hills. Explain why the coaster is designed in this way. 5. What is the potential energy of a 450 N diver standing on a 10 m diving board? Show your work. 6. Compare the kinetic energy of two Corvettes that are traveling down the road. One car is faster than the other. Energy Conversions & Conservation of Energy 7. Name a device that will convert chemical energy into another form. Give its energy conversion. 8. Compare the amount of light, and heat energy in a light bulb to the amount of electrical energy it receives. 9. Identify the form of energy found in your food and tell the forms of energy it gets converted into throughout the day. Be sure to explain what is taking place at the time of the conversion. 10. Judge a television and a flashlight in their ability to demonstrate the conversion of electrical energy into light and sound. 11. A pendulum stops swinging and a friend tells you that the energy it has is lost/gone. Using what you have learned, how do you respond to your friend? 12. In every energy conversion, some energy is changed into _________. 13. What makes nuclear energy a valuable source of energy? 14. Give the energy conversion made by plants. 15. A television uses 800 J of electrical energy. Its electrical energy is converted into 350 J of light energy, 250 J of sound energy, 90 J of mechanical energy, and how much heat energy?