Solar and Lunar Eclipses
advertisement

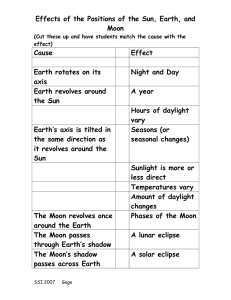
Solar and Lunar Eclipses What is an eclipse? • An eclipse occurs any time something passes in front of the Sun, blocking its light. This can be the Earth or the Moon. Is there more than 1 kind of eclipse? • Lunar Eclipse- When the Earth casts a shadow on the moon, causing the moon to go dark. Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and casts a shadow on the Moon (Full Moon) • Solar Eclipse- When the Moon casts a shadow on the Earth, causing the sun to go dark. The Moon comes between the Sun and Earth and casts a shadow on part of Earth (New Moon) Lunar Eclipses • The Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, blocking th Sun’s light, and causing the moon to glow red. • Umbra – The dark inner portion of the shadow cone. • Penumbra – the lighter outer portion of the shadow. Types of Solar Eclipses • Total Solar Eclipse – can only occur if you are at the exact spot within the moon’s umbra (which isn’t very big). • Partial Solar Eclipse – Visible is you are in the penumbra of the shadow. Only some of the moon will be shadowed. • Annular Eclipse – occurs when the moon is farthest from the Earth in its orbit. This makes the moon look smaller, so during the eclipse you see an outer ring of light from the Sun. Total Solar Eclipse – can only occur if you are at the exact spot within the moon’s umbra (which isn’t very big). Partial Solar Eclipse – Visible if you are in the penumbra of the shadow. Only some of the moon will be shadowed. Annular Eclipse – occurs when the moon is farthest from the Earth in its orbit. This makes the moon look smaller, so during the eclipse you see an outer ring of light from the Sun. How often do Eclipses Happen? • That depends!! Lunar Eclipses happen more often than Solar Eclipses. • Why? Well everyone who is experiencing nighttime during a lunar eclipse can see it. • But you have to be at the exact spot on Earth to see a Solar Eclipse. • The spot on Earth is so small, that the same place only sees a Solar Eclipse every 350 years!! Why Don’t We See Lunar Eclipses More Often? • Well, lunar eclipses don’t happen everyday because the Moon’s orbit is tilted. So, during most months, the Moon is above or below the Earth. Eclipse Seasons • Syzygy- The times where the Moon, the Earth, and the Sun line up perfectly for an eclipse. Earth-Moon-Sun Relationship Earthshine Project, BBSO (http://www.bbso.njit.edu/espr/fig10.html Earth-Moon-Sun Relationship Sphere – a round, three-dimensional object whose surface at all points is the same distance from its center Axis – an imaginary line around which an object spins Earth-Moon-Sun Relationship Rotation – the spinning of an object around its axis Revolution – the orbiting of one object around another, like Earth revolving around the sun Ellipse – an elongated, closed curve; the shape of planetary orbits Why do we have Seasons They are caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis, 23½0 Equinox – when the noon sun is directly overhead at the equator, equal hours of daylight and darkness Solstice – when the noon sun is directly overhead at either 23½0N (Tropic of Cancer) or 23½0S (Tropic of Capricorn) latitude, coincides with the 1st day of summer or winter Path of the Ecliptic • The apparent path of the Sun across the sky. In summer, the Sun's path is longest, and so are the days. In winter, the Sun's path is shortest, and so are the days. The Moon The Moon • 2. 3. 4. Earth’s only natural satellite 384,000km away, 1/6th the gravity of Earth Noon temp. of 1300C, night temp. of -1750C Surface features 1. Dark, flat plains called marias 2. Bright areas called highlands MOOOON The period of rotation equals the period of revolution around the Earth Apollo 11 put Neil Armstrong and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin on the moon on July 16th, 1969 Tides - Caused by moon’s gravitational pull - Spring Tide – the moon, Earth and sun align - Neap Tide – when the moon, Earth and sun form a right angle