Cold War
advertisement

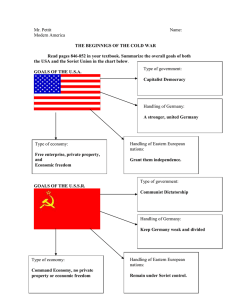
Cold War During World War II, the Allies hoped to prepare a postwar peace which would endure for generations. The cornerstone of that peace would be the United Nations. But this peaceful world order did not come to be. Instead, hostility between the Soviet Union and the United States erupted and threatened to bring about a third world war. This period of hostility became known as the cold war. America claimed that the Soviet Union started the cold war by violating the Yalta Agreement of 1945. Instead of granting freedom to those East European nations that it liberated from the Nazis, the Soviet Union imposed communist rule on them. In addition, the Soviet Union closed the border between Soviet-dominated Eastern Europe and Western Europe. This border, and the restrictions on movement and thought that it represented, became known as the "iron curtain." Meanwhile, the Soviets blamed cold war hostility on "anti-communist" hysteria in the U.S. and other western capitalist countries. Cold war tension increased when the Soviet Union attempted to extend communism through so-called "wars of national liberation." In carrying out this policy, the Soviet Union encouraged rebellions in other nations. One such revolt was fomented in Greece in 1946. Under the leadership of President Truman, the U.S. responded quickly to these Soviet actions. In 1947, the President proclaimed the Truman Doctrine. In it, the U.S. promised to help other nations resist threats to their "free institutions and national integrity." Acting on this promise, the U.S. sent military supplies to Greece and the communist-led revolt failed. The U.S. also established the Marshall Plan (1948) which helped European nations rebuild their war-torn economies. The U.S. established the Point Four program in 1950 to help the needy in other parts of the world. In addition to being humanitarian, these programs attempted to make countries less vulnerable to communist-led insurgencies. The N.A.T.O. alliance further strengthened European security. Under this alliance the U.S., Canada, Iceland, and nine Western European nations pledged to help each other if any were attacked. Communist expansion in Asia presented a more difficult challenge to the U.S. After World War II, Chinese communists resumed their efforts to control China. Despite the shipment of U.S. military supplies to the non-communist government of China, the communists won (1949). In 1950, North Korea (under a communist government) invaded South Korea. Until then, the United Nations Security Council had been unable to block such aggression because of Soviet Union vetoes. But in June 1950 the Soviet Union was boycotting the Security Council. Taking advantage of this unique opportunity, the Security Council voted to request member nations to create a United Nations force to block further conquest of South Korea. Meanwhile, America readjusted to peace-time life after World War II. But the transition was not easy. Since the economy was still geared toward wartime production, consumer products, such as automobiles, were scarce. The demand for scarce products caused prices to rise. Workers demanded pay increases to match the rising cost of living. When employers granted raises, the costs of production went up, causing even more inflation -- a phenomenon called the wage-price spiral. When employers rejected wage requests, as they increasingly did, unions often retaliated by calling strikes. The growing labor problems and cold war concerns created an atmosphere which helped political conservatives. Led by conservative Republicans, Congress passed the Taft-Hartley Act in 1947 over President Truman's veto. This law weakened the power of labor unions. One clause of the act outlawed closed-shop agreements. Another clause allowed states to ban union-shop agreements. The conservative mood of the postwar period also frustrated Truman's efforts at economic and civil rights reforms. The conservative revival also contributed to the defeat of the liberal Democratic presidential candidate, Adlai Stevenson, in 1952 and the election of the more conservative Republican candidate, Dwight D. Eisenhower.