Chapter 6 - Section 2 Foreign Affairs Trouble the Nation
advertisement

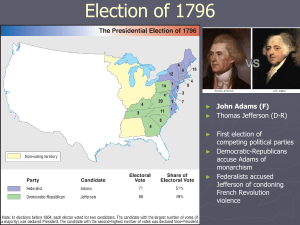
Chapter 6 - Section 2 Foreign Affairs Trouble the Nation Main Idea – Events in Europe sharply divided public opinion in America, which strengthened the first party system (Federalists vs. Republicans) in the 1790s. U.S. Response to Events in Europe - French Revolution – resulted in a war between France and Great Britain o Republicans – pro-French o Federalists – pro-British o President Washington – Neutrality Act of 1793 – stated that the U.S. would not join either side in the war - Great Britain – still controlled several forts in the American Northwest o Jay’s Treaty (1794) – Britain agreed to remove troops from U.S. soil, but were allowed to maintain fur trading ties with Native Americans on U.S. soil Angered Republicans, especially western farmers Spain – controlled Florida and land west of the Mississippi River and New Orleans o Pinckney’s Treaty (1795) – U.S. got access to the port of New Orleans Important for shipping agricultural goods on the Mississippi River - - Washington’s “Farewell Address” – Washington’s advise to the nation after deciding not to seek a 3rd term as president o Argued that political parties were dangerous to the U.S. o Argued that U.S. should avoid “entangling” alliances with foreign nations President John Adams Provokes Criticism - - Election of 1796 – John Adams (Federalist) vs. Thomas Jefferson (Republican) o John Adams won, which left Jefferson as Vice-President o Adams won the North, Jefferson won the South = sectionalism – def. – placing interests of one region over those of the nation as a whole XYZ Affair (1798) – French diplomats demanded a bribe from US ambassadors o SIG – resulted in an undeclared naval war with France The Alien and Sedition Acts (1798) – laws passed by Federalist Congress o Alien Acts – increased the time it took to become a citizen, which hurt the growing Republican Party o Sedition Act – set fines and jail time for people disparaging the government Resulted in jail time for several Republican printers and newspaper editors - Virginia and Kentucky Resolutions (1798) – Jefferson and Madison’s reaction to the Alien and Sedition Acts o Claimed Alien and Sedition Acts violated 1st Amendment rights o Argued in favor of Nullification – def - states could declare an act of congress unconstitutional