Phases and Their Changes
advertisement
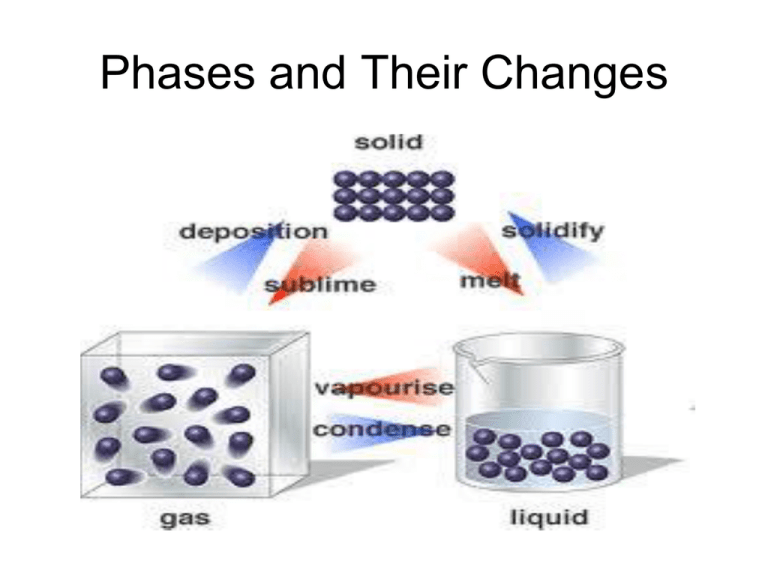
Phases and Their Changes Essential Question: What are the properties of the states of matter and how do they change? Melting vs Freezing points? Evaporation vs. Condensation points? Sublimation vs. Deposition points? List the 4 phases of matter Seconds Left: 140 120 130 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 100 110 180 1.Solid 2.Liquid 3.Gas 4.Plasma Use a diagram to describe the three most common phases of matter Seconds Left: 140 120 130 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 100 110 180 Phase Change Diagram Phases of matter are PHYSICAL PROPERTIES. What is necessary to cause a change in phase in the three most common phases? Seconds Left: 140 120 130 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 100 110 180 Energy. An increase in energy will cause a solid to change to a liquid and a liquid to change to a gas. There is no such thing as adding or removing cold. Describe SOLID This screen will disappear in 3 120 130 140 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 80 100 110 1 minutes. Seconds Remaining. The solid phase of matter occurs when the material has a definite volume or size and distinct shape at a given temperature. Describe LIQUID Seconds Remaining: 140 120 130 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 100 110 180 A liquid has a definite volume, but it takes the shape of its container with the aid of gravity. Describe GAS Seconds Remaining: 140 120 130 30 40 50 60 70 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 180 20 160 90 150 170 100 110 180 The volume of a gas depends on its temperature and the surrounding pressure. It will take the shape of its container if the container is closed. Therefore Definite Volume Definite Shape • Solid Yes Yes • Liquid Yes No • Gas No No But what happens if you raise the temperature to super-high levels… between 1000°C and 1,000,000,000°C ? Will everything just be a gas? STATES OF MATTER PLASMA A plasma is an ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases • Plasma is the have an indefinite common state shape and an of matter indefinite volume. STATES OF MATTER SOLID Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place LIQUID Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other GAS Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds PLASMA Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles Some places where plasmas are found… 1. Flames 2. Lightning The Sun is an example of a star in its plasma state 3. Aurora (Northern Lights) COLD PLASMA ??? • In contrast, non-thermal or cold plasma has only a small fraction of its atoms ionized. Examples of cold plasma include fluorescent lamps and neon signs. Neon Lights could more accurately be called "plasma lights", as the light comes from the plasma inside of them. Triple Point Phase Change Diagram Phases Phases is the term scientist use to more properly define solid, liquids and gases. It means the same as the term “state” Phase is defined as “a part of matter that has uniform properties through out the entire substance” Phases change As scientists we can change phases. We can change a solid into a liquid and a liquid into a gas. When two phases exist at the same time it is called equilibrium. Equilibrium is a dynamic condition in which two opposing changes occur in equal rates in a closed system Equilibrium To have equilibrium we need to have both a temperature and pressure. When we have both a measured temperature and pressure two or three states will exist at the same time. Ice melting into water, water freezing into ice. Phase Diagrams Scientist have phase diagrams to show exactly the temperature and pressure must be achieved to have a solid, liquid, gas, two phases or all three phases A phase diagram by definition is “a relationship between physical states that deals with temperature and pressure.” Phase diagram of water. Pressure is in atmopheres (normal pressure is 1 atm) Temperature is in celcius (water boils at 100) Each of the lines represent equilibrium (two states exist at the same time) Point C is called the critical point Critical point: is the point on which liquids and gases are indistinguishable (can’t tell the difference Point A is called the Triple Point The Triple point is the temperature and pressure in which gas, liquid and solid all exist in equilibrium Video • Sublimation • Freezing • Freezing Waves Vapor Pressure • The molecules in a liquid are constantly moving and running into each other. • Sometimes they will “bounce” out of the container they are in. • As a result, a faint vapor will exist over most liquids. Vapor Pressure • Vapor Pressure is the pressure of vapor over a liquid at equilibrium with the atmosphere. • When water boils the vapor pressure exceeds the atmospheric pressure and the molecules leave the liquid with little impediment. Vapor Pressure • So then how do puddles evaporate and why can clothes dry outside when the temperature is below freezing??? • Water molecules are always moving and are always escaping from their container. Heat makes them move faster or slower. Research 1. Pick out three different elements or substances. A Solid, A Liquid and A Gas. 2. Not water. Tap Water is O.K. 3. Find their melting, freezing point, condensation, evaporation point, and sublimation, deposition point. In Celsius. 4. Select a synonym for each of the six phase changes in #3. 5. Give an example of each.