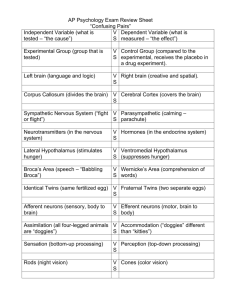
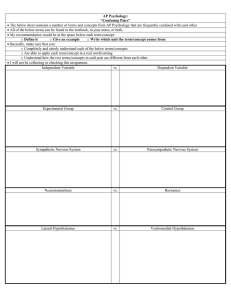
1. Independent Variable (what is tested) v. Dependent Variable... 2. Experimental Group (group that is tested) v. Control...
advertisement

1. Independent Variable (what is tested) v. Dependent Variable (what is measured) 2. Experimental Group (group that is tested) v. Control Group (compared to the experimental, receives the placebo in a drug experiment. 3. Left brain (side of the brain that is mostly language and logic) v. Right brain (side of the brain that is mostly creative and spatial). 4. Corpus Callosum (divides the brain) v. Cerebral Cortex (covers the brain) 5. Sympathetic Nervous System (“fight or flight”) v. Parasympathetic (calming) 6. Neurotransmitters (chemicals in the nervous system) v. Hormones (chemicals in the endocrine system) 7. Lateral Hypothalamus (part of the hypothalamus that stimulates hunger) v. Ventromedial Hypothalamus (part of the hypothalamus that suppresses hunger) 8. Broca’s Area (part of the brain that makes words) v. Wernicke’s Area (part of the brain that comprehends words) 9. Identical Twins (comes from the same fertilized egg) v. Fraternal Twins (comes from two separate eggs) 10. Sensory neurons (body to brain neurons) v. Motor neurons (brain to body neurons) 11. Assimilation (the process of absorbing new information into an existing schema) v. Accommodation (the process of adjusting old schemas or developing new ones to incorporate new information) 12. Bottom-up processing (starts with the sensations and works to make big picture – sensations) v. Top-down processing (breaks down big picture into details – perception) 13. Rods (night and peripheral vision, black, white, and shades of gray) v. Cones (day, detailed, and color vision) 14. Classical conditioning (involuntary learning) v. operant conditioning (voluntary learning) 15. Primacy effect (first items remembered in a list) v. Recency effect (last items remembered in a list) 16. Anterograde amnesia (can’t make new memories) v. retrograde amnesia (can’t remember old memories) ***don’t forget proactive interference and retroactive interference*** 17. Implicit memory (non-declarative and skills memory) v. Explicit memory (declarative and factbased memory) 18. Recall memory (no cues – short answers and essays) v. Recognition memory (some hints – multiple choice) 19. Algorithms (step-by-step problem solving method) v. Heuristics (rule-of-thumb problem solving method) 20. Representative heuristics (obstacle to problem solving basing decisions on stereotypes) v. Availability heuristics (obstacle to problem solving basing decisions on available info) 21. Phonemes (basic sound units) v. Morphemes (basic units of meaning) 22. Fluid Intelligence (intelligence based on logic) v. Crystallized Intelligence (acquired knowledge based on life experiences) 23. Validity (test measures what it should measure) v. Reliability (test yields same scores on a retest) 24. Achievement test (tests that test what you’ve learned) v. Aptitude test (tests that you’re your potential) 25. Intrinsic motivation (doing something for personal satisfaction) v. Extrinsic motivation (doing something for rewards) 26. Internal locus (you control the environment) v. External locus (environment controls you) 27. Type A (multitasking, high stress personality) v. Type B (low stress personality)