Estimated Test Date: ___________________
advertisement

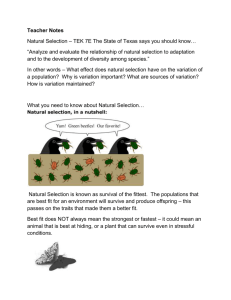
Estimated Test Date: ___________________ Fundamental Concepts and Skills 1. Geologic Time – Understand how the Earth was believed to have developed as well as the geologic time periods. a. PreCambrian: any time before the Cambrian period (the first period of the Paleozoic era). b. Paleozoic – The Age of Fish and Amphibians: “paleo”: ancient or old age “zoic”: animal life c. Mesozoic – The Age of Reptiles Means middle animal life. d. Cenozoic – The Age of Mammals Means recent age of animals; is divided into epoch since it was so recent. 2. Describe the perceived origins of life and the scientists who contributed to them. a. Theory of Vital Force – spontaneous generation. b. Biogenesis c. The Oparin Hypothesis. d. Endosymbiont Hypothesis and the theory of the first cells on Earth. e. Contributions of Redi, Pasteur, Miller and Urey, etc. 3. Describe the contributions Darwin had to the evolutionary theory. a. His travels and observations (Galapagos turtles and finches). b. His collaboration and publications with fellow researchers such as Malthus and Lamarck. 4. Describe how changes in the environment and natural selection result in changes in populations. a. All populations produce more offspring then the environment can support. b. This leads to a struggle with only a fraction of the offspring surviving. c. There is great variety among individuals of a population. d. Thos individuals best fit to the environment survive and produce more offspring. e. The unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce leads to gradual changes in a population, generation after generation. 5. Describe the evidence for evolution from molecular biology. a. Closely related organisms have very similar DNA and amino acid sequences. b. Fewer differences in these sequences are seen between closely related species. c. More differences are seen between more distantly related species. Reading pp. 417-434 pp. 8-11; 13; 424; 427-428 pp. 369-387 pp. 397-410 pp. 393-396 6. Describe the basis for the current system for classification. a. Organisms are grouped based on structural similarities – Analogous and Homologous. b. Organisms are grouped based on fossil evidence of common ancestors – Useful and Vestigial. c. Organisms are grouped based on similarities in developmental stages – Embryological. d. Organisms are grouped on similarities in DNA. 7. Describe how populations grow. a. A population is a group of interbreeding individuals that live in the same place at the same time, competing with one another for food, water, shelter and mates. b. The available resources (food, water, shelter, and mates) regulate population growth. c. Populations grow the fastest when there are excess resources available. d. Populations stop growing when the amount of resources start to run out. The carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals in a population that can survive on available resources. e. A resource that an organism needs to survive is known as a limiting factor. Assessments Field Trip to the Natural History Museum Peppered Moth Lab Woolybooger Experiment Sex and the Single Guppy Population Webquest pp. 382-385 pp. 435-440; Chapter 5