Chapter 6 - Section 1 Washington Heads the New Government
advertisement

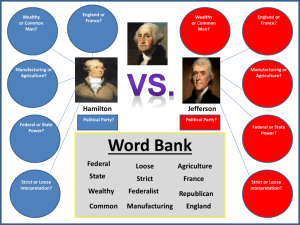
Chapter 6 - Section 1 Washington Heads the New Government Main Idea – Disagreements between President Washington’s Secretary of Treasury, Alexander Hamilton, and his Secretary of State, Thomas Jefferson, led to the development of the Federalist and Democratic-Republican parties. The New Government Takes Shape - - Executive Branch: o President – George Washington o Vice-President – John Adams o Cabinet – department heads who advise the president Secretary of the Treasury (economy) – Alexander Hamilton Secretary of State (foreign affairs) – Thomas Jefferson Secretary of War (defense) – Henry Knox Judicial Branch: o Judiciary Act of 1789 – def. – defined the Supreme Court as chief justice and 5 associate judges, and established a lower federal court system Hamilton and Jefferson Debate - Alexander Hamilton (Secretary of the Treasury) o Believed in a strong central government o Favored the wealthy upper class elites, despised commoners o Favored commerce and industry for the future of the nation’s economy o Favored a loose interpretation of the Constitution o Popular in the North, especially New England - Thomas Jefferson (Secretary of State) o Preferred a weak central government with strong state governments o Favored the common man, distrusted the rich o Favored agriculture for the future of the nation’s economy o Favored a strict interpretation of the Constitution o Popular in the South and the West - Hamilton’s Economic Plan – controversial, led to the creation of political parties o Funding at Par – plan to pay off old bonds with new bonds Upset Revolutionary War veterans who had sold their old bonds o Assumption of state debts by the federal government Upset states that had already paid off their debts Compromise to Southern states - new capital = Washington DC o Bank of the United States – designed to issue paper money, hold federal tax funds, and link wealthy investors to the success of the U.S. government Jefferson and James Madison argued it would favor the wealthy classes, and that it was unconstitutional SIG – debate erupted over interpretation of the Constitution o Jefferson and Madison = strict o Hamilton = loose o Excise tax – def. – tax on a product’s manufacture, sale, or distribution Passed on manufacture of whiskey The First Political Parties and Rebellion - Washington tried to avoid party politics but almost always sided with Hamilton - Federalists = followers of Alexander Hamilton Republicans (Democratic-Republicans) = followers of Thomas Jefferson - The Whiskey Rebellion (1794) – farmers in western Pennsylvania refused to pay the excise tax on whiskey in defiance of federal law o Put down by the federal militia o SIG – demonstrated the power of the new central government