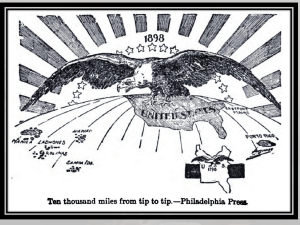
What is imperialism? materials and new markets
advertisement

Imperialism Study Guide Name____________________________ U.S.II5a,U.S.II5b, U.S.II1i Block______ Date_________________ What is imperialism? A policy by which an industrialized nation takes control of a colony and uses it for raw materials and new markets What often influences the United States’ involvement in international affairs? Economic interests Public opinion What were the causes for the Spanish American War? Protection of American business interests (such as sugar) in Cuba American support of Cuban rebels to gain independence from Spain Rising tensions between Spain and the United States as a result of the sinking of the USS Maine in Havana Harbor on Feb. 15th, 1898. Exaggerated news reports of events, also known as “yellow journalism” o (Exciting and exaggerated stories printed by a newspaper to gain more readers and get Americans to support the war) What were the results/effects of the Spanish American War? (Think: Treaty of Paris, 1898) The United States emerged as a world power Cuba gained independence from Spain The United States gained possession of the Philippines, Guam and Puerto Rico o (Think: PopRocks Go POP!) Who were the Rough Riders during the Spanish American War? A group of athletes, miners, cowboys, etc. who fought in Cuba at San Juan Hill Who was the leader of the “Rough Riders” during the Battle of San Juan Hill? Assistant Secretary of the Navy, Teddy Roosevelt (this was before he was President!) What was the name of Teddy Roosevelt’s foreign policy when he was President? “Big Stick” Diplomacy What was the Monroe Doctrine? It was presented by President James Monroe in 1823; it stated that Europe should stay out of the Americas and America would stay out of Europe. Why did Roosevelt expand the Monroe Doctrine? What is this called? It was a way to prevent European involvement in the affairs of Latin American countries It was called the “Roosevelt Corollary” What did the Roosevelt Corollary do? Asserted the United States’ right to interfere in the economic matters of other nations in the Americas (North America and Latin America-Central and South America) Claimed the United States’ right to exercise international police power Advocated “Big Stick” Diplomacy. Big Stick was used to free Panama from Columbia, so the U.S. could built the Panama Canal. What country did the United States help to gain its independence so a canal could be built? Panama The U.S. took over construction from France; it took ten years to build and cost $380 million It provided a shortcut from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean for military and commercial ships It saved travel time and increased trade for the United States and other nations What countries, territories, or regions did the United States take control of during the era of imperialism? How and why for each? Hawaii Alaska Cuba (as a protectorate) Philippines Guam Puerto Rico Panama China Identify the countries involved in the Spanish American War. Label and color them on the map below. (LPII.2.1) Think: US, Spain, Cuba, Philippines, Puerto Rico, Guam