Baggett/Carr/Neithercut Name ____________________________ APUSH (Unit 5, #5)
advertisement

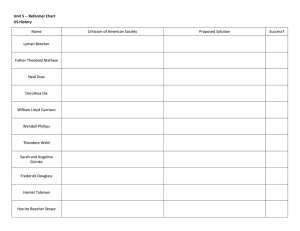
Baggett/Carr/Neithercut APUSH (Unit 5, #5) Name ____________________________ Date ________________ Pd ________ The Pursuit of Perfection: Social Changes & Reforms from 1820s to 1850s I. The Rise of Evangelicalism A. The end of established churches led to competition for converts & evangelicalism based on self-improvement B. Second Great Awakening (1800-1830s) 1. Era of religious revivalism that preached saving souls through conversion & repentance 2. Charles G. Finney used dramatic “soul-shaking” revivals emotionalism, & week-long tent meetings 3. The impact of the Second Great Awakening a. The burned-over district of New York state became a center for new religious ideas & social reformers b. New churches were formed in the North & South (Mormons, Millerites, Onedia community, Shakers) c. Revivalism focused on combating sin & led to an era of social reform in the 1830s II. Moderate Social Reforms A. Northern revivals inspired social reforms to save lost souls through conversion, morality, & temperance B. Evangelism brought new changes to white, middle-class families by emphasizing “Cult of Domesticity” C. Growth of free public schools from 1820-1850 to promote moral training 1. Means of social advancement, teaching the “3 R’s”, & the protestant work ethic 2. Horace Mann saw schools as means to teach virtue to immigrant & poor children D. Reformers built new prisons & poorhouses; Dorothea Dix was the most important advocate for mental asylum reform III. Radical Social Reform A. Radical reformers split from moderates in the 1830s B. Abolitionism 1. William Lloyd Garrison & his American Anti-Slave Society demanded immediate emancipation (The Liberator) 2. Black abolitionists like Frederick Douglass & Sojourner Truth related the realities of slavery & helped runaways 3. Not all Northerners wanted to end slavery, especially in urban areas & near Mason-Dixon line 4. Radical abolitionists were hurt by in-fighting & many left Garrison to form the Liberty Party in 1840 C. Women’s Rights 1. Abolitionism raised awareness of women’s inequality 2. At Seneca Falls in 1848, Mott & Stanton rejected cult of domesticity & advocated gender equality & suffrage D. Utopian communities were formed by reformers tired of trying to change society 1. Utopian Socialism 2. Shakers & Oneida Community were religious utopian communities based on the second coming of Christ E. Transcendentalism was a philosophic movement, led by Emerson, that connected individuals to universal spiritual forces IV. Conclusions