Major Theories of Development Kohlberg’s
advertisement

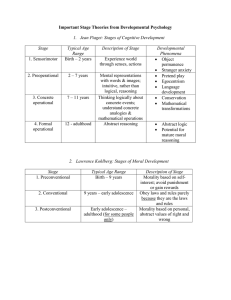
Major Theories of Development ¤ Know all for the Test!!! Define morality and describe Kohlberg’s stages of moral development. Focused on moral reasoning –why people think the way they do about right and wrong 1. 2. 3. Level Stage What Determines Right and Wrong Preconventional – great importance to the authority of adults 1 – action is wrong if its punished Punishment by adults 2 – action is right if its rewarded 3 – want approval of those close to them Reward by adults Rules set by close people 4 – more concerned with the rules of broader society 5 – don’t see societies rules as absolute Rules set by society 6 – figure out right and wrong based on abstract ethical principles Rules based on abstract ethical principles Conventional – children value rules in which they follow to get approval from others Postconventional – become more flexible and consider what’s personally important to them Rules set by society, judged by what’s personally important Outline Piaget’s four main stages of cognitive development, and comment on how a child’s thinking changes during these four stages. Stage – age range Description Developmental Highlights Sensorimoter (birth-2) Experiencing the world through senses and actions – (looking, touching, mouthing, and grasping) Preoperational (2-6 or 7) Representing things with words and images, use intuitive rather than logical reasoning Concrete Operational (7 – 11) Thinking logically about concrete events, grasping concrete analogies and performing math Object permanence – the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived Symbolic Thought – represent objects in terms of mental symbols Stranger Anxiety – fear of strangers Pretend play Egocentrism – the difficulty taking another’s point of view Language development Conservation – the principle that quantity remains the same despite changes in shape Reversibility – the ability to mentally reverse actions 8+4=12 12-4=8 Decentration – the ability to focus on several Formal Operational (12 – adulthood) Abstract reasoning aspects of a problem Abstract logic Ability for moral reasoning Identify Erikson’s eight stages of psychosocial development and their accompanying issues. Give examples and descriptions. Stage Conflict Faced 1 6 Trust vs. Mistrust – if the caretakers meet babies needs, the baby becomes attached and develops a sense of security, otherwise, they may develop a mistrustful, insecure attitude Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt – if effective in learning tasks they may develop autonomy or sense of doubt or shame about themselves Initiative vs. Guilt – may become more self-confident or develop a sense of guilt Industry vs. Inferiority – may have a sense of competence or a sense of inferiority Identity vs. Role confusion – develop a sense of identity or are still confused as to who they are and their role Intimacy vs. Isolation 7 Generativity vs. Self-absorption 8 Integrity vs. Despair – become content or disappointed about their lives and fearful of the future 2 3 4 5 Typical Age Range First year of life Major Challenge(s) 1–3 Gaining independence – feeding themselves, toilet training, and dressing themselves 3–6 Acting in a socially responsible way – must learn to control their impulses Competing with peers, preparing for adult roles 6 – 12 Having basic needs met, attaching to people Adolescence Determining one’s identity and direction in life Early Adulthood Developing intimate relationships or become isolated and lonely Being productive either through parenting or job Evaluating one’s life Middle Adulthood Old Age