UNIT 2 Part A Cell Theory / Structure & Function Test Date:______
advertisement

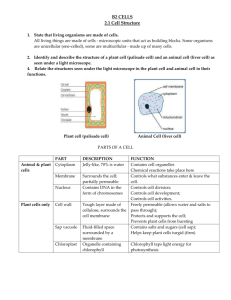
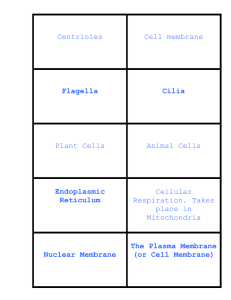
UNIT 2 Part A Cell Theory / Structure & Function Test Date:______ Essential Concepts and Skills 1. Explain why cells are called the basic units of life. a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are the basic unit of life. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (Hooke/Leeuwenhoek/Schlieden & Schwan / Virchow) (use foldable) 2. Describe specific examples that illustrate the relationship between cell structure and cell function. a) The shape of the cell is related to the job of the cell. b) Red blood cells are smooth and round so they can easily slip through very small blood vessels (capillaries). c) Muscle cells are long and elastic so they can contract and move an organism. d) Paramecia are covered with cilia and shaped like a torpedo so they can swim. e) Surface to volume ratio- Mitochondria has folds to increase surface; increase energy 4. a) b) c) Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are much simpler and usually smaller cells. Eukaryotes have a membrane bound nucleus in their cells and prokaryotes don’t. Members of the Kingdom Archaea / Bacteria (blue-green algae and bacteria) are prokaryotes; members of the protist, fungi, plant, and animal kingdoms are eukaryotes. d) Identify diagrams of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (see back of paper) 5.Describe the difference between plant and animal cells Plant Cell Wall Chloroplast Animals Multiple small Vacuole Centrioles READINGS Chapter 3 p.61- 62 Online- 44 Fun Facts p. 63-64 p.66-67 diagram: Online Text Page 47 diagram: p.75 -Notes -Envelope 1 Large Vacuole 6. Identify the parts of the microscope and give the function of each part. a. Eyepiece: magnifies the sample 10x b. Stage: holds the slide c. Diaphragm: varies the amount of light from the lamp d. Coarse adjustment: focuses the scanning and low power objectives e. High-power objective: magnifies the sample 40x f. Low-power objective: magnifies the sample 4x g. Fine adjustment: focuses the high power objective h. Medium-power objective: magnifies the sample 10x 7. Given the magnification of the eyepiece and the objective lenses, be able to determine the total magnification of a field of view. Total magnification = eyepiece magnification x objective magnification p. 19 - 20 p. 806-807 Online Text 23-28 8. Identify in a diagram and describe the function of chloroplast, mitochondria, ribosome, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus located inside the nucleolus, makes the ribosomes for the cell. c) Nuclear Membrane (envelope) bilipid layer that surrounds the nucleus. d) Ribosomes make proteins using amino acids. e) Mitochondria turn food into energy; breaking down glucose. f) ER (smooth & rough) holds ribosomes & transports proteins within the cell. g) Golgi body packages and sends proteins out of the cell. h) Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes and breaks down what the cell no longer needs. i) Cell membrane (plasma membrane) controls what materials enter and leave the cell because of diffusion or transport (homeostasis) . This membrane is flexible j) Cilia – hair-like structures that help in food capture & movement of the organism. k) Flagella - flagella is one long "whip-like" structure used only for movement. l) Cytoplasm – Jelly like substance that surrounds organelles & acts as a shock absorber. m) Vacuoles permanent storage of many substances for the cell. - Plants have 1 & animal cells has many n) Centrioles specialized microtubules that aide in reproduction of animal cells only o) Cell wall* gives support and structure to plant cells. Due to cellulose being rigid. p) Chloroplast* contains chlorophyll & uses sun’s energy to make food through photosynthesis. q) Capsule- only found in prokaryotic cells that cover the outside of cell. Honors – r) Cytoskeleton- internal organelles that give cells support & structure s) Vesicle- Form naturally in the cell to hold or move liquids/fluids: examples are: lysosomes, vacuoles, transport, and secretion. Mercer Middle Model Loudoun County Public Schools Aldie, VA p. 68-74 diagram p.74 Envelope Notes Online Text Cell Membrane -Page 51 Cell Nucleus -Page 54 Remainder of Organelles Page 57