Life After the Civil War Westward Expansion 1849-1890
advertisement
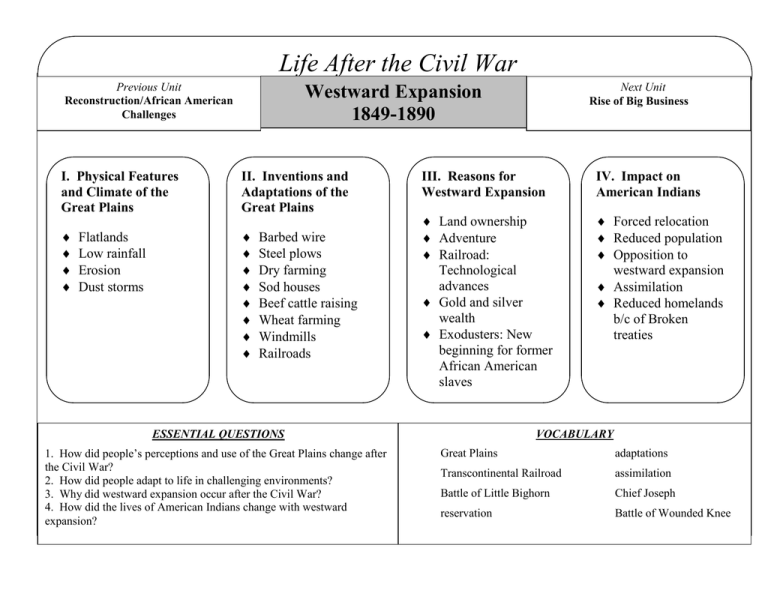
1 Life After the Civil War Previous Unit Reconstruction/African American Challenges I. Physical Features and Climate of the Great Plains II. Inventions and Adaptations of the Great Plains Flatlands Low rainfall Erosion Dust storms Next Unit Rise of Big Business Westward Expansion 1849-1890 Barbed wire Steel plows Dry farming Sod houses Beef cattle raising Wheat farming Windmills Railroads III. Reasons for Westward Expansion IV. Impact on American Indians Land ownership Adventure Railroad: Technological advances Gold and silver wealth Exodusters: New beginning for former African American slaves Forced relocation Reduced population Opposition to westward expansion Assimilation Reduced homelands b/c of Broken treaties VOCABULARY ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS 1. How did people’s perceptions and use of the Great Plains change after the Civil War? 2. How did people adapt to life in challenging environments? 3. Why did westward expansion occur after the Civil War? 4. How did the lives of American Indians change with westward expansion? Great Plains adaptations Transcontinental Railroad assimilation Battle of Little Bighorn Chief Joseph reservation Battle of Wounded Knee 2 Describe the picture using adjectives. If you lived here, what would you do for fun? List 2 places where this picture might be. What type of people would not like to live here? What problems/dangers would you face Why would some people rather live here? here than New York City? What kind of people would like to live here? To survive here, what would you have to be able to do? 3 The Great Plains After the Civil War, people changed the way they viewed the vast interior of the continent. Because of new technologies, people saw the Great Plains not as a “treeless wasteland” but as a vast area to be settled. Where is it? (Can you name all these states?) This place makes me think of… -Gold Rush California 1849 - Comstock Lode (Nevada silver) -Black Hills Mining (South Da What did people think before the Civil War? What did people think after the Civil War? Who qGO The Plains were called the “Great American Desert.” Rainfall was scarce and unpredictable. There were frequent damaging storms and swarms of hungry insects. The land was hard to farm, since it had never been plowed. Herds of wild bison roamed the land. It was a long way from civilization. The wind blew long and hard; there were few trees. Would you go to the Great Plains? Why or why not? because … Irrigation and a decade of unusually wet weather in the 1870s made the Plains habitable. Crops flourished, and farmers grew food for themselves and cash crops like wheat. Railroads brought fresh settlers and supplies. Pioneers enjoyed being independent and selfsufficient. Many people found life too lonely and difficult in the prairie. NO GO 4 II. Invention and Adaptation in the Great Plains barbed wire, California, cattle, dry farming, goods, mechanized farming, Nebraska, sod houses, Rocky Mountains, High Sierra, steel plows, subsidy, wheat, windmills New Tools and Techniques Adaptation of Existing Technology Transcontinental Railroad __________ __________ made it possible to prepare uncultivated land for planting. To pump water for their crops, farmers put the wind to work with __________. Railroad engineers crossed the __________ __________ and the __________ __________. Pioneers protected their homesteads with fences made of __________ __________. Immigrants brought hearty strains of __________ suited to the climate of the Plains. Railroads transported people out West and western __________ East for sale. Settlers on the Plains lived in __________ __________ made of earth and grass. Entrepreneurs herded wild __________ to market. Because they received a large government __________, railroads sold land for low prices. __________ __________ helped farmers produce more crops with less work. __________ __________ made it possible to grow crops with little rain. The TCRR stretched 1,700 miles from __________ to __________. Template © 2003 Edwin Ellis, Graphicorganizers.com 5 Record 10 Facts from Charlie Brown onto the Train 6 Question Battle at Little Bighorn V S Event at Wounded Knee Date (When) Who? Big ARMY Names Who? Big Native American Chief Names Tribes Location (Where did it take place?) Conflict (Why) Result (What happened in the end?) Compare and Contrast SOL II.4a Answer the questions using the hand-outs. 7 F Forced relocation from traditional lands to reservations (Chief Joseph, Nez Perce) R Reduced population through warfare and disease (Battle of Wounded Knee) O A R Opposition by American Indians to westward expansion (Battle of Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull, Geronimo) Assimilation attempts and lifestyle changes (e.g., reduction of buffalo population) Reduced their homelands through treaties that were broken Y Manifest Destiny: Forced relocation from homelands to reservations (Chief Joseph, Nez Perce) B Buffalo: Reduced population life resource killed. (Battle of Wounded Knee) B Battles: American Indians fight settlers. (Battle of Little Bighorn, Wounded Knee, Sitting Bull, Geronimo) A Assimilation leads to life changes D Disease and Death due to Manifest Destiny and settlers. These are the negative effects of Westward Expansion and a differing perspective on land ownership for Native Americans. Pick one to help you remember. 8 F A Y A R O R CREATE A Picture to match each Letter. B B D CREATE A Picture to match each Letter. 9